So you’ve decided to try your hand at growing lettuce in the Lone Star State. With its hot and dry weather conditions, cultivating lettuce in Texas might seem like a daunting task. But fear not! In this article, we will provide you with some valuable tips and tricks on how to successfully grow lettuce in the Texas climate. From choosing the right lettuce varieties to providing optimal care and maintenance, we’ve got you covered. Let’s get started on this leafy green adventure!

Choosing the Right Varieties
Consider heat-tolerant varieties
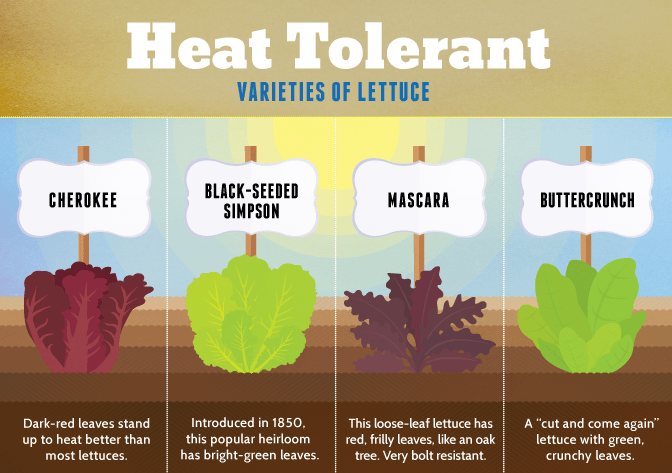
When growing lettuce in Texas, it’s crucial to choose heat-tolerant lettuce varieties. The scorching temperatures during the summer months can cause lettuce to bolt and become bitter. Look for varieties like Buttercrunch, Black Seeded Simpson, and Red Sails, which are known for their ability to withstand high temperatures.
Select varieties suitable for different seasons
Texas has a diverse climate, with varying temperatures throughout the year. To ensure a successful lettuce harvest, choose varieties that are suitable for different seasons. For spring and fall planting, opt for cool-season varieties like Romaine, Bibb, and Oakleaf lettuce. For summer planting, choose heat-tolerant varieties as mentioned earlier.
Opt for bolt-resistant varieties
Bolting is a natural process in lettuce where the plant prematurely goes to seed, resulting in bitter and inedible leaves. To avoid bolting, opt for bolt-resistant lettuce varieties. These varieties, such as Summercrisp and Batavian lettuce, have been bred specifically to delay the bolting process and maintain the flavor and texture of the leaves.
Try different lettuce types
Lettuce comes in various types, each with its own unique flavor and texture. Experiment with different types like Romaine, Butterhead, Crisphead, and Looseleaf lettuce. Each type has its own characteristics and can add variety to your salads and meals.
Preparing the Soil
Test the soil’s pH
Before planting lettuce, it’s important to test the soil’s pH level. Lettuce prefers a slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. Testing the soil will help you determine if any necessary adjustments need to be made to create ideal growing conditions for your lettuce.
Improve drainage and fertility
Lettuce requires well-draining soil to prevent root rot and other water-related issues. Amend the soil by adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve drainage. Additionally, ensure the soil is fertile by incorporating a balanced fertilizer or organic amendments to provide essential nutrients for the lettuce plants.
Add organic matter
Incorporating organic matter into the soil is beneficial for lettuce growth. It helps improve soil structure, enhances nutrient availability, and assists in moisture retention. Mix in compost or well-rotted manure before planting to enrich the soil with organic matter and create a healthy growing environment for your lettuce.
Avoid compacted soil
Lettuce roots require oxygen to grow and thrive. Compacted soil restricts root growth and leads to poor nutrient absorption. Prior to planting, loosen the soil using a garden fork or tiller to improve aeration and prevent compaction. This will ensure that the lettuce plants have room to develop healthy root systems.

