So you’ve probably noticed before that when you pull a radish out of the ground, sometimes it splits open. It might seem like a random occurrence, but there’s actually a scientific explanation behind it. The splitting of radishes is due to a combination of factors, including rapid growth, fluctuations in moisture levels, and soil conditions. When a radish grows quickly, it can outpace its own skin, leading to the splitting that you see. In this article, we will explore the science behind why radishes split and uncover some interesting insights into this peculiar phenomenon.

Root Growth and Water Absorption
The role of roots in plant growth
Roots play a crucial role in the overall growth and development of plants, including radishes. They serve as the anchor, providing stability to the plant and allowing it to extract nutrients and water from the soil. In addition to their structural support, roots also facilitate the absorption of essential water and nutrients that are vital for plant growth and survival.
How radishes absorb water
Water absorption in radishes primarily occurs through their roots. The root system of radishes consists of fine, hair-like structures called root hairs. These root hairs have a large surface area, which allows for efficient uptake of water and dissolved nutrients from the soil. As water is absorbed, it travels along the roots and is transported to other parts of the plant, contributing to its growth and development.
Factors that can affect root growth
Several factors can impact the growth of radish roots. Soil texture and composition significantly influence root development. Loose, well-draining soil allows roots to penetrate easily and grow freely, whereas compacted or heavy clay soils may hinder root growth. The presence of rocks or other obstructions in the soil can also impact root elongation. Additionally, temperature, sunlight, humidity, and nutrient availability can all affect root growth, and subsequently, water absorption in radishes.
The impact of water absorption on radish splitting
Water absorption is crucial for radish growth, but excessive water intake can lead to splitting of the roots. When radishes absorb an excess amount of water, the cells within the roots expand rapidly. This rapid expansion puts pressure on the root tissues, causing them to crack or split. The result is often an undesirable splitting of the radish root, which not only affects its appearance but also its texture and taste. Understanding the factors that contribute to radish splitting can help gardeners and farmers employ strategies to prevent this issue.
Variations in Radish Types
Different radish varieties and their characteristics
Radishes come in various types, each with its own set of characteristics. Common types include but are not limited to round radishes, long radishes, and winter radishes. Round radishes are typically small and globe-shaped, with a milder flavor. Long radishes, as the name suggests, are elongated and may have a slightly spicier taste. Winter radishes, on the other hand, are larger and have a longer growing season. Understanding the different radish varieties is important for selecting the appropriate type based on personal preferences, growing conditions, and susceptibility to splitting.
Understanding the anatomy of radish roots
To comprehend the factors that contribute to splitting, it is essential to understand the anatomy of radish roots. Radish roots consist of an elongated section called the primary root, which gives rise to lateral roots. These lateral roots branch out and form a network, enabling the radish to absorb nutrients and water effectively. The root tip, known as the meristem, is responsible for root growth and elongation. By understanding the different parts of the radish root, growers can gain insight into the potential causes of splitting.
How radish size and shape can contribute to splitting
The size and shape of radishes can impact their susceptibility to splitting. Larger radishes, especially those that have been allowed to grow beyond their optimal size, tend to have a higher likelihood of splitting. The increased volume of water absorbed by larger radishes can cause more significant pressure on the root tissues, leading to splitting. Similarly, certain radish shapes, such as elongated or tapered roots, may be more prone to splitting due to the distribution of internal pressures within the root.
The influence of radish genetics on splitting tendency
The genetic makeup of radishes can also contribute to their tendency to split. Some varieties and cultivars naturally have a higher predisposition to splitting, even under optimal growing conditions. This inherent splitting tendency can be attributed to genetic factors that affect root development and water regulation within the plant. By selecting radish varieties that are less prone to splitting, gardeners can mitigate the risk of encountering this issue.

Environmental Factors
The effect of temperature on radish growth
Temperature plays a significant role in radish growth and development. Radishes are cool-season crops that prefer moderate temperatures between 50-70°F (10-21°C). Extreme temperatures, particularly high heat or frost, can hamper root growth and inhibit water absorption. When exposed to high temperatures, radish roots may become stressed, causing uneven growth and increased susceptibility to splitting. Similarly, exposure to frost can damage the roots, leading to decreased water absorption and subsequent splitting if the plant tries to compensate for the water loss by sudden intake.
