So you’ve decided to try your hand at growing lettuce in the great state of Texas, but you’re not quite sure when the best time to do so is. Well, worry no more! In this article, we’ll uncover the optimal time frames for growing lettuce in Texas, ensuring that you have a successful and abundant harvest. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner looking to flex your green thumb, this guide will provide you with all the insights you need to cultivate crisp and delicious lettuce in the Lone Star State. Let’s dive in!
Best Time to Grow Lettuce in Texas
If you’re a lettuce enthusiast in Texas, you may be wondering about the best time to grow this delicious and versatile leafy green. Growing lettuce in Texas can be a rewarding experience, but it’s important to understand the climate conditions, suitable lettuce varieties, ideal growing locations, soil preparation, planting techniques, proper watering and irrigation practices, pest and disease management, harvesting methods, and even succession planting for a continuous harvest. In this comprehensive article, we will explore all these aspects to help you make the most of your lettuce cultivation in the Lone Star State.
Climate Conditions in Texas
Texas encompasses a wide range of climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics. It’s crucial to understand the climate of your specific region to determine the optimal time for growing lettuce. Typically, Texas experiences hot summers and mild winters, making it necessary to consider the impact of these varying conditions on lettuce cultivation.
Understanding Texas’ Climate Zones
Texas can be divided into several climate zones, including the Humid Subtropical Zone, the Semiarid Zone, and the Trans-Pecos Zone. Each zone has its own set of temperature ranges and weather patterns, which can significantly influence lettuce growth. To ensure successful lettuce cultivation, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the climate zone in your locality.
