So you’ve been growing your own lettuce and now you’re ready to take it to the next level – seed harvesting. But where do you begin? In this beginner’s guide, we’ll walk you through the process of harvesting lettuce seed. From knowing when to harvest to ensuring the seeds are fully mature, we’ve got you covered. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will help you become a pro at harvesting lettuce seed in no time. So grab your gardening gloves and let’s get started!
Choosing the Right Lettuce Variety
When it comes to harvesting lettuce seed, the first step is to choose the right lettuce variety that is suitable for seed harvesting. Not all lettuce varieties are ideal for seed production, so it’s important to select those that are known to produce high-quality seeds.
Determining the Types of Lettuce Suitable for Seed Harvesting
There are generally two types of lettuce that are most commonly suitable for seed harvesting: open-pollinated and heirloom varieties. Open-pollinated lettuce varieties are those that can be pollinated by insects or the wind, whereas heirloom varieties are typically open-pollinated but have been passed down through generations. These types of lettuce varieties tend to produce stable and reliable seeds, making them great options for seed harvesting.
Considering Climate and Growing Conditions
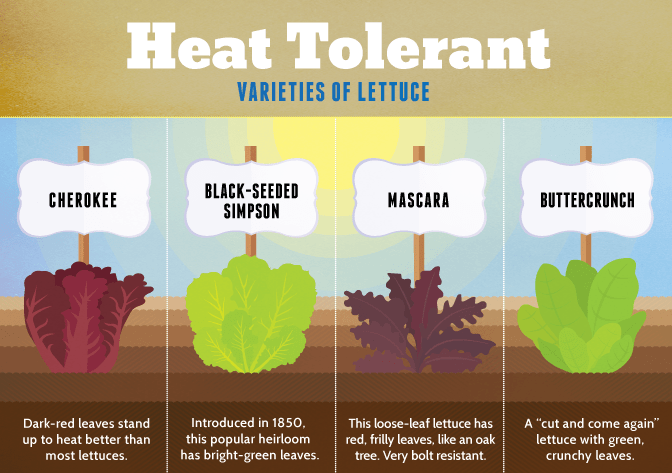
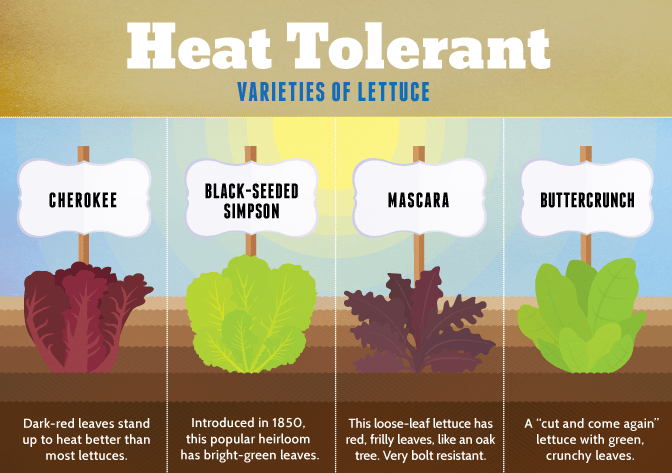
Another factor to consider when choosing a lettuce variety for seed harvesting is the climate and growing conditions in your area. Lettuce is a cool-season crop, so it’s important to choose a variety that is well-suited to the climate in which you are growing. Some lettuce varieties are more heat-tolerant, while others prefer cooler temperatures. Consider the average temperatures and length of your growing season to ensure the lettuce variety you choose will thrive and produce viable seeds.
Selecting Open-Pollinated or Heirloom Lettuce Varieties
Once you have taken climate and growing conditions into account, it’s time to select the specific open-pollinated or heirloom lettuce variety that best suits your needs. There are numerous options available, each with its own unique characteristics – from different leaf shapes and colors to varying levels of heat and cold tolerance. Research different varieties and choose the one that aligns with your preferences and growing conditions.
Lettuce Planting and Growing Basics
Once you have chosen the right lettuce variety for seed harvesting, it’s important to understand the basics of planting and growing lettuce. Properly preparing the soil, selecting the right planting method, providing adequate water and fertilizer, and managing pests and diseases are all essential for successful lettuce seed production.