The role of sunlight in radish development
Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, which fuels their growth. Adequate sunlight exposure promotes healthy leaf development and sugar production in radishes. However, excessive sunlight, especially in combination with high temperatures, can lead to stress and premature bolting in radishes. Bolting is when the plant rapidly grows upwards and focuses its energy on producing flowers and seeds rather than developing the root. This diversion of resources can result in smaller, underdeveloped roots that are more prone to splitting.
The impact of humidity on radish splitting
Humidity refers to the amount of moisture present in the air, and it can affect radish growth in various ways. High humidity levels can create a damp environment that encourages fungal growth and increases the risk of diseases affecting radish roots. Fungal infections can weaken the root tissues and make them more likely to split. On the other hand, low humidity levels can lead to excessive water loss through evaporation, resulting in dehydration and stress for the radish plant. Both excessive humidity and low humidity can indirectly contribute to splitting by compromising the overall health of the radish roots.
How soil conditions can influence splitting
Soil conditions, including texture, composition, structure, and nutrient content, all play a role in radish growth and splitting. As mentioned earlier, loose, well-draining soil is optimal for root development, while compacted or heavy clay soils can impede growth and water absorption. Additionally, imbalances in soil nutrients can directly affect root health and growth, potentially leading to splitting. Proper soil preparation, including amendment with organic matter and regular soil testing, can help ensure favorable conditions for radish growth and minimize the risk of splitting.
Watering Practices
The importance of consistent watering for radish health
Consistent watering is vital for the overall health and well-being of radishes. Radish roots require a steady supply of moisture to perform their crucial functions, including water absorption and nutrient uptake. Inconsistent watering, such as alternating periods of drought and excessive moisture, can stress the plants and result in uneven growth or splitting. By maintaining a consistent watering schedule and ensuring that the soil remains consistently moist but not waterlogged, gardeners can promote healthy radish development and minimize the risk of splitting.
The risks associated with overwatering radishes
While sufficient water is necessary for radish growth, overwatering can be detrimental. Excessive water intake can lead to overly rapid growth and turgor in the root tissues, which can eventually result in splitting. Overwatering can also create an anaerobic environment in the soil, inhibiting the supply of oxygen to the roots and impeding their function. It is essential to strike a balance and avoid overwatering by monitoring soil moisture levels and adjusting watering practices accordingly.
How underwatering can lead to radish splitting
On the contrary, underwatering can also contribute to radish splitting. Insufficient water supply can lead to stress in the radish plant, causing the roots to shrink and the tissues to become weakened. When exposed to a sudden influx of water, such as during irregular watering practices, the stressed roots may struggle to absorb and distribute the water effectively, resulting in splitting. Proper watering, with consistent and adequate moisture levels, is key to preventing both overwatering and underwatering, thereby reducing the risk of splitting.
Best practices for watering radishes to prevent splitting
To prevent splitting, it is crucial to implement best practices for watering radishes. Gardeners should aim for consistent soil moisture, avoiding both insufficient watering and overwatering. Mulching around the base of the plants can help retain soil moisture and prevent excessive evaporation. Using drip irrigation or a soaker hose can provide a slow and steady supply of water directly to the roots, reducing the risk of root stress and subsequent splitting. Monitoring the soil moisture levels regularly and adjusting watering practices according to weather conditions can also aid in preventing splitting.

Nutrient Levels and Imbalances
The essential nutrients required for radish growth
Radishes, like all plants, require a combination of essential nutrients to support their growth and development. These nutrients include macronutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are needed in relatively large quantities. Additionally, radishes require various micronutrients, including calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and iron (Fe), among others. Adequate nutrient availability is crucial for healthy root formation and function, as well as overall plant vigor.
The consequences of nutrient deficiencies or excesses
Imbalances in nutrient levels can have significant impacts on radish growth and root health. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to stunted growth, inadequate root development, and weakened tissues, making the radishes more susceptible to splitting. Excessive nutrient levels, on the other hand, can result in overgrown and distorted roots, as well as imbalances in water regulation within the plant. Both nutrient deficiencies and excesses can compromise the overall vitality of radishes, increasing the risk of splitting.
