Zucchini, a versatile and easy-to-grow vegetable, can be a delightful addition to any garden. But have you ever wondered how far apart you should plant your zucchini for optimal growth and yield? In this article, we will guide you through the spacing requirements for planting zucchini, ensuring you have a bountiful harvest and healthy plants. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or a novice enthusiast, this comprehensive spacing guide will provide you with the knowledge and confidence needed to cultivate thriving zucchini plants in your very own backyard. So, grab your gardening tools and let’s get started on creating a lush and fruitful zucchini patch!
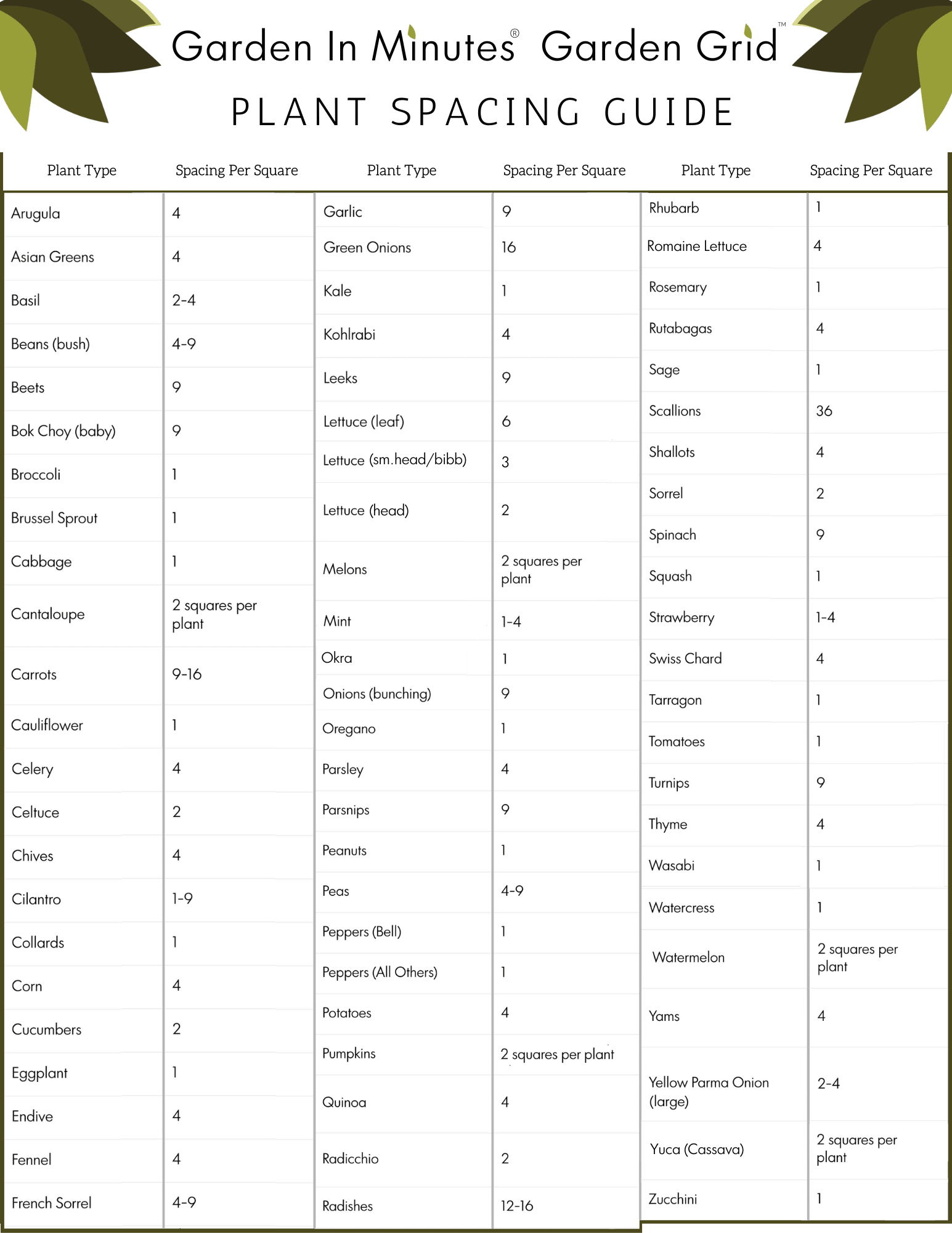
Spacing Guide for Planting Zucchini
Zucchini is a versatile and bountiful vegetable that can be easily grown in your own backyard. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, understanding the proper spacing techniques is crucial for the success of your zucchini plants. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about spacing in order to ensure healthy and productive zucchini plants. So grab your gardening gloves and let’s get started!