Preparing the Soil for Lettuce Planting
Before planting lettuce, it’s crucial to prepare the soil to create an optimal growing environment. Start by removing any weeds or debris from the planting area. Loosen the soil using a garden fork or tiller, and mix in a generous amount of organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure. This will provide the lettuce plants with the necessary nutrients and improve the soil structure for healthy growth.
Choosing the Right Planting Method
There are two common methods for planting lettuce: direct seeding and transplanting. Direct seeding involves sowing the lettuce seeds directly into the garden bed, while transplanting involves starting the seeds indoors and then transplanting the seedlings into the garden once they are big enough. Both methods can be successful, but the choice will depend on your preferences and the specific requirements of the lettuce variety you are growing.
Providing Adequate Water and Fertilizer
Lettuce plants require consistent moisture to grow well and produce high-quality seeds. Regular watering is crucial, especially during dry periods or hot weather. Consider using a drip irrigation system or watering at the base of the plants to minimize wet foliage, which can lead to diseases. Additionally, regular fertilization with a balanced fertilizer or organic amendments will help provide the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and seed production.
Managing Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases can pose a threat to lettuce plants and potentially affect seed production. Common pests that can attack lettuce include aphids, slugs, and caterpillars. Regular monitoring and appropriate pest control measures such as handpicking, using insecticidal soaps, or implementing natural predators can help manage pest problems. Fungal diseases like powdery mildew and damping-off can also impact lettuce plants. Proper plant spacing, good air circulation, and avoiding over-watering can help prevent and manage these diseases.

Understanding Lettuce Seed Production
To successfully harvest lettuce seeds, it’s important to understand the process of bolting and flowering, as well as the structure and formation of lettuce flowers and seeds.
The Process of Bolting and Flowering
Bolting is a natural process in lettuce where the plants send up a tall flower stalk. This is triggered by various factors such as temperature changes, day length, and stress. Once the lettuce plant bolts, it begins to produce flowers, which are vital for seed production. Understanding and identifying the stages of bolting and flowering in lettuce plants will help you determine the right time to start observing the seed development process.
Lettuce Flower Structure and Seed Formation
Lettuce flowers are typically small and yellow, and they consist of both male and female reproductive parts. The male part is called the stamen and produces pollen, while the female part is called the pistil and contains the ovary where the seeds form. Proper pollination between the male and female flower parts is essential for seed development. By understanding the flower structure and the role each part plays in seed formation, you’ll be better equipped to ensure successful seed production.
Factors Affecting Seed Production
Several factors can affect the quality and quantity of seeds produced by lettuce plants. Adequate pollination is crucial, and this can be influenced by factors such as bees’ activity, weather conditions, and the presence of other flowering plants that attract pollinators. Temperature and humidity levels can also impact seed development and maturation. Being aware of these factors and providing favorable conditions will increase the chances of successful lettuce seed production.
Determining Seed Maturity
In order to harvest lettuce seeds at the right time, it’s important to understand how to determine seed maturity. Observing lettuce flowering and seed head formation, monitoring seed development, and performing seed viability tests can all help in assessing when the seeds are mature and ready for harvest.
Observing Lettuce Flowering and Seed Head Formation
As the lettuce plants continue to develop, they will produce flower heads that contain the developing seeds. Observing the progression of flowering and the appearance of seed heads is an important step in determining seed maturity. Once the flowers have opened and started to dry out, and the seed heads have formed and become firm, it’s a good indication that the seeds are maturing.
Monitoring Seed Development
Regular monitoring of seed development is crucial to ensure you harvest the seeds at the optimal time. Keep a close eye on the seed heads and observe any changes in color, texture, or size. The seeds should continue to develop and fill out within the seed heads. Careful observation and familiarity with the specific lettuce variety you are growing will guide you in determining when the seeds are mature enough for harvest.
Performing Seed Viability Tests
To further confirm seed maturity and viability, it can be helpful to perform seed viability tests. One common test is the germination test, where a sample of seeds is placed on a moist paper towel or in a germination tray. After a set period of time, the percentage of seeds that have germinated can be recorded. This will provide an indication of the overall seed viability and help determine if the seeds are ready for harvesting.

Harvesting Lettuce Seeds
Once the lettuce seeds have reached maturity, it’s time to harvest them. Choosing the right time for harvesting, understanding the proper harvesting techniques and tools, and handling the seeds correctly are all important aspects of successful lettuce seed harvest.
