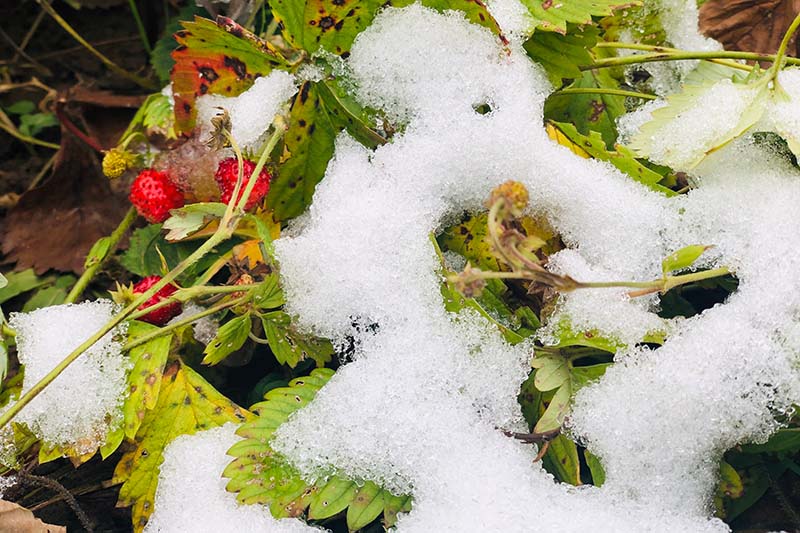
Strawberries, delicate and vulnerable to frost, require adequate protection to ensure their survival during colder months. Covering strawberries for frost is a common practice among growers and gardeners alike. This article delves into the various methods and materials used to shield strawberries from the harmful effects of frost, highlighting the importance of timing and the potential consequences of neglecting this crucial safeguard. By understanding the best practices for covering strawberries in frost, you can safeguard your crop and ensure a bountiful harvest season.

Understanding Frost and Its Impact on Strawberries
What is Frost?
Frost is a natural phenomenon that occurs when the temperature drops below freezing point (0 degrees Celsius or 32 degrees Fahrenheit). It is characterized by the formation of ice crystals on the surface of plants and other objects. Frost can occur during the colder months, particularly in regions with a cold climate or during transitional seasons such as spring and fall.
How Does Frost Affect Strawberries?
Strawberries are highly vulnerable to frost damage due to their delicate nature and shallow root system. When frost occurs, the ice crystals that form on the plant’s tissues can cause cellular damage. This damage can lead to wilting, browning, and even death of the plant. The severity of the damage depends on the duration and intensity of the frost event. Frost can affect all parts of the strawberry plant, including the leaves, flowers, and fruit.
Importance of Protecting Strawberries from Frost
Protecting strawberries from frost is crucial for maintaining the productivity and sustainability of strawberry crops. Frost damage can have significant economic repercussions for farmers, as it can lead to reduced yields and decreased quality of the fruit. Additionally, frost-damaged plants are more susceptible to diseases and pests, further compromising their overall health and productivity. It is essential for strawberry growers to implement effective frost protection measures to minimize the negative impact of frost on their crops.
Common Methods to Cover Strawberries for Frost Protection
Row Covers
Row covers are a popular method for protecting strawberries from frost. These covers consist of lightweight, breathable fabrics, such as spunbonded polypropylene or floating row cover material. Row covers are laid directly over the strawberry plants, forming a protective barrier against the cold air. They help trap heat from the ground and prevent frost formation on the plants. Row covers also provide additional benefits, such as protection from pests and early-season warmth for accelerated growth.
Mulch
Mulching is another effective method of frost protection for strawberries. Applying a layer of organic or inorganic mulch around the base of the plants helps insulate the roots and retain soil warmth. Common organic mulch options include straw, hay, and leaves, while plastic mulch is a popular inorganic alternative. Mulching not only protects against frost but also helps suppress weeds, retain soil moisture, and improve overall plant health.