Winter Temperatures in Different Regions
While Texas winters are generally mild, it’s essential to keep track of the average winter temperatures in different regions. Frost can damage lettuce plants, so planting at the right time is crucial. Consulting local resources or the USDA hardiness zone map can provide valuable information about specific regions and their average winter temperatures.
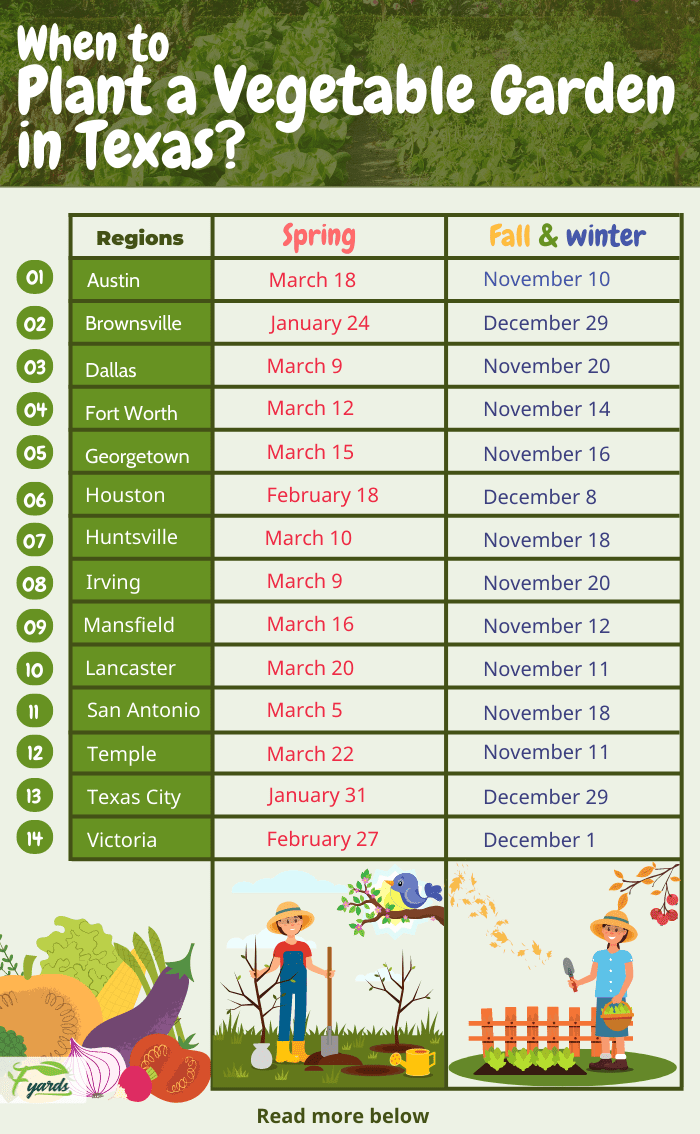
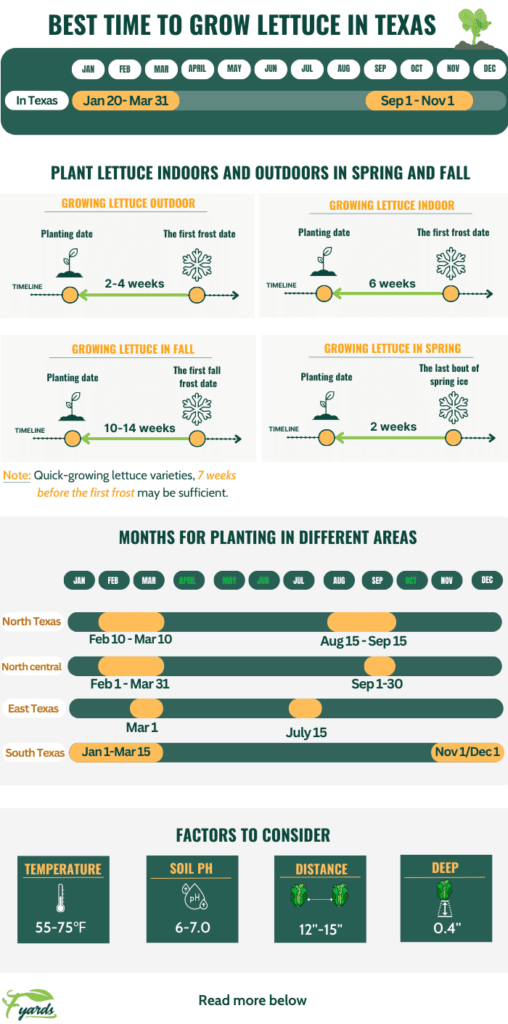
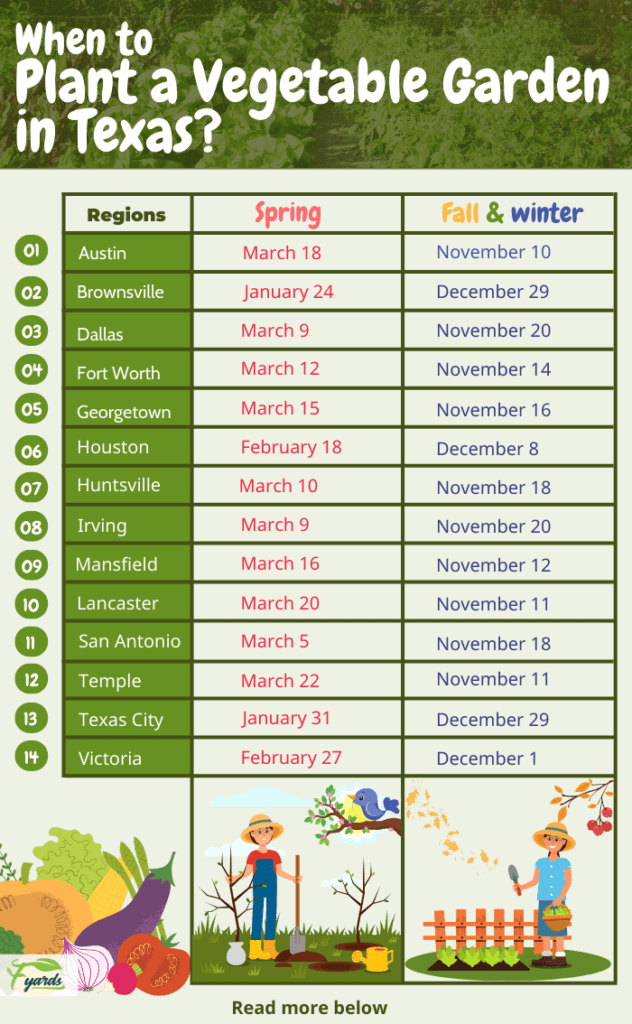
Average Frost Dates in Texas
Another important consideration is the average frost dates in your area. Lettuce is quite sensitive to frost, so it’s essential to choose the right time to plant to avoid any potential damage. The average frost dates vary across Texas, so knowing these dates will help you determine the appropriate time to start your lettuce cultivation.
Types of Lettuce to Grow in Texas
Choosing the right lettuce varieties is essential for a successful harvest in Texas. Given the climatic conditions of the state, it’s crucial to select heat-tolerant and cold-tolerant lettuce types that can thrive in the fluctuating temperatures experienced throughout the year.
Heat-Tolerant Varieties
For the scorching Texas summers, it is recommended to focus on growing heat-tolerant lettuce varieties. These types of lettuce have been specifically bred or selected to withstand the high temperatures without bolting or turning bitter. Heat-tolerant varieties, such as ‘Salanova,’ ‘Black Seeded Simpson,’ or ‘Jericho,’ can be great options for Texas gardeners.

Cold-Tolerant Varieties
Texas winters may be milder compared to other regions, but it’s still important to choose lettuce varieties that can handle the occasional cold snaps. Cold-tolerant lettuce varieties, like ‘Winter Density,’ ‘Winter Marvel,’ or ‘Arctic King,’ can thrive in the cooler temperatures and extend your lettuce growing season well into the winter months.
