Achieving optimal growth and yields in strawberry cultivation requires careful consideration of various factors, one of which is the depth of planting. In the pursuit of answering the pivotal question “How deep to plant strawberries?” this article aims to provide an in-depth analysis and comprehensive insight into the ideal planting depth for strawberries. By examining scientific research, expert recommendations, and practical experiences, this article will equip you with the necessary knowledge and guidance to make informed decisions when it comes to planting strawberries at the appropriate depth for maximum success.
Choosing the Right Depth
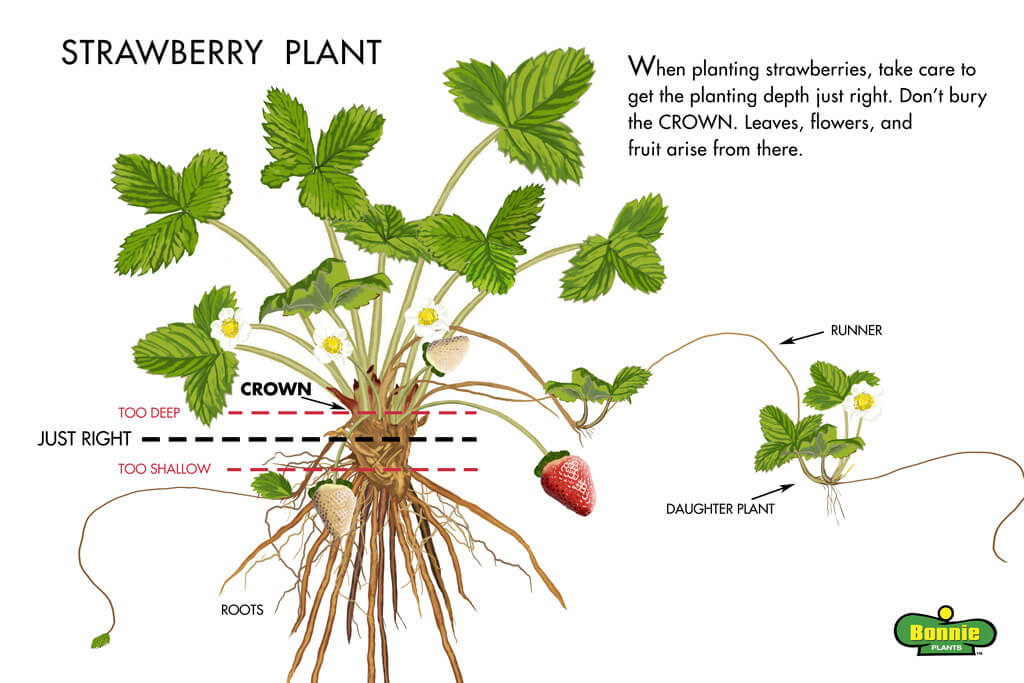
When it comes to planting strawberries, choosing the right depth is crucial for the successful growth and development of your plants. The depth at which you plant your strawberries can impact their ability to establish strong root systems, access sufficient nutrients and water, and withstand various environmental conditions. There are several key factors to consider when determining the appropriate planting depth for strawberries, including the type of strawberry variety, the local climate and soil conditions, and the age and size of the plants. By understanding these factors and following planting depth guidelines, you can ensure the optimal growth and productivity of your strawberry plants.
Factors to Consider
Before determining the planting depth for your strawberries, it is important to consider several factors that can influence the overall health and performance of your plants. One of the primary factors to consider is the type of strawberry variety you are planting. Different strawberry varieties have specific growth habits and requirements, including their preferred planting depths. It is essential to research and understand the specific needs of the strawberry variety you are working with to ensure the best results.
Local climate and soil conditions are also significant considerations when determining the planting depth for strawberries. Regions with hot climates or heavy rainfall may require deeper planting depths to protect the plants from excessive heat or moisture. Similarly, soil conditions such as drainage capacity and nutrient levels can impact how deep your strawberries should be planted. Conducting a soil test can provide valuable information about the quality and composition of your soil, allowing you to make any necessary amendments before planting.