Plastic Tunnels
Plastic tunnels, also known as low tunnels or hoop houses, are structures made of plastic sheeting or greenhouse film supported by hoops or frames. These tunnels are placed over rows of strawberry plants and provide a controlled microclimate, enhancing frost protection. Plastic tunnels trap heat from the sun, creating a warmer environment inside and shielding the strawberries from frost damage. Proper ventilation is essential when using plastic tunnels to prevent excessive heat build-up and ensure the health of the plants.
Cold Frames
Cold frames are another option for frost protection, especially in smaller-scale strawberry cultivation. These structures are essentially box-like structures with transparent tops, usually made of glass or polycarbonate, that allow sunlight to enter and trap heat inside. Cold frames provide excellent insulation and can be placed directly over strawberry plants. They offer an additional benefit of extending the growing season by creating a favorable environment for early-season growth and protecting plants during late-season frost events.
Straw or Hay
Applying a layer of straw or hay around strawberry plants can provide effective frost protection. Straw or hay acts as an insulating barrier, preventing the cold air from reaching the plants. It also helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and provide a clean surface on which the strawberries can grow. When using straw or hay as a covering method, it is essential to ensure that the material is clean and free from weed seeds to prevent the growth of unwanted plants.
Portable Greenhouses
Portable greenhouses, also known as high tunnels or hoop houses, are temporary structures made of metal or PVC frames covered with plastic sheeting. These greenhouses provide an enclosed environment for strawberry plants, offering protection from frost, wind, and other unfavorable weather conditions. Portable greenhouses are relatively easy to assemble and disassemble, making them a convenient option for temporary or seasonal use. However, proper ventilation is crucial to prevent excessive heat build-up and maintain optimal growing conditions.
Blankets or Tarps
Using blankets or tarps as a form of frost protection is a cost-effective and easily accessible method for small-scale strawberry growers. These covers can be spread over the plants during frost events to trap heat and prevent frost formation. However, it is essential to ensure that the blankets or tarps are securely anchored to prevent them from blowing away in windy conditions. Additionally, blankets and tarps may restrict air circulation, so vigilance is required to prevent excessive moisture buildup and disease development.
Watering Techniques
Utilizing specific watering techniques can help protect strawberries from frost damage. By watering the plants before a frost event, you can take advantage of the latent heat released during the freezing process. This heat helps keep the plants’ tissues above the critical temperature for frost damage. However, it is crucial to water carefully to avoid excessive moisture, as wet foliage can increase the risk of disease development. Drip irrigation or soaker hoses are recommended watering methods to minimize foliage moisture.
Using Heat Sources
In extreme frost situations, supplemental heat sources can be used to provide additional protection to strawberry plants. Electric heaters, heat lamps, or even small campfires can generate heat and raise the temperature within a covered area. These heat sources should be used with caution and proper safety measures to avoid fire hazards and damage to the plants. It is important to monitor the temperature closely and ensure that the heat source is safely positioned and controlled.
Combinations of Various Methods
To maximize the effectiveness of frost protection, a combination of different covering methods can be employed. For example, using row covers in conjunction with mulching or combining cold frames with plastic tunnels can provide enhanced insulation and protection against frost. It is essential to carefully consider the specific needs of the strawberry plants and the environmental conditions to determine the most suitable combination of frost protection methods.
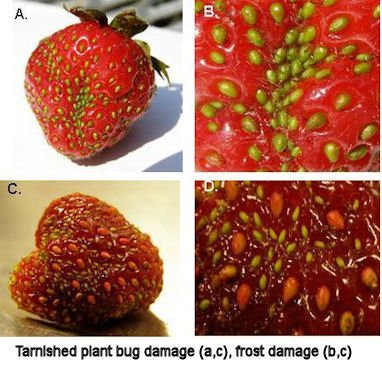
Factors to Consider Before Covering Strawberries for Frost
Weather Forecast
Before deciding on a specific frost protection method, it is crucial to closely monitor the weather forecast. Understanding the predicted temperature, duration of cold temperatures, and potential frost events allows growers to plan and implement appropriate protection measures. Different frost protection methods have varying degrees of effectiveness, and selecting the most suitable method depends largely on the severity and duration of the expected cold weather conditions.