Planting Time and Location
Observe the average temperatures
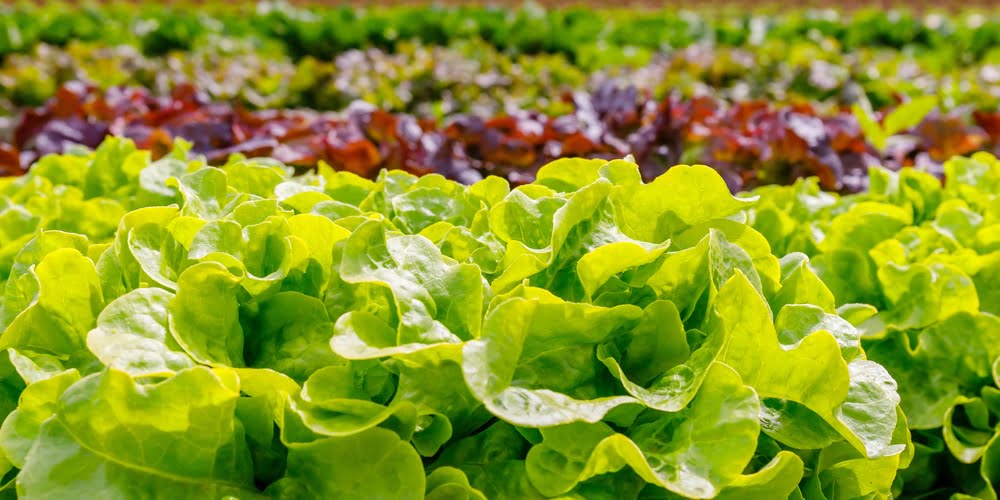
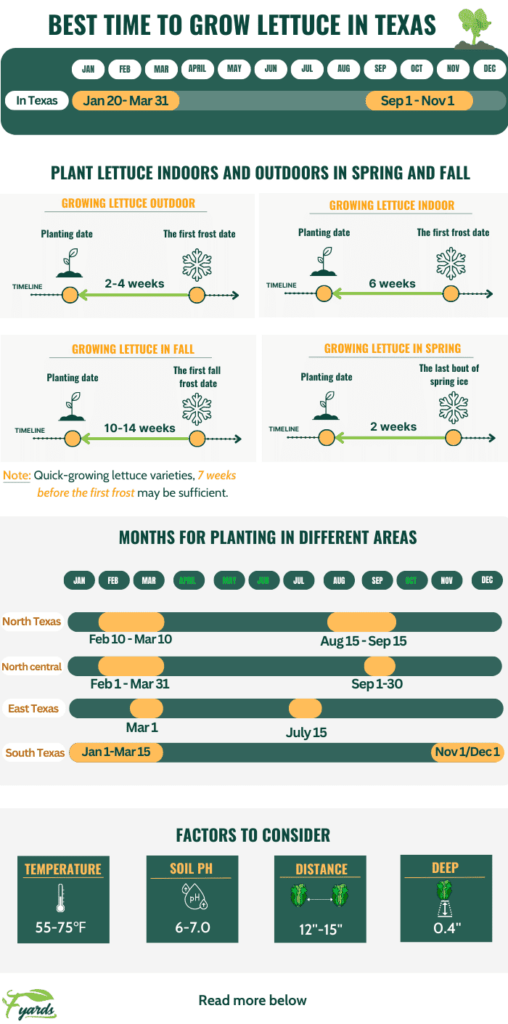
Before planting lettuce, it’s essential to observe the average temperatures in your region. Lettuce prefers cool temperatures between 45°F and 75°F for optimal growth. Avoid planting during extreme heatwaves or frosty periods, as these conditions can negatively impact lettuce germination and overall plant health.
Determine the right season to plant
In Texas, lettuce can be grown both in the cool seasons of spring and fall, and as a summer crop with heat-tolerant varieties. Plant lettuce in early spring, as soon as the soil can be worked, for a bountiful harvest before the scorching summer temperatures arrive. For a fall crop, sow lettuce seeds in late summer, around 8-10 weeks before the first expected frost.
Choose a suitable planting location
Selecting the right planting location is crucial for lettuce success. Choose a spot that receives partial shade, especially during the hot afternoon sun in Texas. Lettuce prefers cooler conditions and can become stressed or bolt quickly under intense heat. Consider planting near taller plants or structures that provide shade to help protect your lettuce from excessive sun exposure.
Consider shade or partial shade
It’s important to provide some shade to your lettuce plants, especially during the scorching Texas summers. If you don’t have a naturally shaded location in your garden, consider using shade cloth or planting lettuce near taller plants that will provide some relief from the sun’s intensity. This will help prevent wilting, bolting, and ensure better lettuce quality.
Starting Seeds Indoors
Gather necessary supplies
Before starting seeds indoors, gather all the necessary supplies. You’ll need seed trays or pots, a seed-starting mix, a watering can or spray bottle, and labels to keep track of the different lettuce varieties. Additionally, a grow light or a sunny spot near a window is essential to provide adequate lighting for the seedlings’ growth.
