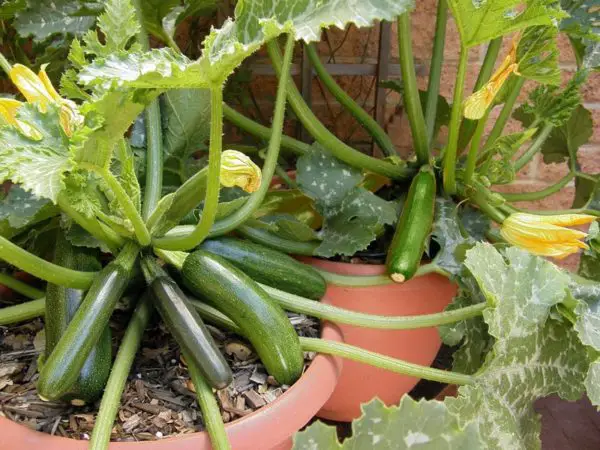
Are you a gardening enthusiast in California looking to grow your own zucchini? Wondering when is the optimal time to plant this versatile vegetable? Well, look no further! In this article, we will shed light on the best time to plant zucchini in California, allowing you to maximize your harvest and enjoy delicious, homegrown zucchinis all season long. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will provide you with the essential information to ensure a successful zucchini planting experience. So grab your gardening gloves and let’s dig in!
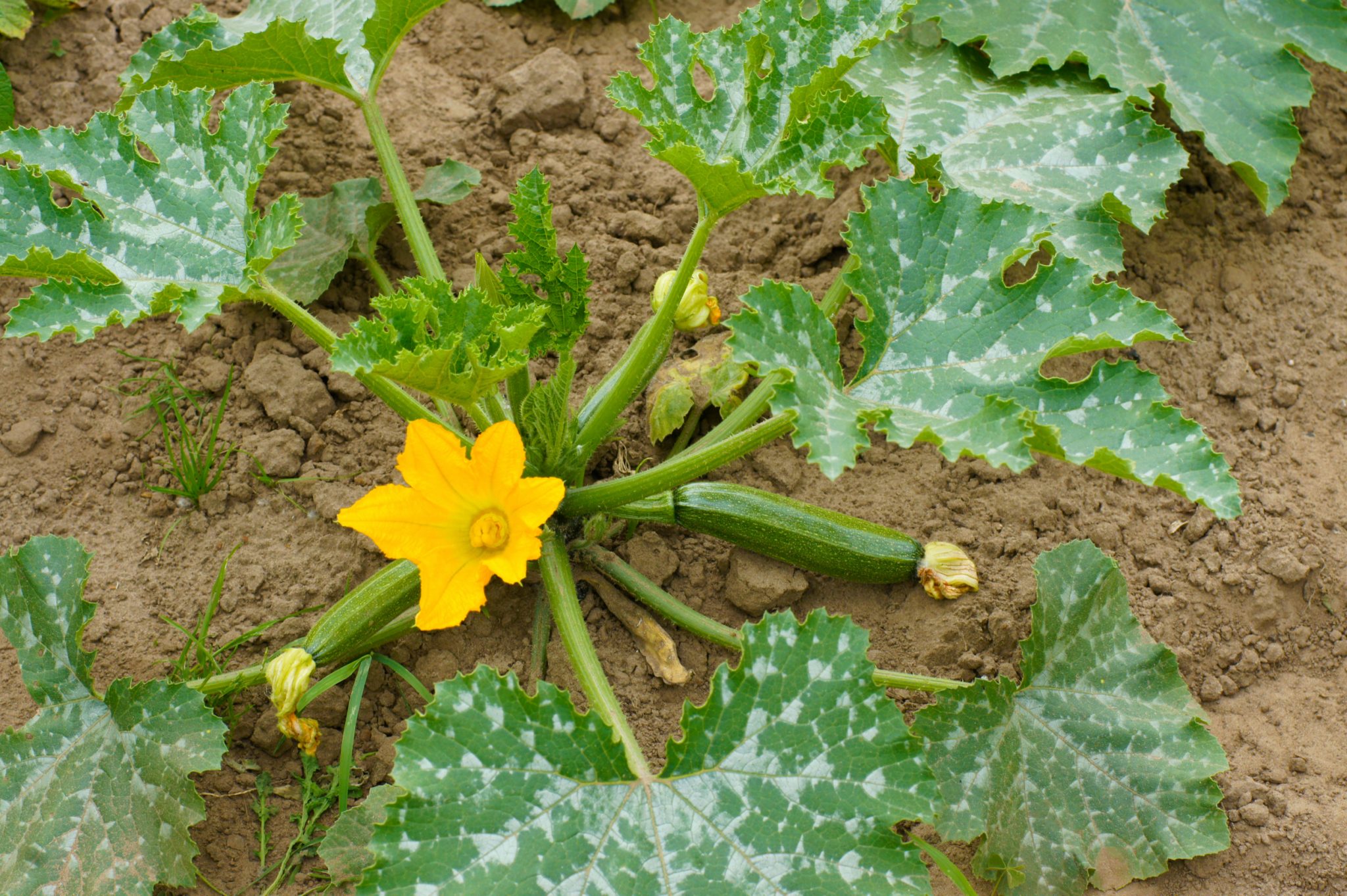

Factors to Consider for Planting Zucchini
Climate
When deciding to plant zucchini, one of the first factors you need to consider is the climate of your region. Zucchini plants thrive in warm temperatures, so it’s essential to choose a location with a suitable climate for their growth. In general, zucchini plants prefer a climate with a long, warm growing season and temperatures between 70°F and 90°F. However, they can tolerate slightly cooler temperatures, down to around 60°F. If you live in a region with hot summers, you may need to provide some shade or protection for your zucchini plants when the temperatures reach their peak.
