When planning to grow your own grapevine, determining the appropriate spacing between each plant is crucial for ensuring optimal growth and productivity. Planting grapes at the correct distance provides sufficient room for the vines to spread and develop their root systems, allowing them to absorb nutrients effectively while avoiding unnecessary competition. In this article, we will guide you through the factors to consider and the optimal spacing techniques to implement when deciding how far apart to plant grapes.
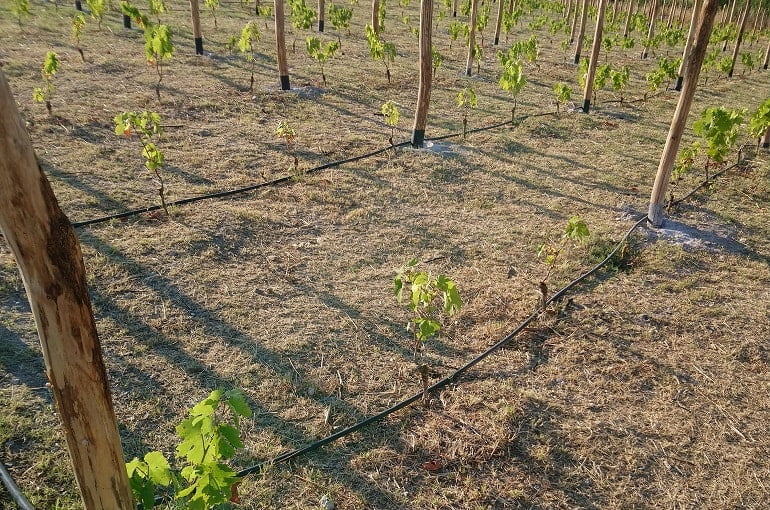

Choosing a Vineyard Site
When considering starting a vineyard, it is crucial to carefully choose the site where the grapevines will be planted. Several factors must be taken into account to ensure the success and productivity of the vineyard. These factors include climate and hardiness zones, soil conditions, sunlight exposure, and drainage.
Consider Climate and Hardiness Zones
The climate of a region is one of the most important factors when choosing a vineyard site. Grapes thrive in specific temperature ranges, and different grape varieties have varying tolerance to cold or heat. It is essential to select a site that falls within the appropriate hardiness zone for the desired grape variety.
Evaluate Soil Conditions
The soil in which grapevines are planted greatly influences their health and productivity. Different grape varieties have varying preferences for soil types, including factors such as drainage, pH levels, and nutrient content. Evaluating soil conditions in the potential vineyard site is crucial to ensure that the chosen soil will support healthy grapevine growth and fruit development.
Optimal Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight exposure plays a vital role in the photosynthesis process, which is crucial for grapevines to produce energy and grow. Choosing a vineyard site with optimal sunlight exposure is essential for the vines to receive enough sunlight throughout the day. Factors such as slope, orientation, and nearby obstructions should be considered when determining the ideal sunlight exposure for the vineyard.
Factor in Drainage
Proper drainage is essential for grapevines to avoid excess water saturation in the soil, which can lead to root damage and diseases. Assessing the natural drainage patterns of the potential vineyard site is crucial to ensure that excess water can effectively drain away from the roots. Additionally, the soil’s ability to retain adequate moisture should also be considered to avoid drought stress on the grapevines.
Spacing Between Grapevines
After selecting the ideal vineyard site, determining the proper spacing between grapevines is crucial for maximizing vine health, fruit quality, and overall vineyard management. Adequate spacing allows for proper air circulation, sunlight penetration, and efficient vineyard maintenance.
Row Spacing
Row spacing refers to the distance between rows of grapevines. The appropriate row spacing depends on various factors, including vine vigor, training system, and accessibility for machinery and equipment. Generally, row spacing ranges from 6 to 12 feet, allowing enough room for vine growth, maintenance, and harvest operations.
Plant Spacing within Rows
Plant spacing refers to the distance between individual grapevines within a row. The suitable plant spacing within rows is influenced by grapevine variety, training system, and desired vine density. The spacing can range from 4 to 10 feet, providing enough space for vines to grow and develop properly.
Reasons for Adequate Spacing
Adequate spacing between grapevines is essential for several reasons. Sufficient space allows for proper root development, reducing competition for water and nutrients among the vines. It also facilitates effective disease and pest management by allowing air circulation, sunlight exposure, and accessibility for treatments. Additionally, optimal spacing ensures efficient vineyard management practices, including pruning, training, and harvesting.

Factors Influencing Vine Spacing
Several factors significantly influence the spacing between grapevines in a vineyard. These factors include the grapevine variety, training system, and vine vigor.
Grapevine Variety
Different grapevine varieties have varying growth habits, including canopy size, vine vigor, and spread. Varieties with vigorous growth may require more space between plants to avoid overcrowding, while less vigorous varieties can be planted at closer distances. Understanding the growth characteristics of the grapevine variety is crucial when determining the optimal spacing.