Determining the Right Spacing
Understanding Zucchini Plant Size
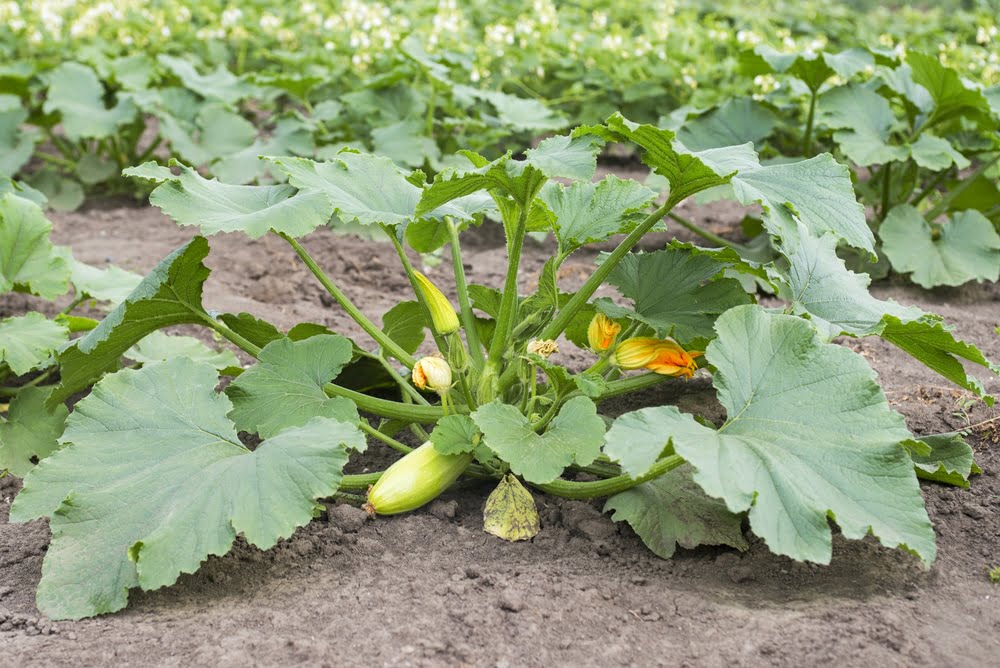
Before you start planting your zucchini, it’s important to consider the size that your plants will eventually reach. Zucchini plants are known for their vigorous growth and can become quite large, spreading out both above and below the ground. On average, zucchini plants can grow up to 2-3 feet tall and require ample space to thrive. Keep this in mind when planning your planting area.
Considering Planting Method
Another factor to consider when determining the right spacing for your zucchini plants is the method of planting you choose. Zucchini can be either directly seeded or transplanted, each with its own advantages and considerations. Direct seeding involves sowing the seeds directly into the ground, while transplanting involves starting the seeds indoors and then moving them outdoors once they have established. The method you choose will affect the spacing requirements.
Accounting for Air Circulation
Air circulation is crucial for the health of zucchini plants. Proper spacing allows for adequate air movement, which helps prevent the development of fungal diseases and promotes overall plant vigor. When plants are spaced too closely together, the lack of airflow can lead to damp conditions, providing a breeding ground for various plant pathogens. By ensuring proper spacing, you can minimize the risk of disease and maximize the productivity of your zucchini plants.