Finally, the age and size of your strawberry plants should also be taken into account when determining the planting depth. Younger and smaller plants typically require shallower planting depths compared to more mature and larger plants. Planting at the appropriate depth ensures that the roots are adequately covered while allowing the crown of the plant to remain above the soil surface.
Planting Depth Guidelines
While there is some variation in planting depth recommendations depending on the strawberry variety and local conditions, there are general guidelines you can follow to ensure the optimal planting depth for your strawberries.
For June-bearing strawberries, it is generally recommended to plant them with the crown at or just above the soil surface. This helps to prevent crown rot and encourages vigorous root growth. On the other hand, everbearing and day-neutral strawberry varieties are typically planted slightly deeper, with the crown buried ¼ to ½ inch below the soil surface. This deeper planting depth helps to encourage strong root development and enables the plants to better tolerate heat and drought conditions.
In addition to considering the varieties and their specific planting depths, it is important to ensure that the planting holes are wide enough to accommodate the roots without bending or crowding them. This provides sufficient space for the roots to grow and avoids any restrictions that could hinder the plant’s development.
By following these planting depth guidelines and considering the various factors that influence strawberry growth, you can establish a solid foundation for your plants and maximize their potential for success.
Preparing the Soil
To set your strawberry plants up for success, it is crucial to prepare the soil properly before planting. The condition of the soil and its ability to provide essential nutrients, support root growth, and drain excess water can significantly impact the health and productivity of your strawberries. By taking the time to improve the soil condition and ensure adequate drainage, you can create an optimal growing environment for your plants.
Soil Condition Requirements
Strawberries thrive in well-drained soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Soil that is too acidic or alkaline can affect nutrient availability and the overall health of your plants. Conducting a soil test before planting can help determine the pH level and identify any necessary amendments, such as adding lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it.
Additionally, incorporating organic matter into the soil can greatly enhance its fertility and structure. Organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, improves soil moisture retention, promotes nutrient availability, and enhances soil texture. It also provides a steady release of nutrients over time, reducing the need for additional fertilizers.
Improving Drainage
Proper drainage is essential for avoiding waterlogged soil, which can lead to root rot and other detrimental conditions for strawberries. To improve drainage, you can amend the soil with materials such as coarse sand or perlite. These materials increase soil porosity and allow excess water to drain away more freely. Additionally, avoiding low-lying areas or compacted soils can help prevent water pooling and enhance overall drainage.
It is also important to ensure that the planting area has proper slope and grade to prevent water from accumulating around the plants. Raised beds or mounds can be created to promote better drainage and avoid waterlogged soil.
Adding Organic Matter
Incorporating organic matter into the soil not only improves soil fertility but also enhances its structure and water-holding capacity. Before planting, amend the soil with well-rotted compost, aged manure, or other organic materials. This can be done by spreading a layer of organic matter over the planting area and incorporating it into the top 8 to 10 inches of soil using a garden fork or tiller. Organic matter not only provides essential nutrients for your plants but also improves soil aeration and moisture retention, creating a favorable environment for root growth and overall plant development.
By properly preparing the soil and ensuring adequate drainage and nutrient availability, you can provide your strawberry plants with an optimal growing environment that supports their health and productivity.
Planting Techniques
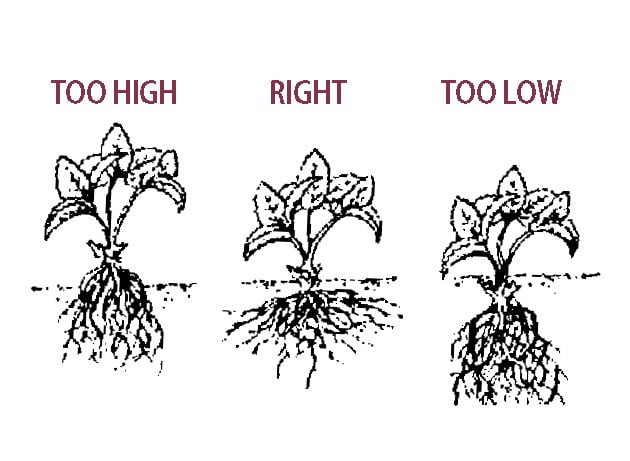
The way strawberries are planted can significantly impact their ability to establish and thrive. Understanding the different planting techniques for bare-root and container-grown plants, as well as the importance of proper spacing, is crucial for achieving successful strawberry cultivation.