Training System
The training system used in a vineyard affects the vine’s overall shape, canopy management, and potential for growth and fruit production. Training systems such as trellis, pergola, or head training can influence the spacing between grapevines. Systems that require more extensive canopy growth may require wider spacing to allow for proper air circulation and sunlight exposure.
Vine Vigor
Vine vigor refers to the overall growth and vitality of grapevines. Vines with high vigor tend to produce more foliage and require more resources, such as water and nutrients. These vigorous vines may benefit from wider spacing to avoid overcrowding and ensure proper nutrient uptake. On the other hand, vines with lower vigor can be planted more closely together.
General Guidelines for Grape Spacing
While specific spacing requirements can vary depending on various factors, some general guidelines can provide a starting point for grape spacing in a vineyard.
Standard Spacing Recommendations
For most grape varieties, a common standard row spacing is 8 to 10 feet, allowing sufficient room for machinery access and vineyard management. Within each row, a spacing of 6 to 8 feet between grapevines is typically recommended. These standard recommendations aim to strike a balance between vine health, fruit quality, and operational efficiency.
Adapting Spacing to Suit Conditions
It is essential to consider the specific conditions of the vineyard site when determining spacing. Factors such as soil fertility, water availability, and climate should be taken into account. In less fertile soils or arid climates, wider spacing between grapevines may be necessary to ensure adequate access to resources. Conversely, in more fertile soils or regions with high rainfall, closer spacing may be suitable.
Considerations for Different Training Systems
The choice of training system also influences grapevine spacing. For example, vineyards using a vertical trellis system may require wider spacing between rows to accommodate a larger canopy. In contrast, vineyards implementing a head training system may allow for closer spacing between grapevines. Adjustments to spacing should be made based on the specific requirements of the chosen training system.

Planting Distance for Various Grape Types
Different grape types, such as table grapes, wine grapes, and raisin grapes, have varying spacing requirements based on their growth habits and intended use.
Table Grapes
Table grapes are grown for fresh consumption and require an appropriate balance between vine vigor and fruit quality. The recommended spacing for table grapes can range from 4 to 8 feet within rows, depending on the variety. Spacing rows around 6 to 10 feet apart is generally suitable to ensure proper air circulation and sunlight exposure for healthy fruit development.
Wine Grapes
Wine grapes are primarily cultivated for winemaking. The spacing for wine grapes depends on the desired grape quality, vine vigor, and canopy management. Generally, wine grapes require wider spacing compared to table grapes, ranging from 6 to 10 feet between plants within rows and 8 to 12 feet between rows. This spacing allows for optimal fruit ripening, effective vineyard management, and disease prevention.
Raisin Grapes
Raisin grapes are typically spaced further apart compared to table and wine grapes. The larger spacing allows for proper air circulation and sunlight exposure, essential for the drying process that transforms grapes into raisins. The recommended spacing for raisin grapes can range from 8 to 12 feet between plants within rows and 10 to 14 feet between rows.
Spacing Recommendations for Different Regions
The climate and specific region in which a vineyard is located can significantly influence the ideal spacing between grapevines. Considerations must be made for cool climate regions, moderate climate regions, and warm climate regions.
Cool Climate Regions
In cool climate regions, where temperatures can drop significantly, wider spacing between grapevines is often recommended. The increased spacing allows for better airflow between vines, reducing the risk of cold air pocket formation and subsequent vine damage. The recommended spacing for cool climate regions can range from 8 to 10 feet between plants within rows and 9 to 12 feet between rows.
Moderate Climate Regions
Moderate climate regions offer favorable conditions for grape cultivation. The spacing recommendations for these regions fall within the standard ranges mentioned earlier. An appropriate spacing of 6 to 8 feet between grapevines within rows and 8 to 10 feet between rows generally suits moderate climate regions, ensuring healthy vine growth and fruit quality.
Warm Climate Regions
In warm climate regions, where high temperatures and intense sunlight are common, wider spacing is beneficial to prevent excessive vine stress. The increased spacing allows for better air circulation and reduces the risk of diseases associated with high humidity. Recommended spacing ranges from 7 to 9 feet between plants within rows and 9 to 12 feet between rows in warm climate regions.

Assessing Vine Density
Vine density refers to the number of grapevines per unit area in a vineyard and greatly influences vineyard management and overall grape quality. Properly assessing vine density is essential for maximizing vine health and fruit production.
Plant Density Calculation
To determine vine density, the total vineyard area must be known, along with the desired spacing between grapevines. By dividing the vineyard area by the product of row spacing and plant spacing within rows, the number of grapevines for a given vineyard can be calculated. This calculation ensures that the appropriate number of grapevines is planted in the available space.