Soil Preparation
To give your zucchini plants the best chance of success, it’s important to prepare the soil properly before planting. Zucchini plants prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. Before planting, loosen the soil to a depth of 10-12 inches and incorporate compost or aged manure to improve its fertility and drainage. Additionally, make sure the soil pH is between 6 and 7, as zucchini plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil conditions. Testing the soil pH and making any necessary adjustments before planting will help ensure that your zucchini plants have the right soil environment for optimal growth.
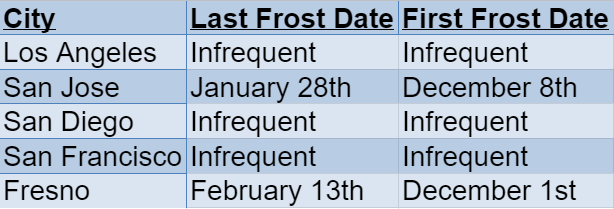
Frost Dates
Another crucial consideration when planning to plant zucchini is the last spring frost date in your location. Zucchini plants are highly sensitive to frost and cannot tolerate freezing temperatures. So before you start planting, it’s important to determine when the risk of frost has passed in your region. This information will help you determine the best time to start seeds indoors or directly sow them in the garden. You can find local frost date information through online resources, local gardening centers, or by contacting your local cooperative extension office.
Companion Planting
Companion planting refers to the practice of planting different plants together to maximize their growth and health while minimizing pest and disease problems. When it comes to zucchini, certain companion plants can help deter pests, improve pollination, and enhance overall garden health. Some good companion plants for zucchini include herbs like dill and oregano, which can attract beneficial insects. Marigolds are also known to repel pests that commonly affect zucchini plants. Consider incorporating these compatible plants into your zucchini garden for a healthier and more productive growing environment.
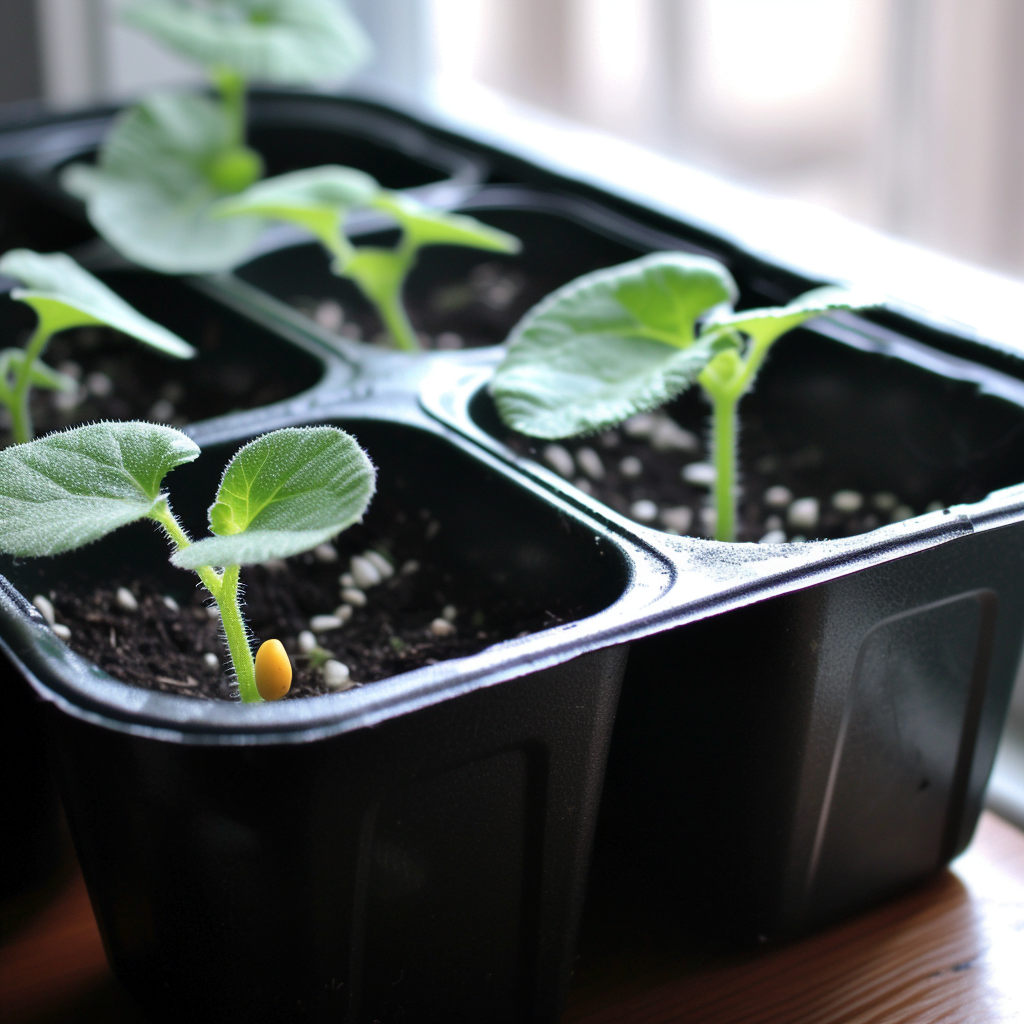
Best Time to Start Seeds Indoors
Determining the Last Spring Frost Date
Before starting your zucchini seeds indoors, you need to determine the last spring frost date. This date is vital because zucchini plants cannot be moved outside until the risk of frost has passed. By knowing this date, you can count backward to determine the optimal time to start your seeds indoors.
Counting Back from the Last Frost Date
To find the best time for starting your zucchini seeds indoors, subtract the number of weeks needed for the seeds to germinate and grow into healthy seedlings from the last spring frost date. Zucchini seeds typically take around 7-10 days to germinate, and the seedlings need 3-4 weeks to become strong enough for transplantation.
Using a Seed Starting Calendar