Use a quality seed-starting mix
Using a high-quality seed-starting mix is crucial for successful seed germination. These mixes are specifically formulated to provide the right balance of moisture retention and drainage for young seedlings. Fill your seed trays or pots with the seed-starting mix, ensuring there are no large clumps or debris that could impede seedling growth.
Sow seeds and provide proper care
Sow the lettuce seeds according to the package instructions, usually around ¼ inch deep. After sowing, gently cover the seeds with a thin layer of the seed-starting mix and mist the surface with water to ensure even moisture. Place the seed trays or pots in a warm spot or under grow lights, maintaining a consistent temperature between 60°F and 70°F. Keep the soil evenly moist, but not overly wet, throughout the germination period.
Transplant seedlings when ready
Once the lettuce seedlings have developed a few true leaves and are large enough to handle, they can be transplanted into larger pots or directly into the garden. Before transplanting, harden off the seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions over the course of a week. When planting outdoors, ensure the soil has warmed up and there is no longer a threat of frost.
Direct Seeding in the Garden
Prepare the garden bed
Before direct seeding lettuce in the garden, prepare the bed by removing any weeds, rocks, or debris. Loosen the soil to a depth of 6 to 8 inches, incorporating compost or well-rotted manure to improve fertility and drainage. Smooth the soil’s surface to create a level planting bed for the lettuce seeds.
Sow lettuce seeds directly
Sow lettuce seeds directly in the garden by scattering them evenly over the prepared soil. Follow the recommended spacing on the seed packet, usually around 6 to 12 inches apart depending on the lettuce variety. Lightly press the seeds into the soil or cover them with a thin layer of sifted compost, as lettuce seeds require light for germination.
Thin the seedlings
Once the lettuce seedlings have emerged and have grown a few inches tall, thin them to the appropriate spacing. Overcrowding can hinder the development of healthy lettuce heads or leaves. Gently remove the weakest seedlings, leaving the strongest ones to grow and mature. Thinning allows for better air circulation and ensures adequate nutrition for the remaining lettuce plants.
Protect the seedlings from pests
Lettuce seedlings can be vulnerable to pests such as slugs, snails, and rabbits. Protect your seedlings by using organic pest control methods like applying diatomaceous earth, setting up physical barriers like fences or netting, or using homemade repellents. Regularly check for signs of pest damage and take necessary measures to protect your lettuce plants.
Watering Needs
Provide consistent moisture
Lettuce plants require consistent moisture for optimal growth. Water your lettuce regularly, ensuring the soil remains consistently moist but not waterlogged. Avoid letting the soil dry out completely, as this can lead to wilting and bitterness in the leaves. Consistent moisture is especially important during hot and dry periods in Texas when evaporation rates are high.
Avoid overwatering
While providing consistent moisture is important, it’s equally crucial to avoid overwatering lettuce. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases. To prevent overwatering, check the moisture content of the soil by inserting your finger or a moisture meter into the soil. Only water when the top inch of soil feels dry.
Use a drip irrigation system
To ensure efficient and targeted watering, consider using a drip irrigation system for your lettuce. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone of the plants, minimizing water waste through evaporation or runoff. It also helps prevent excess moisture on the leaves, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
Mulch to conserve moisture
Applying a layer of organic mulch around your lettuce plants can help conserve moisture in the soil. Mulch acts as a protective barrier, preventing rapid evaporation and reducing weed growth. Organic mulch, such as straw or shredded leaves, also adds nutrients to the soil as it breaks down over time, further benefiting your lettuce plants.

Fertilizing Tips
Test the soil’s nutrient levels
Before fertilizing your lettuce, it’s essential to test the soil’s nutrient levels. A soil test will help you determine if any specific nutrients are lacking, allowing you to make informed decisions about the appropriate fertilizer to use. Testing your soil annually will ensure your lettuce plants receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and development.
Choose a balanced fertilizer
When it comes to fertilizing lettuce, choosing a balanced fertilizer with equal amounts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) is ideal. Look for a fertilizer with an NPK ratio of around 10-10-10 or similar. This balanced blend will provide the necessary nutrients for overall lettuce health, promoting vigorous growth and tasty leaves.
Apply fertilizer at the right times
Lettuce plants benefit from regular fertilization throughout their growth cycle. Apply a balanced fertilizer at planting time to provide initial nutrients for the seedlings. Additionally, side-dress the plants with a light application of the same balanced fertilizer once they have established and started actively growing. Follow the package instructions for the appropriate application rates.
