If you’re eager to grow butternut squash in Zone 7, it’s essential to know the best time to plant them. With its creamy texture and rich flavor, butternut squash has become a popular garden staple. To ensure a successful harvest, it’s important to plant these delectable fruits at the right time. So, let’s explore the ideal planting period for butternut squash in Zone 7 and get ready to enjoy an abundance of homegrown goodness.
Factors to Consider
Climate
When determining the best time to plant butternut squash in Zone 7, it is essential to consider the climate of the region. Zone 7 typically experiences a moderate climate with hot summers and mild winters. It falls within a temperature range of 0 to 10 degrees Fahrenheit (-18 to -12 degrees Celsius). The rainfall in this zone is relatively consistent throughout the year, with an average annual precipitation of around 40 to 50 inches (101-127 cm). Understanding the climate conditions will help in planning the planting schedule and taking appropriate measures for successful butternut squash cultivation.
Soil Temperature
Soil temperature is a crucial factor to consider before planting butternut squash. The ideal soil temperature for successful germination and growth of butternut squash is between 70 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21-29 degrees Celsius). It is important to ensure that the soil is warm enough before sowing or transplanting the seeds. Measuring the soil temperature using a soil thermometer can provide accurate information and guide you in determining the right time to plant.
Frost Dates
Frost dates play a significant role in determining the appropriate timing for planting butternut squash. Two important dates to consider are the last spring frost and the first fall frost. Butternut squash is a warm-season crop that does not tolerate frost. The last spring frost date marks the end of significant frost occurrences in the spring, while the first fall frost date indicates the onset of frost in the fall. By knowing these dates, you can ensure that your butternut squash plants are not exposed to freezing temperatures, which can severely damage or kill them.
Seed Starting
Deciding between starting seeds indoors or direct seeding in the garden is a crucial step in planning when to plant butternut squash. Starting seeds indoors allows you to get a head start on the growing season and gives the plants a better chance to establish before the weather warms up. Generally, it is recommended to start butternut squash seeds indoors about 3-4 weeks before the last spring frost date. This allows adequate time for the seedlings to develop and be ready for transplanting into the garden.

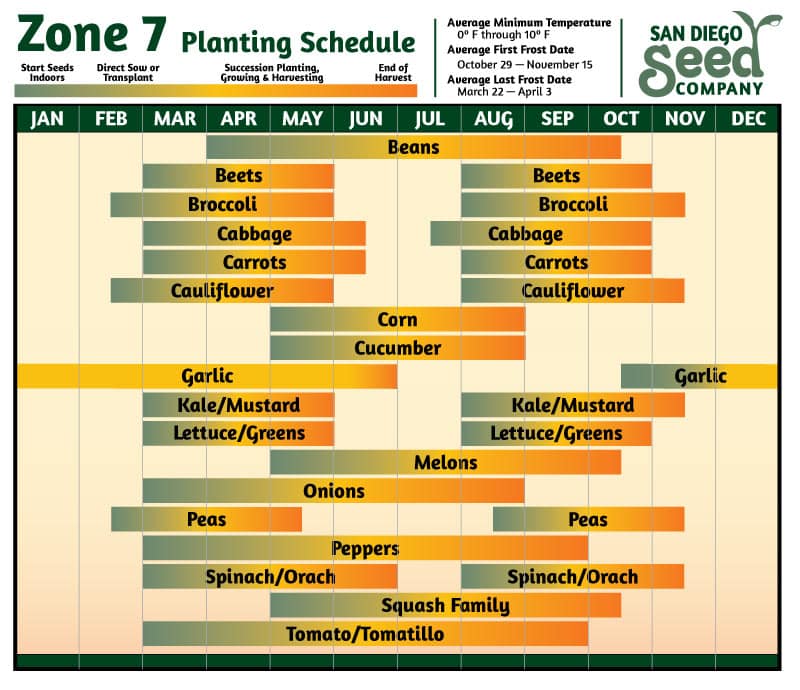
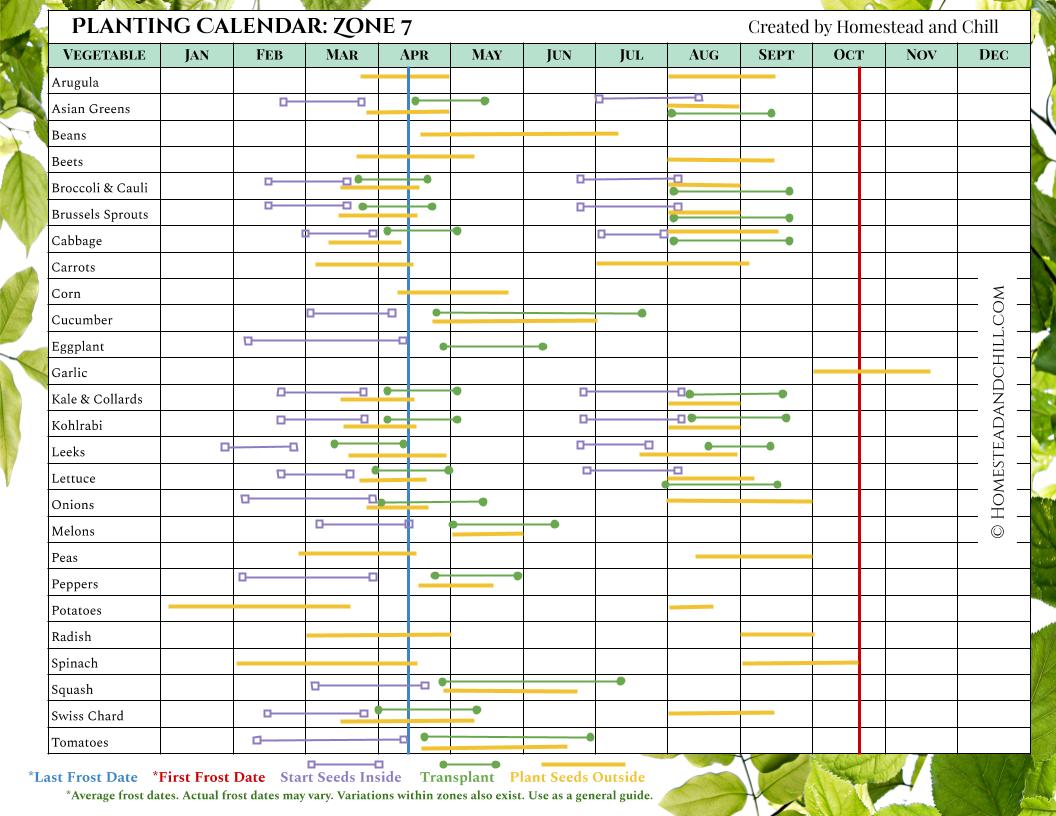
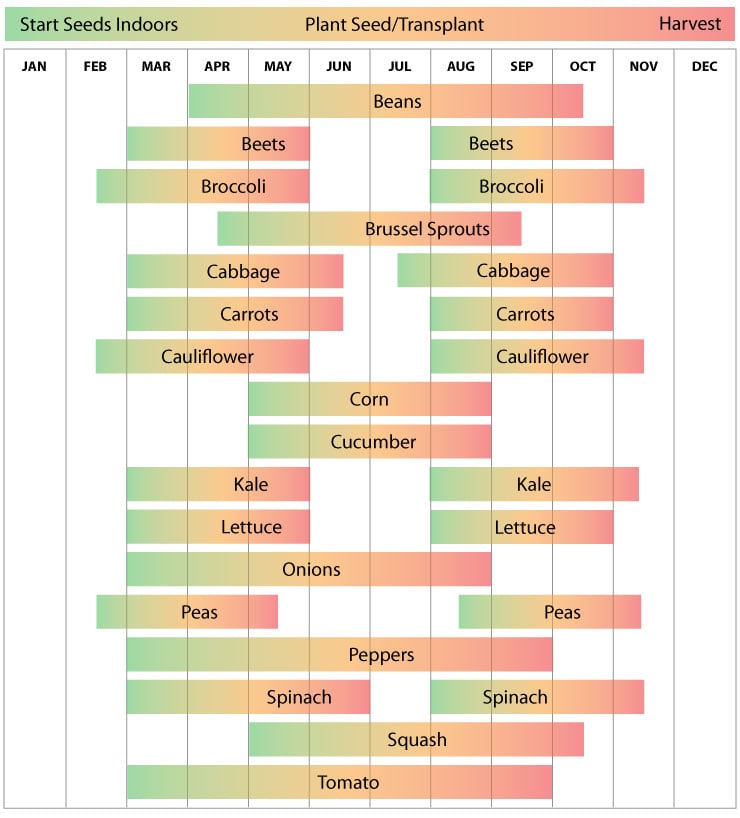
Planting Schedule
Creating a planting schedule ensures that you have a well-organized plan for when to plant butternut squash. It takes into account various factors such as climate, frost dates, seed starting, and the specific requirements of butternut squash. The planting schedule outlines the timeline for starting seeds indoors, transplanting seedlings, and direct seeding in the garden. It also considers succession planting to extend the harvest period. A well-planned planting schedule maximizes the chances of a successful and abundant butternut squash harvest.