If you prefer a more straightforward approach, you can use a seed starting calendar specific to your region. These calendars provide recommended planting dates for various crops, including zucchini, based on the last spring frost date. Simply find your frost date on the calendar and follow the suggested timeline for starting zucchini seeds indoors. This method takes the guesswork out of seed starting and ensures you give your zucchini plants the best head start before moving them outdoors.
Best Time to Transplant Seedlings
When Seedlings are 3-4 Weeks Old
Once your zucchini seedlings have reached 3-4 weeks of age and developed a robust root system, they are ready for transplantation into the garden. At this stage, the seedlings should have several sets of true leaves and be around 3-4 inches tall. This size ensures that they can withstand the stress of transplanting and continue to grow vigorously in their new location.
After the Last Frost Date
Transplanting seedlings should always occur after the last frost date in your region. As mentioned earlier, zucchini plants are not frost-tolerant, so it’s crucial to wait until the risk of frost has passed. Planting your seedlings outdoors before the danger of frost has subsided can lead to severe damage or even death of the plants.
When Soil Temperature is 60°F or Higher
Another essential factor to consider when transplanting zucchini seedlings is the soil temperature. Zucchini plants thrive in warm soil, so make sure the soil temperature is consistently at or above 60°F before moving your seedlings into the garden. Cold soil can stunt the growth of zucchini plants and make them more susceptible to disease and pest issues. Using a soil thermometer can help you accurately assess the soil temperature and ensure optimal conditions for transplantation.
Direct Seeding Zucchini in the Garden
Determining the Last Spring Frost Date
Before directly sowing zucchini seeds in the garden, it’s necessary to determine the last spring frost date for your area. This date will help you determine when it’s safe to sow zucchini seeds directly in the soil without the risk of frost damaging them. Just like with starting seeds indoors, knowing the last frost date is a crucial factor in successful zucchini planting.
Soil Temperature Considerations
When direct seeding zucchini, it’s essential to consider the soil temperature. Zucchini seeds germinate best when the soil temperature is consistently around 70°F. If the soil temperature is too low, the seeds may rot in the ground without sprouting. To ensure the soil temperature is suitable, you can use a soil thermometer to check the temperature a few inches below the surface. If the soil is still too cold, consider using protective measures like row covers or black plastic mulch to warm up the soil before direct seeding.