Direct Seeding vs. Transplanting
Direct Seeding Pros and Cons
Direct seeding, also known as sowing directly into the ground, offers several benefits for growing zucchini. One advantage is that it eliminates the need for transplanting, which can be time-consuming and increase the risk of transplant shock. Direct seeding also allows for a more natural development of the root system, as the young plants are not disturbed during the transplanting process. However, it’s important to note that direct seeding requires additional patience, as it may take longer for the seeds to germinate and the plants to become established.
Transplanting Pros and Cons
Transplanting zucchini seedlings can be advantageous in certain situations. By starting the seeds indoors, you can extend the growing season and get a head start on your zucchini production. Transplanting also allows you to control the growing conditions more effectively, such as protecting the young plants from unpredictable weather or pests. However, transplanting requires careful handling to avoid damaging the delicate roots of the seedlings, and it may also add extra cost and effort to your gardening process.
Ideal Soil Conditions
Well-Draining Soil
Zucchini plants thrive in well-draining soil that allows excess water to pass through easily. Poorly drained soil can lead to waterlogged conditions, which can cause the roots to rot and the plants to suffer. To ensure proper drainage, it’s essential to amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure. These amendments help improve the soil structure, allowing water to flow freely while still retaining enough moisture for the plants’ needs.
Proper pH Level
Zucchini plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Testing the soil pH before planting can help you determine if any adjustments are needed. If the soil pH is too acidic, you can add lime to raise it. On the other hand, if the soil is too alkaline, sulfur or other acidifying agents can be used to lower the pH. Maintaining the proper pH level ensures that the plants can access essential nutrients in the soil and promotes optimal growth.
Soil Enrichment
To provide your zucchini plants with the necessary nutrients, it’s crucial to enrich the soil before planting. Incorporating organic matter into the soil, such as compost or aged manure, helps improve its nutrient content, texture, and overall fertility. Organic matter also enhances the soil’s water-holding capacity and promotes beneficial microbial activity, creating a thriving environment for zucchini plants. Prioritize soil enrichment to give your plants the best start possible.

Preparing the Soil for Planting
Clearing the Area
Before you begin planting your zucchini, it’s important to clear the planting area of any debris, weeds, or rocks. Clearing the area ensures that the zucchini plants have a clean space to grow without competition from unwanted plants. Remove any existing vegetation, loosen the soil, and create a blank canvas ready for planting.
Loosening the Soil
Zucchini plants have extensive root systems that require loose and well-aerated soil to grow properly. After clearing the area, use a garden fork or a tiller to loosen the soil to a depth of at least 8-10 inches. Breaking up compacted soil allows the roots to penetrate easily and encourages proper drainage. Loosening the soil also helps create a soft bed for the young zucchini seedlings to establish themselves.
Amending the Soil
Once the soil is loosened, it’s time to amend it with organic matter to improve its overall fertility. Spread a layer of compost or aged manure on top of the soil and work it into the top few inches using a garden rake or a hoe. This organic matter provides essential nutrients to the zucchini plants and helps retain moisture in the soil. Aim for a well-mixed soil that is rich in organic content to support healthy plant growth.
Leveling the Bed
After amending the soil, it’s important to level the planting bed to ensure a uniform planting surface. Use a rake or a garden hoe to smooth out any bumps or ridges and create a flat surface. Leveling the bed not only provides a neat appearance but also facilitates irrigation and prevents water from ponding in certain areas. A level bed allows for even distribution of water and nutrients to all the zucchini plants.
Creating Mounds or Hills (Optional)
Creating mounds or hills can be an optional step in preparing the soil for planting zucchini. Mounds or hills help improve soil drainage, especially in areas with heavy or poorly drained soil. To create a mound or hill, simply pile up the amended soil in a circular shape with a height of about 6-8 inches. This elevated planting method promotes better root aeration and can give an extra advantage, especially in regions with frequent rainfall or excessive moisture.