Recommended Lettuce Types for Texas
In addition to heat-tolerant and cold-tolerant varieties, there are several types of lettuce to consider for your Texas garden. Butterhead lettuce, with its tender leaves and mild flavor, is a popular choice. Romaine lettuce, known for its crisp texture and robust taste, is another excellent option. Lastly, leaf lettuce is a versatile choice, with various colors and leaf shapes available that can add visual appeal to your garden.
Choosing the Right Location for Growing Lettuce
Selecting the correct location for growing lettuce is paramount. Lettuce has specific sunlight requirements and can be affected by strong winds and standing water, so finding an ideal spot in your garden is crucial for success.
Sunlight Requirements
Lettuce prefers full sun, but it can also tolerate partial shade, especially in regions with scorching summers. Aim to provide at least six hours of direct sunlight daily to ensure optimal growth. If you live in an area with extremely high temperatures, consider providing some shading during the hottest parts of the day to protect your lettuce plants.
Protection from Strong Winds
Texas is known for its occasional strong wind gusts, which can damage delicate lettuce leaves and disrupt overall growth. By selecting a planting location that has some natural windbreaks, such as fences or trees, you can provide protection for your lettuce plants. Alternatively, you can create artificial windbreaks using materials like mesh screens or row covers.
Avoiding Areas with Standing Water
Lettuce prefers well-draining soil, so it’s important to avoid areas in your garden where water tends to stagnate. Standing water can lead to root rot and other diseases, impacting the growth and health of your lettuce plants. Choose a location that allows excess water to drain away efficiently and avoid areas prone to flooding during heavy rains.
Soil Preparation for Lettuce Cultivation
Preparing the soil before planting lettuce sets the foundation for healthy growth and successful harvests. Consider the following factors when preparing your soil for lettuce cultivation.
Soil pH and Composition
Lettuce prefers slightly acidic soil with a pH ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. Conduct a soil test using a kit readily available at garden centers or consult with your local agricultural extension office to determine the pH of your soil. Adjustments can be made by adding lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it, as necessary.
In terms of soil composition, lettuce grows best in loose, well-draining soil rich in organic matter. Ensure that the soil is loamy and friable, allowing for proper root development and water penetration. If your soil is heavy clay or sandy, you can improve its structure by adding compost or organic matter.
Improving Drainage
Good drainage is crucial for lettuce, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot and other problems. If the natural drainage in your garden is poor, consider building raised beds or mounds to improve the soil’s drainage capabilities. Adding perlite or vermiculite to the soil mix can also enhance drainage.
Amending Soil with Compost or Organic Matter
Adding compost or organic matter to your soil before planting lettuce can greatly enhance its fertility and structure. Work well-rotted compost or aged manure into the top few inches of the soil to provide essential nutrients and improve water retention. Organic matter also aids in weed suppression and overall soil health.
Planting Techniques for Lettuce
Once you’ve prepared your soil, it’s time to decide on the planting technique that best suits your needs. Direct seeding and using transplants are the two primary methods for growing lettuce.
Direct Seeding vs. Transplants
Direct seeding involves sowing lettuce seeds directly into the garden bed. This method is simple and cost-effective, allowing you to control the entire growth process from seed to harvest. Transplants, on the other hand, involve starting lettuce seeds indoors or purchasing young lettuce plants and transplanting them into the garden. Transplants allow for more precise spacing and timing, giving you a head start on the growing season.

Spacing and Planting Depth
For direct seeding, follow the instructions on the seed packet for recommended spacing and planting depth. Generally, lettuce seeds should be sown thinly in rows, with a spacing of 8 to 12 inches between rows. If using transplants, maintain a similar spacing between plants to ensure adequate airflow and prevent overcrowding.
Successive Planting for Extended Harvest
To enjoy a continuous supply of lettuce throughout the growing season, consider successive planting. This involves sowing small batches of lettuce every few weeks, staggering the planting times. By doing so, you can avoid a glut of lettuce all at once and have a steady supply of fresh greens for an extended period.
Watering and Irrigation for Lettuce
Lettuce has specific water requirements to ensure optimal growth and prevent problems such as bolting or bitterness.
Watering Frequency and Amount
Lettuce prefers consistent moisture throughout its growth cycle, so it’s important to water consistently and avoid prolonged periods of dryness. Typically, lettuce plants require about 1 inch of water per week, but this can vary depending on the weather conditions and soil moisture retention capabilities. Monitor the soil moisture regularly by checking the top few inches of soil and adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
Mulching to Retain Soil Moisture
Mulching around your lettuce plants can help retain soil moisture, reduce evaporation, and suppress weed growth. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or shredded leaves, around the plants, taking care to leave a small gap around the base of each lettuce to prevent moisture-related issues.