Strawberries’ Growth Stage
The growth stage of the strawberry plants is an important factor to consider when implementing frost protection measures. Young plants and flowering plants are more susceptible to frost damage compared to established plants. For young plants, extra care is required as their root systems are still developing, and they may be more sensitive to cold temperatures. Flowering plants are at a critical stage, as frost can result in the loss of flowers and subsequently reduce fruit production.
Available Resources and Budget
The availability of resources and budgetary constraints play a role in determining the type of frost protection method that can be implemented. Some methods, such as row covers and mulching, are relatively inexpensive and require minimal investment. On the other hand, structures like portable greenhouses or cold frames may involve higher costs for materials and construction. Careful consideration of available resources and budget will help growers make informed decisions regarding frost protection measures.
Time and Effort Required
Different frost protection methods vary in terms of the time and effort required for installation, maintenance, and removal. For example, row covers and blankets can be quickly and easily placed over the plants during frost events, while portable greenhouses or cold frames may require more time for assembly and disassembly. Growers should consider their available time and labor resources when choosing the appropriate frost protection method.
Potential Risks and Benefits
Each frost protection method has its own set of risks and benefits that should be carefully weighed before implementation. For example, plastic tunnels may provide excellent protection against frost but carry the risk of excessive heat buildup if ventilation is inadequate. Row covers can trap heat effectively but may require more frequent monitoring for proper adjustment and ventilation. It is essential to evaluate the specific risks and benefits associated with each method and choose accordingly.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Cover Strawberries for Frost
Preparing the Strawberry Plants
Before implementing any frost protection measures, it is important to ensure that the strawberry plants are in optimal health. This includes proper watering, fertilization, pruning, and removal of any diseased or damaged plant material. Healthy plants are better equipped to withstand frost events and have a higher likelihood of survival and recovery.
Selecting the Appropriate Covering Method
Based on the factors mentioned earlier, such as weather forecast, growth stage of the plants, available resources, and budget, growers should select the most suitable frost protection method. Consideration should be given to the specific characteristics and needs of the strawberry cultivar being grown, as some varieties may have different requirements for frost protection.
Properly Installing the Covers
When installing the chosen frost protection covers, care must be taken to ensure they are properly secured and provide adequate coverage. Row covers should be tightly secured to prevent wind from dislodging them and allowing cold air to reach the plants. Plastic tunnels should be properly anchored and provide enough height for the plants to grow. Cold frames should be securely placed over the plants, and doors or vents should be opened during sunny days to allow for ventilation.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Covers
Regular monitoring of the covers is crucial to ensure their effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments. For row covers, it is important to check for proper tension and make sure the covers are not in contact with the plants, as this can cause damage. In the case of plastic tunnels or cold frames, monitoring the temperature inside the structure is essential to prevent excessive heat buildup. If temperatures rise too high, proper ventilation should be provided to cool the plants.
Removing the Covers After Frost
Once the risk of frost has passed, it is important to promptly remove the covers to prevent overheating and allow the plants to receive adequate sunlight and airflow. Leaving the covers on for extended periods, especially when temperatures rise, can lead to heat stress, disease development, and reduced growth. Proper timing and coordination with weather patterns are essential when removing the covers to ensure the plants’ continued health and growth.