Choosing the Right Location
Sunlight Requirements
Zucchini plants thrive in full sun, requiring a minimum of six to eight hours of direct sunlight per day. Select a location that receives maximum sunlight throughout the day, preferably a south-facing area of your garden. If your available space has partial shade, make sure it is morning sun, as the zucchini plants need the warmth of the morning sun to promote growth and productivity. Adequate sunlight is essential for the development of healthy and flavorful zucchini fruits.
Protection from Wind
While zucchini plants enjoy basking in the sun, they can be susceptible to wind damage. Choose a location that offers some form of protection from strong winds, such as a wall, a fence, or strategically placed windbreaks. Winds can not only physically damage the plants but also lead to excessive transpiration, which can cause the plants to dry out quickly. By providing a wind-protected environment, you can help your zucchini plants grow in a sturdy and robust manner.
Proximity to Other Plants
Considering the proximity of zucchini plants to other plants is essential for optimal growth and overall garden harmony. Zucchini has large leaves that can shade neighboring plants if positioned too closely. Additionally, certain companion plants can help deter pests or attract beneficial insects, enhancing the overall health of your zucchini plants. When choosing the location for your zucchini, ensure enough space for the plants to grow freely while allowing for companion planting opportunities.
Planting Zucchini Seeds
Seed Depth
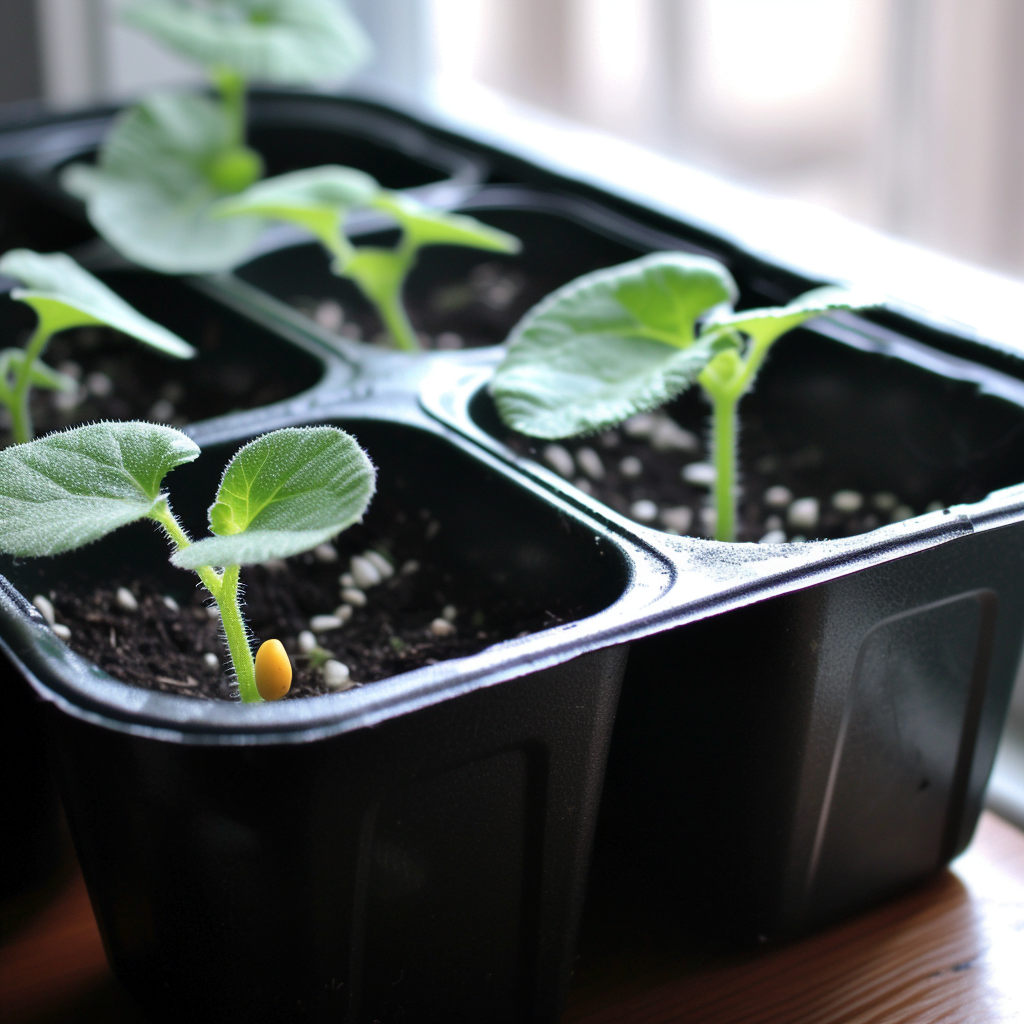
Planting zucchini seeds at the correct depth is crucial for successful germination and healthy seedling development. The general guideline for zucchini seed depth is to plant them approximately 1 inch deep into the soil. Planting the seeds too shallowly can expose them to drying out, while planting them too deeply may hinder the seedling’s emergence. Maintaining the right seed depth provides the optimal conditions for your zucchini seeds to sprout and grow.
Seed Spacing
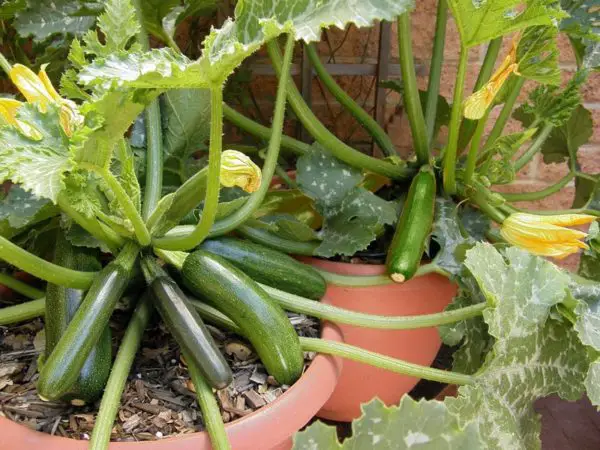