Avoiding Overhead Irrigation
While lettuce needs consistent moisture, overhead irrigation can lead to leaf diseases, such as fungal infections. Whenever possible, opt for drip irrigation or focus the watering at the base of the plants to keep the foliage as dry as possible. This reduces the risk of diseases and ensures healthier plants.

Pest and Disease Management
Just like any other garden crop, lettuce in Texas can face its fair share of pests and diseases. Understanding common pests and diseases and implementing preventative measures can help protect your lettuce plants.
Common Pests in Texas
Some of the common pests that can affect lettuce in Texas include aphids, slugs, snails, and caterpillars such as cabbage loopers or cutworms. Regularly inspect your lettuce plants for any signs of pest infestation, and intervene promptly using appropriate organic pest control methods, such as handpicking or applying insecticidal soap.
Natural Pest Control Methods
Implementing natural pest control methods can help keep pest populations in check without relying on synthetic pesticides. For example, attracting beneficial insects like ladybugs or lacewings to your garden can help control aphids and other pests. Planting companion plants, such as marigolds or chives, can also deter certain pests.
Common Diseases in Lettuce
Lettuce can be susceptible to various diseases, including downy mildew, powdery mildew, and lettuce mosaic virus. To minimize the risk of disease, practice proper crop rotation, avoid overhead irrigation, keep the plants properly spaced for adequate airflow, and promptly remove any diseased leaves or plants to prevent the spread of infection.
Preventative Measures for Disease Management
Maintaining good garden hygiene, such as removing debris and fallen leaves, can help reduce the risk of diseases. Applying organic fungicides or employing biological controls, such as beneficial microbes, can also aid in preventing the onset and spread of diseases. If you suspect a disease outbreak, consult your local agricultural extension office or a certified plant pathologist for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Harvesting Lettuce
Harvesting lettuce at the right time ensures the best flavor and texture. Different types of lettuce have varying maturity times and harvesting methods.
Determining Maturity
Lettuce can be harvested at various stages, depending on personal preference. For baby lettuce or leaf lettuce, you can begin harvesting when the leaves are large enough to be used, typically around 4 to 5 weeks after planting. Butterhead lettuce and romaine lettuce generally mature within 8 to 10 weeks after planting. The outer leaves can be selectively harvested, or you can opt for cutting the entire head, depending on your preference.
Harvesting Techniques
When harvesting leaf lettuce or baby lettuce, remove the outer leaves individually by cutting them at the base. For head lettuce varieties like butterhead or romaine, use a knife to cut the head just above the soil surface. Take care not to damage the remaining plant during the harvest process.
Regrowth Potential for Cut-and-Come-Again
Certain lettuce varieties have the ability to regrow after harvesting, known as cut-and-come-again lettuce. These varieties, often leaf lettuces, can be harvested by cutting the outer leaves while leaving the central core intact. This allows for successive harvests, extending the lettuce-growing season and providing a continuous supply of fresh leaves.
Succession Planting for Continuous Harvest
To enjoy a continuous harvest of lettuce, consider implementing succession planting. As mentioned earlier, by sowing small batches of lettuce seeds every few weeks, you can ensure a constant supply of fresh lettuce leaves. As one batch is harvested, the next one will be ready for harvest, giving you a consistent and extended lettuce-growing season.
Recommended Lettuce Varieties for Texas
To kick-start your lettuce garden in Texas, consider these recommended lettuce varieties that have proven successful in the region.
Butterhead Lettuce Varieties
Butterhead lettuce varieties are known for their tender leaves and mild flavor. Recommended varieties for Texas include ‘Bibb,’ ‘Buttercrunch,’ and ‘Reine des Glaces,’ which all perform well in the state’s climate.
Romaine Lettuce Varieties
Romaine lettuce, with its crisp texture and robust taste, is a favorite among salad enthusiasts. Recommended varieties for Texas include ‘Parris Island,’ ‘Green Towers,’ and ‘Rouge d’Hiver.’
Leaf Lettuce Varieties
Leaf lettuce varieties offer a vast array of colors and leaf shapes, making them a visual delight in any garden. Recommended leaf lettuce varieties for Texas include ‘Red Salad Bowl,’ ‘Black Seeded Simpson,’ and ‘Salad Bowl.’
With a good understanding of the best time to grow lettuce in Texas, suitable lettuce varieties, ideal growing locations, soil preparation, planting techniques, watering and irrigation practices, pest and disease management, harvesting methods, and utilizing succession planting, you can embark on a successful lettuce adventure in the Lone Star State. Enjoy the bounty of fresh, homegrown lettuce, and take pride in your delicious and healthy creations straight from your garden to your plate!