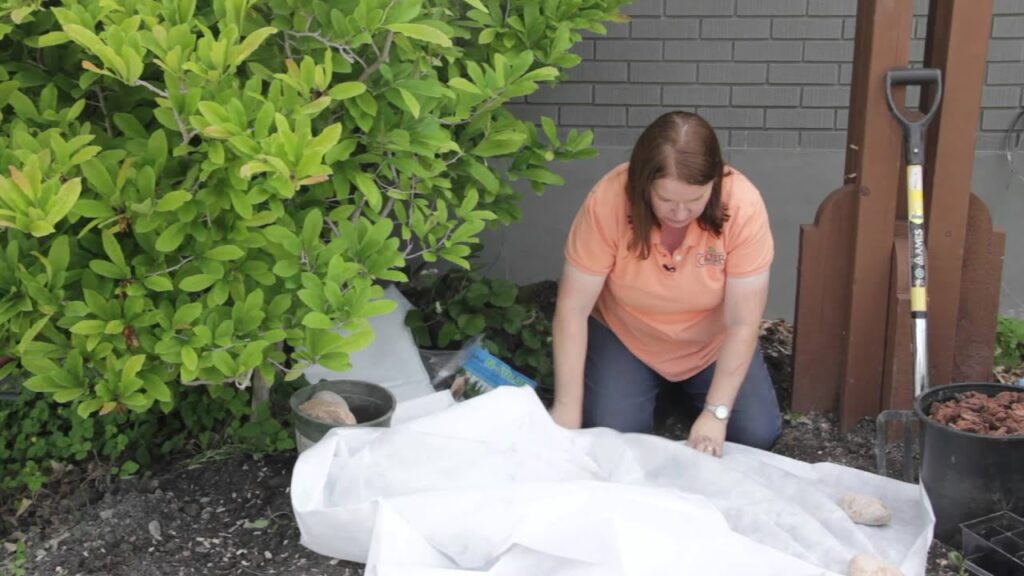

Additional Tips for Frost Protection
Maintaining Good Air Circulation
While protecting strawberries from frost, it is essential to maintain good air circulation to prevent the buildup of excessive moisture and the onset of diseases. Proper airflow helps prevent condensation on the plant’s surface, which can lead to fungal infections and other disease issues. Pruning strawberry plants to provide adequate spacing and removing any weeds or debris around the plants can help promote airflow and reduce the risk of disease development.
Avoiding Direct Contact with Plants
When covering strawberries for frost protection, it is important to ensure that the covers do not come into direct contact with the plants. Direct contact can transfer cold temperatures and potential frost damage to the plant’s tissues. Using support structures, such as hoops or frames, can help elevate the covers and create a gap between the cover and the plants, providing better insulation while avoiding direct contact.
Inspecting for Pests and Diseases
Regular inspection of strawberry plants is essential to identify and address any pest or disease issues promptly. Covering plants for frost protection can create a more favorable environment for pests and diseases, as it provides shelter and increases humidity. Implementing integrated pest management practices, such as scouting for pests, maintaining proper sanitation, and using organic or targeted pesticide options, can help prevent and manage potential pest and disease problems.
Regular Watering
Proper watering is crucial for frost protection and overall plant health. Strawberry plants require consistent moisture, especially during frost events, to help retain heat and maintain their tissues above critical temperatures. However, care should be taken not to overwater, as excessive moisture can increase the risk of diseases, rot, and other water-related issues. Monitoring soil moisture levels and adjusting watering practices accordingly is vital for successful frost protection.
Using Thermometers for Monitoring
Using thermometers to monitor the temperature inside covered areas can provide valuable information for effective frost protection. Placing thermometers at plant height, near the center of the covered area, allows for accurate temperature readings. It is important to regularly check the thermometers during frost events and adjust the covers accordingly, based on the specific temperature thresholds that are known to cause frost damage to strawberry plants.
Potential Challenges and Troubleshooting
Damage Assessment
After a frost event, it is important to assess the extent of the damage to the strawberry plants. Frost-damaged leaves may appear wilted, brown, or black, and the fruit may become discolored or develop soft spots. Carefully evaluating the damage helps determine the appropriate course of action, such as pruning damaged foliage or removing frost-damaged fruit to prevent disease spread.
Effects of Improper Covering
Improperly covering strawberries for frost protection can result in various negative consequences. Covers that are not securely anchored may blow away or become dislodged, exposing the plants to frost damage. Covers that come into direct contact with the plants can transfer cold temperatures and cause tissue damage. Inadequate ventilation inside covered structures can lead to excessive heat buildup, which can stress or kill the plants. Regular monitoring, adjustment, and proper installation techniques are crucial to avoid these issues.
Dealing with Pests and Diseases
Frost protection methods can inadvertently create a more conducive environment for pests and diseases. Increased humidity and reduced airflow under covers or in enclosed structures can promote the development and spread of fungal diseases and the infestation of pests. Regular monitoring, proper sanitation, and integrated pest management practices are necessary to prevent and address these potential issues. Applying preventive measures, such as using disease-resistant cultivars and providing good cultural practices, can also help minimize pest and disease problems.