Choosing the Right Time for Harvesting
Harvesting lettuce seeds at the right time is crucial for ensuring the best quality seeds. Waiting too long can result in seeds scattering or becoming overripe, while harvesting too early may lead to immature seeds that won’t germinate well. Look for signs of seed maturity such as the seed heads turning brown and dry, and the seeds easily separating from the seed head when gently rubbed. This is an indication that the seeds are ready to be harvested.
Harvesting Techniques and Tools
Lettuce seed harvesting can be done using simple techniques and a few basic tools. One common method is hand-harvesting, where the seed heads are gently squeezed or rubbed to release the seeds into a container or bag. Another approach is cutting the seed heads off with clean scissors or pruners, ensuring that the seeds are caught in a collection container. The choice of technique may depend on personal preference and the size of the seed harvest.
Collecting and Handling Lettuce Seeds Properly
When collecting lettuce seeds, it’s important to handle them with care to maintain their viability. Avoid rough handling or crushing the seeds, as this can damage the delicate embryos inside. Place the harvested seeds in a clean, dry container, and remove any remaining chaff or debris. It’s also a good idea to label the container with the lettuce variety and the date of harvest to ensure proper organization and easy identification later on.
Processing and Cleaning Lettuce Seeds
After harvesting, it’s necessary to process and clean the lettuce seeds to remove any chaff or debris. This will help ensure the seeds are clean, dry, and ready for long-term storage.
Removing Chaff and Debris
To remove chaff and debris from harvested lettuce seeds, a simple winnowing technique can be used. This involves gently pouring the seeds from one container to another in front of a gentle breeze or using a fan set on low. The lighter chaff and debris will be blown away, leaving behind the heavier and more valuable seeds. Repeat the process several times if necessary until the seeds are clean and free of unwanted material.
Drying Seeds for Long-Term Storage
Properly drying the lettuce seeds is crucial for long-term storage. Spread the cleaned seeds in a single layer on a clean and dry surface such as a paper towel or a fine mesh screen. Place them in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and let them air dry for about a week or until they are completely dry. Once dry, the seeds can be stored in suitable containers for future use.

Storing Lettuce Seeds
To ensure the longevity and viability of lettuce seeds, proper storage is essential. Protecting the seeds from moisture, heat, light, and pests will help maintain their quality and increase the chances of successful germination when planted.
Choosing Suitable Containers
When selecting containers for storing lettuce seeds, it’s important to choose ones that are clean, dry, and airtight. Glass jars with tight-fitting lids or resealable plastic bags are good options. Make sure the containers are labeled with the lettuce variety and the date of harvest for easy identification. Store the containers in a cool, dark place away from moisture, extreme temperatures, and pests.
Providing Optimal Storage Conditions
Lettuce seeds require specific storage conditions for long-term viability. Ideally, the storage temperature should be around 32 to 41°F (0 to 5°C), with humidity levels between 35% and 50%. If possible, consider using a refrigerator or a cool basement for seed storage. Avoid storing the seeds in the freezer, as rapid temperature fluctuations can damage the delicate embryos. Regularly check the stored seeds for signs of moisture or pests and discard any compromised seeds.
Labeling and Organizing Seeds
To ensure proper organization and easy access to stored lettuce seeds, labeling is essential. Clearly label each container with the lettuce variety, the date of harvest, and any additional relevant information. This will prevent confusion and help you identify and select the seeds you need for future plantings. Additionally, consider keeping a separate record or seed inventory that includes detailed information about each lettuce variety to help you plan and keep track of your seed collection.
Seed Viability and Germination Testing
To determine the viability of lettuce seeds before planting, conducting seed viability and germination tests can provide valuable insights. These tests will help ensure that the seeds you saved are still viable and capable of germinating successfully.
Determining Seed Viability
Seed viability refers to the percentage of seeds that are still alive and capable of germinating. To determine the viability of your lettuce seeds, a simple germination test can be performed. Take a representative sample of seeds and place them on a moist paper towel or in a germination tray. After a set germination period, count the number of seeds that have successfully germinated to calculate the seed viability percentage.
Conducting Germination Tests
Germination tests simulate the ideal conditions required for seed germination, allowing you to assess the seed viability. Start by moistening a paper towel or using a germination tray with water, ensuring it is not soaking wet. Then, place a representative sample of lettuce seeds on the moist paper towel or in the germination tray. Keep the seeds moist throughout the germination period, which typically ranges from 7 to 14 days. After this time, count the number of seeds that have germinated to determine the germination rate.