When it comes to seed spacing, zucchini plants require adequate room to spread their leaves and develop fruit. Leave approximately 2-3 feet of space between each zucchini seed or seedling. This spacing allows the plants to grow without overcrowding, ensuring ample airflow and preventing the spread of diseases. Proper seed spacing also provides optimal access to sunlight, nutrients, and water, promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing your zucchini harvest.
Caring for Zucchini Seedlings
Watering
Watering is an essential aspect of caring for zucchini seedlings, as they have shallow root systems that require consistent moisture. Water your zucchini plants deeply, aiming for about 1-2 inches of water per week. It’s important to water at the base of the plants, near the soil, rather than overhead, to minimize the risk of developing fungal diseases. To conserve moisture and reduce weed competition, consider mulching around the zucchini plants.
Mulching
Mulching offers numerous benefits to zucchini plants, especially during the hot summer months. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw, grass clippings, or wood chips, around the base of the plants. Mulch helps conserve soil moisture, suppresses weed growth, and regulates soil temperature. Additionally, mulch acts as a protective barrier, preventing soil-borne diseases from splashing onto the leaves during heavy rainfalls. Regularly check the mulch and replenish it as needed throughout the growing season.
Fertilizing
To support the vigorous growth of zucchini plants, it’s important to provide them with proper nutrients. Before planting, incorporate a balanced organic fertilizer into the soil according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This initial fertilization provides a foundation of essential nutrients for your zucchini plants. Additional fertilization may be required as the plants grow and start to produce fruits. Use a side-dressing method, applying a granular organic fertilizer around the base of the plants, or consider using a water-soluble fertilizer for regular feeding.