Frost Damage Recovery
Although frost damage can be detrimental to strawberry plants, many varieties have the ability to recover and resume healthy growth under favorable conditions. After a frost event, providing optimal growing conditions, such as regular watering, adequate sunlight, and appropriate fertilization, can help plants recover. Prompt pruning of frost-damaged leaves and fruits is also beneficial in redirecting the plant’s resources towards healthy growth.
Learning from Challenges for Future Frost Protection
It is essential to view frost protection as a learning opportunity and continuously evaluate and improve upon the methods and techniques used. Assessing the effectiveness of different covering methods, monitoring weather patterns and plant responses, and seeking advice from experienced growers or agricultural extension services can help refine frost protection strategies. Each frost event and its associated challenges provide valuable insights for future decision-making and the development of more effective and site-specific frost protection measures.

Reviewing Different Covering Materials
Benefits and Drawbacks of Row Covers
Row covers provide effective frost protection by trapping heat and creating a barrier against frost. They are typically made of lightweight, breathable fabrics and are relatively inexpensive. However, row covers may require more frequent monitoring and adjustment to ensure proper ventilation and prevent pest and disease issues. They may also restrict plant growth if not adequately anchored or if they come into direct contact with the plants.
Understanding Mulching Materials
Mulching materials, such as straw, hay, or plastic, offer excellent insulation for strawberry plants. Organic mulches like straw and hay provide additional benefits, such as weed suppression and soil moisture retention. Plastic mulches offer superior heat retention but may pose challenges in terms of ventilation and moisture control. Choosing the most suitable mulching material depends on factors such as availability, cost, and specific requirements of the strawberry plants.
Types of Plastic Tunnels
Plastic tunnels, available in various sizes and designs, offer an enclosed environment for strawberries, protecting them from frost and other adverse weather conditions. Low tunnels, which are smaller and closer to the ground, provide easier access and are relatively simple to construct and manage. High tunnels or hoop houses offer more space and greater flexibility but require additional resources for construction and ventilation.
Features of Cold Frames
Cold frames, with their transparent tops and insulated sides, create a favorable microclimate for strawberry plants. They offer excellent insulation and protection against frost and provide growers with the ability to extend the growing season. Cold frames are typically smaller in size, making them more suitable for smaller-scale operations or home gardeners. However, they may require more attention to ventilation to prevent excessive heat buildup.
Straw and Hay Varieties
When using straw or hay as covering materials, selecting the appropriate variety is crucial. Clean and weed-free straw or hay should be chosen to prevent unwanted plants from germinating. Straw and hay should also be free from pathogens or seeds that may introduce diseases or weeds into the strawberry patch. Consulting with local suppliers or agricultural professionals can help identify suitable varieties and ensure the quality of the materials.
Evaluating Portable Greenhouse Options
Portable greenhouses offer a versatile option for frost protection, with the added advantage of creating a controlled environment for strawberry plants. When evaluating portable greenhouse options, factors such as size, construction materials, durability, and ventilation capabilities should be considered. Ideally, portable greenhouses should provide sufficient space for plant growth, allow easy access for maintenance, and offer proper ventilation options to prevent excessive heat buildup.
Comparing Different Blankets or Tarps
Using blankets or tarps for frost protection offers a low-cost and easily accessible option. However, not all blankets or tarps are suitable for this purpose. Choosing blankets or tarps made of breathable materials and ensuring proper anchoring are crucial for effective frost protection. Lightweight and insulated blankets or tarps are preferable to heavy or impermeable ones, as they allow for better air circulation while still providing insulation.
Selecting Appropriate Watering Techniques
When considering watering techniques for frost protection, it is important to balance the moisture needs of the plants with the risk of excessive moisture buildup. Watering the plants prior to a frost event can help retain heat, but caution should be exercised to avoid overwatering. Drip irrigation or soaker hoses can deliver water directly to the plants’ root zones, minimizing foliage wetting and reducing the risk of disease development.
Safe Usage of Heat Sources
Supplemental heat sources, such as electric heaters or heat lamps, can provide additional protection during extreme frost events. When using heat sources, safety and proper ventilation should be top priorities. Heat sources should be positioned and controlled to minimize fire hazards and potential damage to the plants. Monitoring the temperature inside the covered area is essential to ensure a safe and effective balance of warmth without excessive heat buildup.