Bare-Root Plants
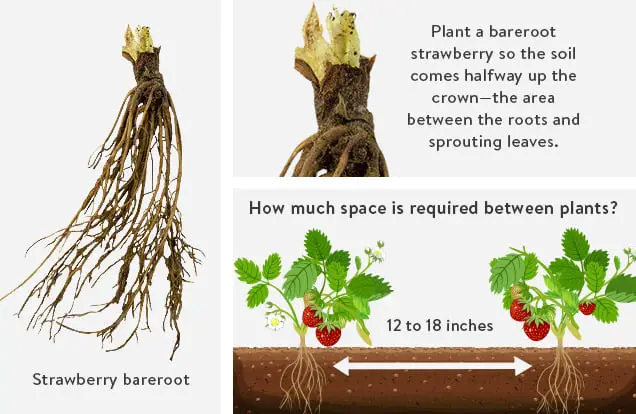
Bare-root plants refer to strawberries that are sold with exposed roots, without any soil or growing medium surrounding them. When planting bare-root strawberries, it is important to soak the roots in water for about 30 minutes before planting. This helps to rehydrate the roots and prepare them for establishment in the soil.
To plant bare-root strawberries, dig a hole that is wide enough to comfortably accommodate the roots without bending or overcrowding them. The planting hole should be deep enough to cover the roots while keeping the crown of the plant above the soil surface. Gently fan out the roots in the planting hole and backfill with soil, ensuring that the roots are adequately covered and the crown remains exposed.
Container-Grown Plants
Container-grown strawberries are plants that have been grown in pots or containers and are sold with their roots intact within the growing medium. When planting container-grown strawberries, it is essential to handle the plants carefully to avoid damaging the root system.
To plant container-grown strawberries, dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the entire root ball of the plant. Gently remove the plant from the container, taking care to minimize root disturbance. Place the plant in the planting hole, positioning it at the appropriate depth with the top of the root ball level with or slightly above the soil surface. Backfill the hole with soil, ensuring that the roots are adequately covered.
Spacing Considerations
Proper spacing is crucial for promoting airflow, preventing disease, and allowing each strawberry plant to access adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients. When planting strawberries, it is generally recommended to space them approximately 12 to 18 inches apart in rows that are 2 to 3 feet apart. This spacing allows the plants to grow and spread without overcrowding, maximizing their overall health and productivity.
Spacing considerations are particularly important for strawberries that produce runners, as leaving enough space between plants allows the runners to establish and develop into new plants without becoming overcrowded. By providing ample space for your strawberry plants, you can ensure optimal growth, minimize the risk of diseases, and maximize fruit production.
By understanding the different planting techniques for bare-root and container-grown plants and following proper spacing guidelines, you can ensure that your strawberry plants have the best chance of thriving and producing abundant fruit.
Planting Process
The planting process for strawberries involves several essential steps that contribute to the successful establishment of the plants and their long-term growth and productivity. By following a systematic approach, you can ensure that each plant is positioned correctly, the soil is properly adjusted, and the plants are adequately supported to thrive in their new environment.
Step 1: Preparing the Planting Area
Before planting your strawberries, it is necessary to prepare the planting area. Start by removing any existing weeds, grass, or vegetation to prevent competition for nutrients and water. Using a garden fork or tiller, loosen the soil to a depth of 8 to 10 inches, ensuring that the soil is aerated and free of clumps. This step helps to create a favorable environment for root growth and allows the plants to establish more easily.