Recommended Varieties
Choosing the right butternut squash varieties that are suitable for Zone 7 is essential for a successful harvest. Some recommended varieties for Zone 7 include ‘Waltham,’ ‘Butterbush,’ and ‘Metro PMR.’ These varieties have proven to be well-adapted to the climate and growing conditions of this region. When selecting varieties, consider factors such as taste preference, yield potential, and disease resistance. Hybrid varieties offer improved disease resistance, while heirloom varieties often boast exceptional flavor. Understanding the characteristics of different varieties will help you make an informed decision.
Preparing the Planting Area
Before planting butternut squash, it is vital to prepare the planting area properly. Start by clearing the area of weeds, rocks, and other debris. This ensures that the butternut squash plants have ample space and resources to grow. The next step is to prepare the soil by loosening it with a garden fork or tiller. This promotes good drainage, allows for root penetration, and encourages healthy plant development. Finally, amending the soil with compost or organic matter helps improve its fertility and provides essential nutrients for the butternut squash plants.
Planting Butternut Squash
Once the planting area is prepared, there are two primary methods for planting butternut squash: direct seeding and transplanting. Direct seeding involves sowing the seeds directly in the garden soil. This method is suitable if the soil temperature is consistently above 70 degrees Fahrenheit (21 degrees Celsius) and there is no risk of frost. Transplanting involves starting the seeds indoors and later transplanting the seedlings into the garden. This method provides a head start in the growing season and helps protect the tender seedlings from adverse weather conditions. When planting butternut squash, ensure proper spacing and depth according to the specific variety’s requirements. Water the plants thoroughly after planting and apply mulch to conserve moisture and suppress weed growth.

Care and Maintenance
To ensure healthy growth and a bountiful harvest, proper care and maintenance of your butternut squash plants are crucial. This includes regular watering, fertilizing, pest control, weed management, and pruning and training.
Watering: Butternut squash plants require consistent moisture, especially during the hot summer months. Water deeply, ensuring the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around the plants helps retain moisture and prevent weed competition.
Fertilizing: Butternut squash is a heavy feeder and benefits from regular fertilization. Apply a balanced organic fertilizer or compost in the planting hole and side-dress with additional compost or a slow-release fertilizer as the plants grow. Follow the recommended application rates to avoid overfertilization.
Pest Control: Common pests that may affect butternut squash include squash bugs, cucumber beetles, and vine borers. Monitor your plants regularly and take appropriate measures, such as handpicking pests, using organic insecticides, or implementing cultural practices like row covers, to prevent infestations.
Weed Management: Keeping the planting area weed-free is essential for the growth and development of butternut squash plants. Regularly remove weeds by hand or use organic mulch to suppress weed growth and retain soil moisture.
Pruning and Training: Although not necessary, pruning butternut squash plants can help improve air circulation and reduce the risk of disease. Prune off any damaged or diseased leaves or vines. Training the vines on trellises or supports can also minimize space requirements and reduce the risk of fruit rot.
By following these care and maintenance practices, you can ensure that your butternut squash plants thrive and produce a plentiful harvest in Zone 7.
In conclusion, determining the best time to plant butternut squash in Zone 7 involves considering various factors such as climate, soil temperature, frost dates, seed starting, and the specific requirements of butternut squash. By understanding the climate, preparing the soil, and following a well-planned planting schedule, you can successfully grow and harvest delicious butternut squash in Zone 7. Remember to choose recommended varieties suitable for this region, provide proper care and maintenance, and enjoy the abundant rewards of your labor. Happy gardening!