Potential Combinations of Various Covering Materials
Combining different covering materials can enhance frost protection by incorporating the benefits of each method. For example, combining row covers with mulching or using plastic tunnels in conjunction with cold frames can provide increased insulation and flexibility. Experimentation and observation are key to determining the most effective combinations for specific growing conditions, strawberry cultivars, and frost risk levels.
Factors Affecting the Success of Frost Protection
Temperature and Duration of Frost
The temperature and duration of frost events are critical factors affecting the success of frost protection measures. Different strawberry varieties have varying degrees of cold tolerance, and their susceptibility to frost damage may vary based on specific temperature thresholds. Monitoring weather conditions and gaining knowledge of the temperature sensitivity of the cultivars being grown allows for timely implementation of appropriate frost protection measures.
Adequate Insulation
Effective insulation is a key factor in protecting strawberries from frost damage. Good insulation, provided by covers, mulch, or structures, helps trap heat and prevent cold air from reaching the plants. Insulation also helps reduce temperature fluctuations and provides a buffer against sudden temperature changes. Proper installation and maintenance of insulation materials are crucial to ensure their effectiveness in providing the necessary protection.
Coverage Density
The density or closeness of the covering materials significantly impacts their effectiveness in frost protection. Dense covers that offer a tight barrier against the cold air provide better insulation than loosely woven or thin materials. However, excessive density may limit air circulation, increase humidity, and potentially create a favorable environment for pests and diseases. Striking a balance between effective insulation and proper ventilation is essential for successful frost protection.
Microclimates in the Strawberry Patch
Microclimates, or localized climate variations within a specific area, can influence the vulnerability of strawberry plants to frost damage. Factors such as topography, the presence of structures or windbreaks, and the arrangement of plants can create variations in temperature and air movement. Identifying and understanding the microclimates in the strawberry patch allows growers to strategically position the plants and tailor frost protection measures to maximize their effectiveness.
Timing of Covering and Uncovering
The timing of covering and uncovering strawberry plants plays a crucial role in frost protection. Covers should be applied before temperatures drop below freezing to prevent frost damage. However, covers should not be left on for extended periods after frost events, especially if temperatures rise, as this can negatively impact plant growth and potentially create other environmental issues. Close monitoring of weather conditions and timely application and removal of covers are essential for successful frost protection.
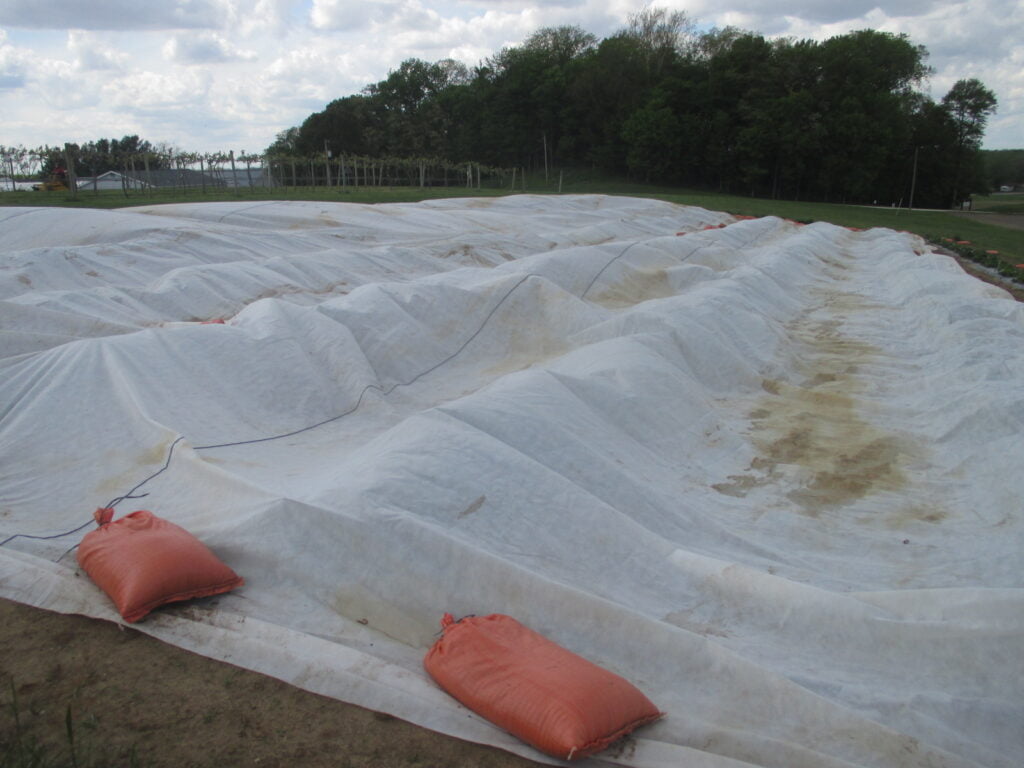

Understanding the Limitations of Frost Protection
Extreme Weather Conditions
Even with the most effective frost protection measures in place, extreme weather conditions can still pose challenges. Severe frost events, prolonged freezing temperatures, or sudden temperature drops can overwhelm the ability of covers and insulation to provide adequate protection. It is important to acknowledge that certain weather conditions may exceed the capacity of frost protection measures, and alternative strategies, such as relocating or temporarily covering plants in extreme cases, may be necessary.