Step 2: Digging the Planting Holes
To ensure proper positioning and adequate space for the roots, dig planting holes that are wide and deep enough to accommodate the size of the strawberry plants. The width of the planting hole should comfortably allow the roots to spread out without bending or crowding, while the depth should be sufficient to cover the roots while keeping the crown of the plant above the soil surface.
Make sure to space the planting holes according to the recommended spacing guidelines for your strawberry variety. This prevents overcrowding and allows each plant to receive sufficient light, airflow, and access to nutrients and water.
Step 3: Adjusting the Soil
Once the planting holes are prepared, it is important to make any necessary adjustments to the soil before placing the plants. If the soil pH needs to be corrected, follow the recommendations from the soil test and incorporate the appropriate amendments. Additionally, if the soil is heavy and compacted, it may be beneficial to mix in organic matter or sand to improve its structure and drainage.
Step 4: Setting the Plants in the Holes
Gently place each strawberry plant in its respective planting hole, ensuring that the roots are properly positioned and not bent or crowded. For bare-root plants, gently fan out the roots before placing them in the hole. For container-grown plants, carefully remove the plant from the container, minimizing root disturbance. Position the plants at the appropriate depth, with the crown level with or slightly above the soil surface.
Make sure to position the plants facing the correct direction, with the leaves facing outward to maximize exposure to sunlight and airflow. This promotes proper growth and helps prevent disease by enhancing drying and reducing excessive moisture on the leaves.
Step 5: Backfilling and Firming
Once the plants are correctly positioned, backfill the planting holes with soil, ensuring that the roots are adequately covered. Gently firm the soil around the plants to eliminate air pockets, provide stability, and establish good root-to-soil contact. However, take care not to compact the soil excessively, as this can hinder root growth and drainage.
After completing the planting process, thoroughly water the newly planted strawberry plants to help settle the soil around the roots and provide much-needed moisture. Avoid over-watering, as this can lead to excessive moisture and waterlogging.
By following these systematic steps in the planting process, you can ensure that your strawberry plants are positioned correctly, the soil is adequately adjusted, and the plants are well-supported to establish and thrive in their new environment.

Post-Planting Care
Once your strawberry plants are in the ground, providing proper post-planting care is essential for their continued health and productivity. This care includes mulching, watering, fertilizing, and weed control.
Mulching
Mulching is a crucial post-planting practice that helps to conserve soil moisture, regulate soil temperature, control weeds, and prevent the spattering of soil onto the fruit. Applying an organic mulch, such as straw, pine needles, or wood chips, around the base of the plants helps to maintain consistent soil moisture levels and suppress weed growth. Mulch also acts as an insulating layer, protecting the plants and their roots from extreme temperatures.
When mulching strawberries, apply a layer of mulch that is approximately 2 to 4 inches deep, taking care to keep it a few inches away from the crown of the plants. This allows proper air circulation and prevents the crowns from becoming excessively moist, which can lead to fungal diseases.
Watering
Proper watering is crucial for the growth and survival of strawberry plants, particularly during the initial establishment period. After planting, it is important to water the plants thoroughly to settle the soil and provide moisture to the roots. Subsequently, continue to water regularly, especially during dry periods, to ensure that the plants receive adequate hydration.
When watering strawberries, it is important to provide deep watering rather than frequent shallow watering. Deep watering encourages the development of deep root systems and enhances the plant’s ability to access water in the soil. To minimize the risk of disease, avoid watering the leaves and foliage and direct the water towards the soil and root zone.
Fertilizing
Strawberries have specific nutrient requirements for optimal growth and fruit production. While incorporating organic matter into the soil during the preparation stage provides a good foundation of nutrients, additional fertilization may be necessary to meet the plants’ nutritional needs.
Before applying any fertilizers, it is important to conduct a soil test to determine the nutrient levels and any deficiencies. This helps to guide the appropriate fertilizer application. Generally, a balanced slow-release fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10 or 14-14-14 can be applied around the plants in early spring and again in late spring or early summer. Follow the fertilizer package instructions for rates and application methods.