Factors to Consider
When assessing vine density, several factors should be considered, including vine vigor, desired yield per acre, and vineyard management practices. Vine vigor influences the overall growth and resource requirements of grapevines, which can affect the optimal vine density. Additionally, the desired yield per acre must be balanced with vine health and fruit quality goals when determining vine density.
Benefits of Higher Density Planting
Planting grapevines at higher density can offer several benefits for vineyard management and grape quality. Higher vine density allows for better canopy management, reducing the need for excessive pruning or trellising. It also enhances competition among grapevines, resulting in smaller berries with concentrated flavors and more intense aromas. Additionally, high-density planting can maximize vineyard land utilization and potentially increase overall grape yield.
Effects of Planting Density on Grape Quality
The planting density of grapevines can have significant impacts on grape quality, including yield and cluster characteristics, sugar levels, fruit development, and aroma and flavor profiles.
Yield and Cluster Characteristics
Planting density influences grape yield by determining the number of grapevines per acre. Higher vine density generally leads to increased cluster density, resulting in a higher number of clusters per vine and potentially higher grape yield. However, excessive vine density can also lead to overcrowding and reduced cluster size, negatively affecting grape quality.
Sugar Levels and Fruit Development
Planting density can affect grape sugar levels and overall fruit development. Higher vine density may result in more competition for resources among grapevines, potentially reducing individual berry size and sugar accumulation. However, optimal vine density can create healthy competition, leading to balanced sugar levels and improved fruit development.
Aroma and Flavor Profiles
Grape density can influence the aroma and flavor profiles of the resulting wine. Higher density planting often leads to smaller berries with higher skin-to-pulp ratios, potentially intensifying flavors and aromas. However, excessive vine density can negatively impact berry development and flavor concentration, resulting in less desirable wine characteristics.
Potential Challenges with Different Spacing
While proper spacing between grapevines offers many advantages, it can also present certain challenges, including disease and pest control, air circulation, sunlight penetration, and vineyard management.
Disease and Pest Control
Close spacing between grapevines can create an environment conducive to the spread of diseases. Limited airflow between densely planted vines can increase humidity, leading to a higher risk of fungal infections. Similarly, pests may find it easier to move between closely spaced vines, increasing the potential for infestations. Effective disease and pest control measures must be implemented to mitigate these challenges.
Air Circulation and Sunlight Penetration
Inadequate airflow and sunlight penetration can be problematic in vineyards with excessively close spacing. Stagnant air and reduced sunlight exposure can create conditions favorable for disease development and reduce overall vine health. Proper spacing between grapevines allows for better air circulation and sunlight penetration, promoting grapevine vigor and minimizing disease risks.
Ease of Vineyard Management
Managing a vineyard with closely spaced grapevines can be more challenging and labor-intensive. Harvesting, pruning, and general vineyard maintenance operations may be more time-consuming and require specialized equipment. Proper spacing ensures ease of access for machinery and simplifies vineyard management practices, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
Practical Considerations for Planting Grapes
Several practical considerations should be taken into account when planning the planting of grapevines, including future expansion plans, equipment and infrastructure, and vineyard layout.
Future Expansion Plans
When determining vine spacing, it is prudent to consider future expansion plans. Allowing sufficient space between grapevines and rows to accommodate potential growth can prevent the need for extensive replanting or significant modifications to the vineyard layout in the future. Planning for scalability is essential for long-term vineyard success.
Equipment and Infrastructure
The equipment and infrastructure required for vineyard operations should also be considered when determining vine spacing. Sufficient spacing between grapevines and rows is necessary to allow for machinery access during various vineyard activities, including pruning, spraying, and harvesting. Additionally, ensuring proper space for irrigation systems, trellising, or support structures is crucial to facilitate efficient vineyard management.
Vineyard Layout
Creating a well-designed vineyard layout is essential for effective vineyard management and productivity. Factors such as topography, soil conditions, and access points should be considered when determining the placement and orientation of grapevines. A well-planned layout maximizes the use of available land, promotes operational efficiency, and enhances overall vine health.
In conclusion, choosing a vineyard site and determining the appropriate spacing between grapevines are crucial considerations when starting a vineyard. Factors like climate, soil conditions, sunlight exposure, and drainage play key roles in selecting the right location. Adequate spacing allows for proper vine growth, disease prevention, and efficient vineyard management. Considerations such as grapevine variety, training system, and regional climate help determine the optimal spacing for grapevines. Understanding the effects of planting density on grape quality is crucial, as it can impact yield, fruit development, and flavor profiles. Overcoming potential challenges associated with grapevine spacing, such as disease control and vineyard management, requires strategic planning. By considering practical factors like future expansion plans, equipment and infrastructure, and vineyard layout, vineyard owners can set themselves up for success in the exciting world of grape growing.