How imbalances in nutrient levels can affect radish roots
Imbalances in nutrient levels can directly influence the health and development of radish roots. For example, a nitrogen deficiency can result in reduced root growth and weaker root tissues, making the radish more prone to splitting. Similarly, an excess of certain nutrients, such as potassium or phosphorus, can disrupt the uptake and distribution of water within the plant, leading to root stress and potential splitting. Achieving a proper balance of nutrients through regular soil testing and appropriate fertilization practices is essential for promoting healthy root growth and minimizing the risk of splitting.
The role of fertilizers in preventing radish splitting
Fertilizers can play a crucial role in preventing radish splitting by ensuring adequate nutrient availability and maintaining a proper nutrient balance. Before applying fertilizers, it is essential to perform a soil test to determine the specific nutrient requirements of the radishes. Based on the soil test results, appropriate fertilizers can be selected and applied in the right amounts and at the right times. This targeted approach to fertilization can help prevent nutrient imbalances and optimize root growth, ultimately reducing the likelihood of splitting.
Disease and Pest Issues
Common diseases that affect radishes and their impact
Radishes are susceptible to various diseases that can affect their roots, leaves, and overall health. Diseases such as damping-off, root rot, and clubroot can weaken the radish roots and make them more prone to splitting. Damping-off, caused by fungal pathogens, can lead to rotting of the radish seedlings before they establish a strong root system. Root rot, also caused by fungi, can infect mature radishes and result in the decay and weakening of the root tissues. Clubroot, caused by a soil-borne pathogen, can cause swelling and deformation of the radish roots, making them more susceptible to splitting.
Pests that can damage radish roots and cause splitting
In addition to diseases, pests can also damage radish roots, increasing the risk of splitting. Root maggots, wireworms, and nematodes are common culprits that can feed on radish roots, causing them to become weakened or disfigured. The feeding activities of these pests can disrupt the internal structure of the root tissues, making them more prone to splitting. Implementing pest management practices, such as crop rotation, insecticidal treatments, and regular monitoring, can help reduce the incidence of pest-related root damage and minimize the risk of splitting.
Preventative measures to reduce disease and pest risks
Preventing diseases and pests from affecting radishes is essential to minimize the risk of splitting. Implementing preventative measures, such as crop rotation, can help break the disease and pest life cycles, reducing their population and potential impact on radishes. Proper sanitation practices, including cleaning garden tools and removing plant debris, can help reduce disease transmission. Regular monitoring of plants for signs of disease or pest infestations allows for early detection and timely intervention. Additionally, selecting disease-resistant radish varieties can offer inherent protection against certain pathogens and pests, mitigating the risk of splitting.
Controlling and treating issues to prevent splitting
If diseases or pests do occur, it is crucial to take prompt action to control and treat the issues. Fungal diseases can be managed through the application of fungicides or biological control agents. For example, copper-based fungicides can help control damping-off and root rot in radishes. Treatment for pest infestations can vary depending on the specific pest. Insecticidal treatments, beneficial nematodes, or cultural practices such as barrier methods can help control and manage pests such as root maggots and wireworms. By effectively controlling and treating diseases and pests, growers can protect the health of radish roots and minimize the risk of splitting.
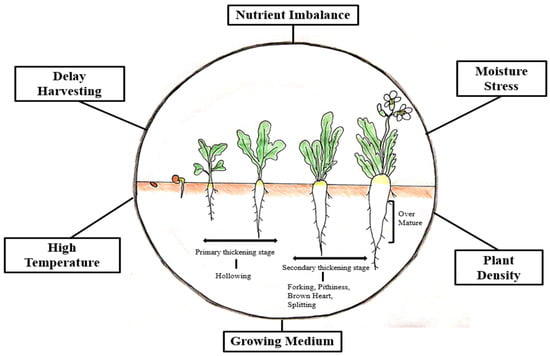
Harvesting and Storage Methods
When and how to harvest radishes to minimize splitting
Harvesting radishes at the appropriate time is crucial to prevent splitting. For most radish varieties, harvesting should occur when the roots are of suitable size and before they become overly mature. Radishes that are left in the ground for too long can grow larger and become more prone to splitting. To harvest radishes, gently loosen the soil around the roots using a garden fork or shovel and carefully lift them from the ground. Taking care not to bruise or damage the roots during harvest can help minimize the risk of subsequent splitting.