Severe Cold Snaps
Severe cold snaps, characterized by rapid and significant drops in temperature, can present a unique challenge for frost protection. The suddenness of these temperature changes may not allow sufficient time for growers to cover or protect the plants adequately. Monitoring weather patterns and utilizing weather forecasting tools can help anticipate severe cold snaps and enable growers to take preventive measures, such as preemptive covering or extra insulation, to minimize potential damage.
Advanced Frost Damage
Despite implementing frost protection measures, advanced frost damage may still occur under severe or prolonged frost conditions. Advanced frost damage is characterized by extensive tissue discoloration, wilted leaves, and significant loss of fruit. While the plants may recover under favorable conditions, more extensive pruning or removal of severely damaged plants may be necessary to promote new growth and ensure the overall health of the strawberry patch.
Varietal Differences in Frost Resistance
Different strawberry varieties exhibit varying degrees of cold tolerance and resistance to frost damage. Some cultivars are bred specifically for improved frost resistance and can withstand colder temperatures without sustaining significant damage. Growers should carefully consider the frost resistance characteristics of different varieties when selecting which ones to cultivate. Choosing cultivars that are well-suited to the specific climate and microclimate conditions can greatly enhance the success of frost protection efforts.
Unsuitable Covering Approaches
Not all covering methods or materials are suitable for every strawberry growing situation. Factors such as cost, labor requirements, available space, and specific environmental conditions must be considered when choosing the most suitable frost protection method. The use of inappropriate or ineffective covering approaches may result in suboptimal protection, pest and disease issues, or other unintended consequences. Tailoring frost protection strategies to individual needs and conditions is crucial for minimizing limitations and maximizing success.
Conclusion
Summary of Frost Covering Methods
Protecting strawberries from frost is essential for maintaining the productivity and health of strawberry crops. Numerous methods, such as row covers, mulching, plastic tunnels, cold frames, and more, can effectively safeguard strawberries from frost damage. Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks, and their suitability depends on factors including weather conditions, plant growth stage, available resources, and budget.
Importance of Tailoring Frost Protection to Unique Needs
Successful frost protection requires careful consideration of various factors and tailoring the chosen methods to meet the unique needs of the strawberry plants and growing conditions. Understanding the limitations and potential challenges of frost protection, as well as evaluating individual risks and benefits, helps growers make informed decisions and improve their frost protection strategies.
Encouraging Successful Strawberry Harvests through Frost Protection
Implementing effective frost protection measures is crucial for ensuring successful strawberry harvests and maintaining the profitability and sustainability of strawberry cultivation. By understanding and implementing the appropriate covering methods, considering necessary factors, and continuously evaluating and improving techniques, growers can significantly reduce the risk of frost damage and enjoy bountiful strawberry yields.