When applying fertilizer, it is important to avoid direct contact with the leaves and foliage, as this can cause leaf burn. Water the plants after fertilization to ensure that the nutrients are carried down to the roots effectively.
Weed Control
Weed control is a critical aspect of post-planting care to maintain the health and productivity of your strawberry plants. Weeds compete with strawberries for nutrients, water, and sunlight, and can significantly impact their growth and yield. Proper weed control helps to minimize competition and create an environment where the strawberries can thrive.
To control weeds, regularly inspect the planting area and remove any weeds or vegetation that emerge. Hand pulling or using a hoe or cultivator can effectively remove weeds. Apply mulch around the plants to suppress weed growth and minimize the need for frequent weeding. Additionally, using pre-emergent herbicides can help prevent weed germination and establish weed-free beds.
By consistently implementing mulching, watering, fertilizing, and weed control practices, you can provide your strawberry plants with the post-planting care they need to thrive and produce delicious fruit.
Managing Depth for Different Varieties
Different varieties of strawberries have specific growth habits and requirements, including their preferred planting depths. Understanding the optimal planting depth for each strawberry variety is crucial for promoting healthy root development, optimal nutrient and water uptake, and overall growth and productivity.
June-Bearing Strawberries
June-bearing strawberries are a popular variety known for producing a single large crop in early to mid-summer. When planting June-bearing strawberries, it is generally recommended to position the crown at or just above the soil surface. This shallow planting depth helps to prevent crown rot and encourages strong root growth. By planting June-bearing strawberries at the appropriate depth, you can ensure that they establish well and produce abundant fruit.
Everbearing Strawberries
Everbearing strawberries, as the name suggests, produce fruit continuously throughout the growing season. These strawberries generally have more extensive root systems compared to June-bearing varieties and benefit from slightly deeper planting. When planting everbearing strawberries, bury the crown ¼ to ½ inch below the soil surface. This deeper planting depth promotes vigorous root development and helps the plants better tolerate heat and drought conditions.
Day-Neutral Strawberries
Day-neutral strawberries are another variety that produces fruit continuously throughout the growing season, regardless of day length. Day-neutral strawberries typically have shallow root systems and prefer planting depths similar to everbearing strawberries. Place the crown of day-neutral strawberries ¼ to ½ inch below the soil surface to encourage strong root growth and provide an optimal planting environment.
By understanding the specific planting depth requirements for different strawberry varieties, you can ensure that your plants have the best possible start and are well-positioned for growth, productivity, and overall success.
Monitoring Plant Performance
Monitoring the performance of your strawberry plants is essential for identifying any issues or anomalies and taking appropriate corrective measures. Observing the plants regularly and being aware of the signs associated with shallow or deep planting can help you make necessary adjustments and ensure optimal growth and productivity.
Signs of Shallow Planting
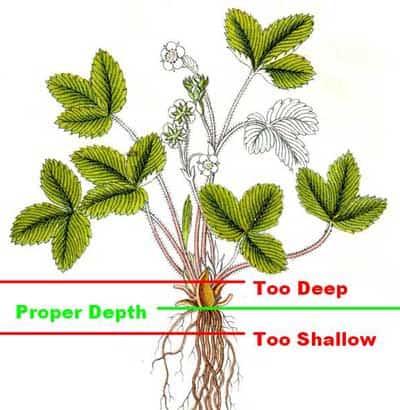
Shallow planting can have detrimental effects on strawberry plants, affecting their root development, stability, and overall performance. One of the most noticeable signs of shallow planting is the exposure of the crown above the soil surface. Additionally, shallow-planted strawberries may exhibit weak root systems, fail to establish good contact with the soil, and display poor overall growth. The plants may also be more susceptible to drying out quickly and struggling to access sufficient nutrients and water.
If shallow planting is suspected, carefully dig around the base of the plant to examine its root system. If the roots are not properly developed or fail to extend into the soil, it may indicate that the plants were not planted at the appropriate depth. In such cases, adjustments should be made to ensure that the crown is properly covered with soil while allowing the leaves to remain exposed.