Monitoring for Pests and Diseases
As with any garden plant, zucchini can be susceptible to various pests and diseases. Regular monitoring is essential to catch any issues early and take appropriate action. Keep an eye out for common pests such as cucumber beetles, squash bugs, or aphids, and take measures to control them if necessary. Implementing organic pest management techniques, like handpicking pests or using insecticidal soap, can help keep your zucchini plants healthy and thriving. Additionally, check for signs of diseases such as powdery mildew or blossom end rot, and address them promptly to prevent further damage.
Providing Support (if needed)
While zucchini plants are generally sturdy and self-supporting, certain varieties or growing conditions may benefit from additional support. If you notice that the plants are sprawling excessively or the fruits are hanging heavily, you can provide support by using stakes, trellises, or cages. These support structures help keep the plants upright, reduce the risk of fruit rot, and make harvesting easier. It’s best to install the supports early in the growing season to avoid disturbing the roots of the plants.

Thinning Out the Seedlings
When to Thin
Thinning out zucchini seedlings is an important step in ensuring healthy plant growth. Thin the seedlings when they have developed their first true leaves, usually when they are about 2-3 inches tall. Thinning at this stage allows the remaining seedlings to have enough space to grow without being crowded, ensuring proper airflow and minimizing the risk of diseases. Additionally, thinning prevents competition among the seedlings for resources, such as water and nutrients.
How to Thin
To thin out zucchini seedlings, gently remove the excess plants, carefully grasping them near the base and pulling them out. Keep the healthiest and strongest-looking seedlings, spacing them approximately 2-3 feet apart. It’s important to handle the seedlings with care to avoid disturbing the roots of the remaining plants. Thinning can be a difficult task, as it requires removing some of the promising seedlings, but it’s an essential step to ensure the best possible growth for your zucchini plants.
Spacing Guidelines for Mature Plants
As zucchini plants mature and start to spread, proper spacing is crucial to ensure continued growth and productivity. Mature zucchini plants should be spaced approximately 3-4 feet apart to allow ample room for the plants to expand and to promote airflow. With sufficient spacing, the leaves can fully develop and capture sunlight, while also providing easy access for harvesting. Maintaining appropriate spacing for mature plants ensures healthy growth and prevents overcrowding in your garden.

Companion Planting with Zucchini
Complementary Plants
Companion planting with zucchini can offer numerous benefits, including pest control, pollination assistance, and enhanced flavor. Some of the best companion plants for zucchini include marigolds, nasturtiums, beans, radishes, and herbs like basil and dill. Marigolds and nasturtiums help deter pests with their strong scent, while beans and radishes can provide natural shade and help conserve soil moisture. Basil and dill attract beneficial insects, such as pollinators and predatory wasps, which contribute to the overall health of your zucchini plants.
Plants to Avoid
While companion planting offers numerous advantages, it’s important to be mindful of certain plant combinations that may not be beneficial for zucchini. Avoid planting zucchini near potatoes, as these two crops are susceptible to similar pests, such as Colorado potato beetles and squash vine borers. It’s also best to keep zucchini away from other members of the squash family, such as pumpkins or cucumbers, as they can cross-pollinate and compromise the flavor and quality of the fruits.
In conclusion, properly spacing your zucchini plants is essential for their health, productivity, and overall success in your garden. By understanding the size of the zucchini plants, considering the planting method, and accounting for air circulation, you can ensure optimal growing conditions. Additionally, taking into account ideal soil conditions, preparing the soil adequately, and choosing the right location contribute to the overall well-being of your zucchini plants. With proper care, watering, mulching, and fertilizing, your zucchini plants will thrive and reward you with a bountiful harvest. So get ready to enjoy the delicious flavors and versatility of your homegrown zucchinis, and happy gardening!