Spacing and Sowing Depth
Proper spacing and sowing depth are vital for healthy zucchini plants. When direct seeding, space the zucchini seeds about 2-3 feet apart in rows that are 4-5 feet apart. This spacing allows adequate airflow and prevents overcrowding, which can lead to disease issues. As for the sowing depth, plant the seeds about 1 inch deep in the soil. Additionally, consider placing a thin layer of mulch around the seeded area to help conserve moisture and suppress weed growth.

Seasonal Planting Considerations
Spring Planting
Spring is generally the preferred season for planting zucchini, as it provides ample warmth and favorable growing conditions. If you reside in a region with mild winters, you can start planting zucchini seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last spring frost date. Once the frost danger has passed, you can transplant the seedlings outdoors or directly sow the seeds in the garden. Spring planting ensures that your zucchini plants have sufficient time to grow and produce before the heat of summertime.
Summer Planting
In some regions with hot summer temperatures, planting zucchini in the summer can be a challenge. Zucchini plants do not tolerate extreme heat well and may struggle to produce fruit in scorching conditions. However, if your summers are relatively mild or you have access to shade, you can still have success with summer planting. Start seeds indoors about 6-8 weeks before the expected transplant date, considering that zucchini plants grow best in temperatures between 70°F and 90°F. Providing shade and adequate watering during hot spells can help protect your plants and ensure a good harvest.
Fall Planting
Fall planting is a favorable option for regions with mild winters or climates that experience a second growing season. By planting zucchini in the fall, you can take advantage of the cooler temperatures and potential extended harvest. Start seeds indoors about 6-8 weeks before the first expected frost date in your region. Transplant the seedlings outdoors once the soil temperature and weather conditions are suitable. Fall planting allows you to enjoy fresh zucchini well into the cooler months and make the most of your gardening season.
Maintaining and Harvesting Zucchini
Providing Proper Care
To ensure healthy and productive zucchini plants, it’s essential to provide them with proper care throughout the growing season. Zucchini plants require regular watering, ideally providing about 1 inch of water per week. Ensure the soil is consistently moist but not waterlogged, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases. Additionally, applying a balanced fertilizer every 4-6 weeks can help replenish essential nutrients and promote vigorous growth. Regularly inspect your plants for pests and diseases, and promptly address any issues to prevent them from spreading.
Identifying and Treating Common Pests and Diseases
Zucchini plants can be susceptible to various pests and diseases that can affect their health and productivity. Common pests that may target your zucchini plants include aphids, squash bugs, cucumber beetles, and vine borers. It’s important to regularly inspect your plants for signs of pest infestation, such as wilting leaves, yellowing, or chewed foliage. Implementing organic pest control methods like handpicking, using insecticidal soaps, or introducing beneficial insects can help mitigate pest problems.
In terms of diseases, zucchini can be affected by powdery mildew, which manifests as a white powdery coating on the leaves. Providing adequate air circulation and avoiding overhead watering can help prevent powdery mildew. If detected, applying a fungicide labeled for powdery mildew control can help manage the disease. Proper sanitation and crop rotation practices can also help prevent the occurrence of other common zucchini diseases, such as bacterial wilt or blossom end rot.
Harvesting Zucchini
Once your zucchini plants start producing fruit, it’s important to know the proper way to harvest them to ensure optimal taste and quality. Zucchini is best harvested when the fruits are young and tender, usually around 6-8 inches in length. Harvesting zucchini regularly when they reach the desired size encourages more fruit production and prevents the fruits from becoming overly large and tough. Use a sharp knife or pruning shears to cut the zucchini from the plant, avoiding any excessive pulling or twisting that could damage the plant. Harvesting your zucchini with care will not only ensure the best flavor and texture but also promote continued plant growth and future harvests.

Conclusion
Planting zucchini can be a rewarding and enjoyable experience, but it’s important to consider several factors to ensure successful growth and a bountiful harvest. By considering the climate, preparing the soil, taking into account frost dates, and implementing companion planting, you can lay a solid foundation for your zucchini plants. Understanding the best time to start seeds indoors or directly sow in the garden and when to transplant seedlings will help you time your planting for optimal growth. Additionally, taking into account seasonal planting considerations and providing proper care throughout the growing season will ensure healthy plants and abundant harvests. With attention to these factors and a little bit of patience and care, you’ll soon be enjoying delicious zucchini straight from your garden.