Signs of Deep Planting
Deep planting can also pose challenges to the growth and development of strawberry plants. When strawberries are planted too deep, the crown can become excessively buried, hindering proper airflow and increasing the risk of crown rot and disease. Plants that are too deep may exhibit slow growth, yellowing leaves, and limited fruit production.
To determine if your strawberries are planted too deep, examine the position of the crown in relation to the soil surface. If the crown is buried too deeply, carefully adjust the soil level around the base of the plant, ensuring that the crown is at the appropriate height above the soil surface. By correcting the planting depth, you can help the plants establish stronger root systems and improve their overall performance.
Adjusting Depth if Needed
If you observe signs of shallow or deep planting in your strawberry plants, it is important to make the necessary adjustments promptly. Modifying the planting depth can help the plants establish better root systems, access sufficient nutrients and water, and ultimately thrive in the growing environment.
To adjust the planting depth, carefully dig around the base of the plant without damaging the roots. Gently lift the plant out of the ground, adjust the soil level around the roots, and replant the strawberry at the appropriate depth. Ensure that the crown is positioned correctly, either at or just above the soil surface for June-bearing strawberries, or slightly below the surface for everbearing and day-neutral varieties.
By monitoring the performance of your strawberry plants and making necessary adjustments to the planting depth, you can optimize their growth and productivity and ensure a successful harvest.
Potential Problems and Solutions
Growing strawberries can sometimes be challenging due to various potential problems and conditions that can affect their health and productivity. Understanding common issues, such as root rot, frost damage, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies, can help you identify and address these problems effectively.
Root Rot
Root rot is a common problem that can affect strawberry plants, particularly in poorly drained soils. Excessive moisture and poor soil conditions can lead to the growth of fungal pathogens, causing the roots to rot and the plants to decline. Signs of root rot include stunted growth, yellowing leaves, wilting, and poor fruit production.
To prevent root rot, it is important to ensure that the planting area has good drainage by improving the soil structure and avoiding areas prone to waterlogging. Planting strawberries at the appropriate depth, as well as providing proper spacing and mulching, can also help reduce the risk of root rot. Additionally, avoiding excessive irrigation and only watering when necessary can help maintain proper moisture levels in the soil, minimizing the risk of fungal pathogens.
Frost Damage
Strawberries can be susceptible to frost damage, especially during spring when cold temperatures can harm the blossoms and immature fruit. Frost damage can cause the flowers and fruit to become discolored, wither, or drop prematurely.
To protect strawberry plants from frost damage, it is important to monitor weather forecasts and take preventive measures when frost is expected. Covering the plants with row covers, blankets, or other protective materials can help shield them from extreme temperature fluctuations. Additionally, planting strawberries in areas with good air drainage and avoiding low-lying or frost-prone spots can help minimize the risk of frost damage.
Pest Infestations
Strawberries can attract various pests, including aphids, spider mites, slugs, and snails. These pests can damage the leaves, flowers, and fruit, leading to reduced plant vigor and crop yield. Signs of pest infestations can include distorted or discolored leaves, holes in the leaves or fruit, webbing, and the presence of the pests themselves.
To manage pest infestations, it is important to regularly inspect your strawberry plants and take appropriate measures if pests are detected. Cultural practices such as proper sanitation, removing weeds and debris, and maintaining good airflow can help minimize pest populations. Additionally, using organic or chemical control methods, such as insecticidal soaps or biological controls, can be effective in managing specific pests. It is essential to identify the specific pests and seek appropriate methods for control.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Strawberries require adequate nutrients for healthy growth and abundant fruit production. Nutrient deficiencies can manifest in various ways, including stunted growth, yellowing leaves, poor fruit development, and low yields. Common nutrient deficiencies in strawberries include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and iron.
To address nutrient deficiencies, it is important to conduct a soil test to identify any imbalances or deficiencies. Based on the soil test results, you can apply the appropriate fertilizers or soil amendments to provide the lacking nutrients. Regularly fertilizing your strawberry plants with a balanced fertilizer can help prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote optimal growth and productivity. Avoid over-fertilization, as this can lead to excess nutrient buildup and potential toxicity.