Interpreting Germination Results
Interpreting the results of germination tests will provide insights into the quality and viability of your lettuce seeds. A germination rate of 80% or higher is generally considered good, indicating that the majority of the seeds have the potential to germinate and grow successfully. If the germination rate is below 80%, it may be a sign that the seed viability is lower, and you should consider using fresher seeds or adjusting your planting practices accordingly.

Seed Saving and Preservation
Saving and preserving lettuce seeds is an important practice that promotes genetic diversity and ensures a continuous supply of high-quality seeds. By properly storing and caring for saved seeds, you can maintain the unique characteristics of each lettuce variety and contribute to seed sustainability.
Maintaining Genetic Diversity
Saving lettuce seeds allows you to maintain the genetic diversity of different lettuce varieties. This is important because diverse genetic traits can provide resilience and adaptability to changing environmental conditions. By selecting and saving seeds from the strongest and healthiest lettuce plants, you can continue to cultivate varieties that are well-suited to your specific growing conditions and preferences.
Properly Storing Saved Seeds
To maintain the viability of saved lettuce seeds, proper storage is essential. Follow the guidelines discussed earlier for storing lettuce seeds in suitable containers, in a cool and dry environment. Make sure to check the stored seeds regularly for any signs of deterioration or pests. If stored correctly, lettuce seeds can remain viable for several years, allowing you to continue growing your favorite varieties for seasons to come.
Best Practices for Seed Preservation
To ensure the long-term preservation of lettuce seeds, following best practices is important. Start by thoroughly cleaning and drying the seeds after harvest to remove any moisture that could cause them to spoil. Store the seeds in airtight containers and keep them in a cool and dark location to prevent any potential damage from heat or light. Regularly monitor the stored seeds for any signs of deterioration or infestation and take necessary actions if needed. Additionally, it’s beneficial to periodically refresh your seed collection by saving fresh seeds and replacing older ones.
Tips and Troubleshooting
While harvesting lettuce seeds can be a rewarding experience, there are some common mistakes to avoid, helpful tips for successful harvesting, and troubleshooting techniques to address any issues that may arise.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One common mistake when harvesting lettuce seeds is waiting too long to harvest, leading to seed scatter or overripeness. Harvesting too early can result in immature seeds with low germination rates. Be sure to carefully observe the seed development stages and harvest the seeds at the optimal time. Another mistake to avoid is inadequate labeling and organization of stored seeds, which can lead to confusion and difficulty in proper seed selection.
Tips for Successful Lettuce Seed Harvesting
To enhance your success in lettuce seed harvesting, consider the following tips:
- Start by choosing lettuce varieties that are known for seed production success.
- Provide optimal growing conditions, including proper soil preparation, adequate water, and fertilizer.
- Monitor the bolting and flowering stages to accurately determine the right time for seed harvest.
- Use proper harvesting techniques, such as hand-harvesting or cutting the seed heads, to avoid damage to the seeds.
- Clean and dry the harvested seeds thoroughly before storing them to prevent spoilage.
Troubleshooting Seed Harvesting Issues
If you encounter any issues during the lettuce seed harvesting process, troubleshooting can help address them. If seeds are not maturing or the seed heads are not forming, it may be due to unfavorable growing conditions or a lack of pollinators. Inadequate watering or improper fertilization can also impact seed production. Consider adjusting these factors and ensuring proper pollination to improve seed development. Additionally, if seeds are not germinating well during viability tests, it may indicate low seed quality or improper storage conditions. Review your seed saving and storage practices to identify and address any potential causes.
By following these tips and troubleshooting techniques, you can improve your lettuce seed harvesting skills and enjoy a bountiful supply of high-quality seeds for your future plantings.
In conclusion, harvesting lettuce seeds is a rewarding process that allows you to save and preserve the genetic diversity of different lettuce varieties. By understanding the various stages of seed production, from selecting the right lettuce variety to properly storing the seeds, you can successfully harvest and store lettuce seeds for future planting seasons. Remember to observe the lettuce flowering and seed head formation, perform seed viability tests, and use proper harvesting techniques and tools. With proper care and attention, you can enjoy the benefits of seed saving and contribute to the sustainability of lettuce varieties in your garden.