Consider organic fertilizers
For organic gardening enthusiasts, organic fertilizers offer an excellent alternative to synthetic options. Use compost, well-rotted manure, or organic liquid fertilizers to supply nutrients to your lettuce plants. These organic fertilizers not only provide essential nutrients but also improve soil structure and promote overall soil health.
Managing Pests and Diseases
Inspect plants regularly
Regularly inspect your lettuce plants for any signs of pests or diseases. Look for chewed leaves, holes, spots, discoloration, or unusual growth patterns. Early detection is key to preventing pests and diseases from spreading and causing significant damage to your lettuce crop. Act promptly if any issues are observed.
Control aphids and caterpillars
Aphids and caterpillars are common pests that can infest lettuce plants. To control aphids, introduce natural predators like ladybugs or use insecticidal soaps or neem oil. For caterpillars, handpicking or using organic biological controls like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) can be effective. Regularly inspect the underside of leaves, as these pests often hide there.
Prevent fungal diseases
To prevent common fungal diseases like powdery mildew and downy mildew, practice good cultural and watering practices. Avoid overhead watering, which can splash water onto the lettuce leaves and create a favorable environment for fungal growth. Proper spacing and good airflow between plants can also help prevent the spread of fungal diseases.
Practice crop rotation
Implementing crop rotation is essential in preventing the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil. Avoid planting lettuce or other related crops in the same spot year after year. Rotate lettuce with non-related crops, such as tomatoes or peppers, to disrupt pest and disease life cycles and reduce the risk of recurring issues.

Harvesting Lettuce
Monitor the growth of the plants
Lettuce can be harvested at different stages, depending on your preferences. For looseleaf lettuce, you can start harvesting individual leaves when they reach a size you desire. For head lettuce, observe the firmness and size of the lettuce heads to determine when they are ready for harvest. Regularly monitor the growth of your lettuce plants to ensure timely and flavorful harvests.
Harvest individual leaves or entire heads
To harvest looseleaf lettuce, simply snip off the outer leaves using clean scissors or shears. Harvesting individual leaves allows the plant to continue growing and producing more leaves for future harvests. For head lettuce, use a sharp knife to cut the entire head at the base when it reaches the desired size and firmness.
Harvest in the morning
For the best flavor and texture, harvest lettuce in the early morning when it’s at its freshest. The leaves will be crisp and cool from the nighttime temperature drop. Harvesting in the morning also minimizes wilting due to the heat and sun exposure later in the day.
Store harvested lettuce properly
After harvesting, it’s important to store lettuce properly to maintain its freshness. Rinse the lettuce leaves gently to remove any dirt, then pat them dry. Store the leaves in a perforated plastic bag or airtight container lined with paper towels in the refrigerator. Properly stored lettuce can stay fresh for up to a week.
Extending the Growing Season
Provide shade during hot periods
During the scorching Texas summers, providing shade for your lettuce plants can help extend the growing season. Use shade cloth or create temporary structures using row covers to protect the lettuce from intense sun exposure. Shade can also help reduce soil temperature and prevent lettuce from bolting too quickly.
Use row covers or cold frames
Row covers and cold frames are useful tools for extending the lettuce growing season in Texas. Row covers provide insulation and protection from extreme temperatures, while cold frames create a greenhouse-like environment for the lettuce. Both options help regulate temperature and keep the lettuce plants cool during the hotter parts of the year.
Consider succession planting
Instead of planting all your lettuce at once, consider succession planting to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the season. Sow small batches of lettuce seeds every couple of weeks, staggering the planting dates. This way, you’ll have a fresh supply of lettuce at different stages of growth, ensuring a more extended harvest period.
Grow lettuce as a fall crop
Fall is an excellent time to grow lettuce in Texas due to the milder temperatures. Plant lettuce seeds in late summer, around 8-10 weeks before the first expected frost. The cooler weather allows for slower growth and prevents bolting. Enjoy a second lettuce harvest in the fall, taking advantage of the more favorable growing conditions.
Growing lettuce in Texas can be a rewarding experience with proper planning and care. Consider the heat-tolerant and bolt-resistant lettuce varieties, prepare the soil adequately, and choose the right planting time and location. Whether you prefer starting seeds indoors or direct seeding in the garden, providing consistent moisture and appropriate fertilization will ensure healthy lettuce plants. Monitor for pests and diseases, harvest at the right time, and extend the growing season with shade or succession planting. By following these tips and tricks, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of fresh, homegrown lettuce throughout the year.