By being aware of potential problems such as root rot, frost damage, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies, you can take proactive measures to address these issues and ensure the health and productivity of your strawberry plants.
Harvesting Tips
Harvesting strawberries at the right time is crucial for maximizing their flavor, sweetness, and overall quality. Determining the optimal fruit ripeness and using correct harvesting techniques can help you enjoy the full, luscious flavor of freshly picked strawberries.
Determining Optimal Fruit Ripeness
To determine the optimal ripeness of strawberries, observe the fruit color, texture, and flavor. Strawberries should have a bright red color, indicating full ripeness. The fruit should be firm and plump, without any green areas or white tips. Gently squeezing the strawberries can help determine their firmness and readiness for harvesting.
In terms of flavor, ripe strawberries should have a sweet aroma and a delicate, juicy taste. Taste one or two strawberries to assess their sweetness and overall flavor profile. If the strawberries have the ideal combination of color, texture, and flavor, they are ready to be harvested.
Correct Harvesting Techniques
When harvesting strawberries, it is important to use gentle techniques to avoid damaging the fruit or the plants. Here are some tips to ensure correct harvesting:
Hold the strawberry by the stem or the green cap and gently twist it to detach it from the plant. Avoid pulling or yanking the fruit, as this can damage the plant or separate the stem from the fruit.
Use sharp hand pruners or scissors to cut the stem ¼ inch above the fruit if you prefer to harvest with the stem intact. This method can be particularly useful if you plan to use the strawberries for decorative purposes or want to extend their shelf life.
Handle the strawberries carefully to avoid bruising or crushing the fruit. Place them in a clean container or basket, taking care not to stack or overcrowd them.
It is best to harvest strawberries in the morning when the fruit is still cool and the moisture content is higher. This helps preserve the fruit’s quality and extend its shelf life.
By following these guidelines and using correct harvesting techniques, you can enjoy the full flavor and freshness of homegrown strawberries at their peak ripeness.
Conclusion
Proper planting depth is a crucial aspect of successful strawberry cultivation. By considering factors such as strawberry variety, local climate and soil conditions, and the age and size of the plants, you can determine the appropriate planting depth for your strawberries. Preparing the soil, using the correct planting techniques, and ensuring post-planting care are also essential for the plants’ health and productivity. Monitoring plant performance, addressing potential problems, and harvesting at the right time are vital for optimizing your strawberry cultivation. By following these guidelines and techniques, you can create an optimal growing environment and maximize the yield and quality of your homegrown strawberries.
Key Takeaways
- Choosing the right depth for planting strawberries is crucial for optimal growth and productivity.
- Factors to consider include the strawberry variety, climate and soil conditions, and the age and size of the plants.
- Guidelines for planting depth vary based on the variety, with June-bearing strawberries generally planted with the crown at or just above the soil surface, and everbearing and day-neutral varieties planted slightly deeper.
- Proper soil preparation, including adjusting pH and improving drainage, is important for the health and performance of strawberry plants.
- Planting techniques differ for bare-root and container-grown plants, and proper spacing is important for maximizing airflow and plant growth.
- The planting process involves preparing the planting area, digging planting holes, adjusting soil, setting plants at the correct depth, and backfilling and firming.
- Post-planting care includes mulching, watering, fertilizing, and weed control to ensure the plants’ continued health and productivity.
- Different strawberry varieties have specific planting depth requirements, including June-bearing, everbearing, and day-neutral varieties.
- Monitoring plant performance helps identify shallow or deep planting and allows for adjustments if needed.
- Potential problems such as root rot, frost damage, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies can be managed with proper care and intervention.
- Harvesting strawberries at the optimal ripeness and using correct techniques ensures the best flavor and quality.
- Proper planting depth plays a crucial role in the success of strawberry cultivation, leading to healthier plants, higher yields, and more delicious fruit.