Proper handling techniques during harvesting
The handling of radishes during and after harvest can influence their susceptibility to splitting. It is important to handle radishes gently to avoid causing physical damage to the roots. Bruises or cuts can create entry points for pathogens or lead to tissue damage, increasing the risk of splitting during storage or subsequent handling. When harvesting radishes, it is advisable to twist or cut off the leaves, leaving a small portion of the stem intact. This practice helps to maintain the freshness and quality of the radishes, reducing the likelihood of splitting.
The impact of storage conditions on radish quality
Proper storage conditions are essential for maintaining the quality and freshness of radishes. Excessively warm or humid storage environments can accelerate the deterioration of radishes, making them more susceptible to splitting. Radishes should be stored in a cool, dry place, such as a refrigerator or a root cellar, where the temperature and humidity levels can be controlled. It is important to separate radishes from other fruits and vegetables that produce ethylene gas, as exposure to this gas can promote ripening and hasten the process of root deterioration.
Tips to prevent post-harvest splitting
To prevent post-harvest splitting, several tips can be followed. First, it is essential to harvest radishes at the right time, avoiding excessive maturity. Secondly, gentle handling during harvest and subsequent storage is crucial to prevent physical damage to the roots. Proper storage conditions, including cool temperatures and controlled humidity levels, can help maintain the quality and integrity of radishes. Finally, inspecting stored radishes regularly and using the ones more prone to splitting first can reduce the chances of excessive root deterioration and potential splitting.
Cultivation Techniques
Choosing the right planting location for radishes
Selecting an appropriate planting location is fundamental for successful radish cultivation. Radishes thrive in well-draining soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0. Full sun exposure is ideal for optimal growth and root development, although some varieties can tolerate partial shade. Avoid planting radishes in areas prone to waterlogging or areas with heavy clay soils that impede root growth. Choosing a location that meets these criteria can promote healthy radish growth and minimize the risk of splitting.
Preparing the soil to promote healthy radish growth
Proper soil preparation is essential for encouraging healthy radish growth and reducing the likelihood of splitting. Before planting, it is recommended to remove rocks, debris, and large clumps of soil to create a smooth planting bed. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can improve soil drainage, structure, and nutrient content. Tilling or loosening the soil to a depth of 6-8 inches (15-20 cm) allows radish roots to penetrate easily and promotes uniform growth.
Spacing and thinning radishes for optimal development
Radish spacing and thinning practices are critical for preventing overcrowding and ensuring optimal root development. Sow radish seeds at the appropriate spacing, usually 1-2 inches (2.5-5 cm) apart, to provide sufficient room for each plant to grow without competing for resources. As the radish seedlings emerge, it may be necessary to thin them by removing some plants to achieve the desired spacing. Crowded plants can impede root development and increase the risk of splitting, so maintaining proper spacing through thinning is crucial.
How cultivation methods can minimize splitting
The cultivation techniques employed during the growth of radishes can directly influence the incidence of splitting. As previously mentioned, ensuring proper soil preparation, providing adequate spacing, and controlling weeds are crucial aspects of cultivation. By promoting optimal root growth and reducing competition for resources, proper cultivation techniques can help minimize stress on the radish roots, thereby reducing the likelihood of splitting. Additionally, practicing crop rotation and maintaining good overall garden hygiene can help prevent the buildup of diseases and pests that can contribute to root damage and splitting.

Effects of Stress and Mechanical Pressure
The influence of stress on radish plants
Stress, whether from environmental conditions or other factors, can significantly impact the health and viability of radish plants. Radish plants subjected to stress may exhibit signs such as stunted growth, discoloration, and weakened root development. When exposed to stressful conditions, the radish roots may become more susceptible to splitting due to weakened tissues and reduced ability to cope with external pressures. It is vital to minimize stress on radish plants through appropriate growing conditions and management practices to mitigate the risk of splitting.
How mechanical pressure can cause radish splitting
Mechanical pressure, such as accidental trampling or compression by heavy objects, can cause physical damage to radish roots and result in splitting. The fine root hairs and delicate tissues of the radish roots are particularly vulnerable to mechanical pressure. When subjected to excessive or repetitive pressure, the root tissues may rupture or crack, leading to splitting. Avoiding unnecessary foot traffic in radish beds and implementing proper support for nearby structures or equipment can help reduce the risk of mechanical pressure-related splitting.
Preventing stress-related damage to radish roots
To prevent stress-related damage to radish roots, it is crucial to create optimal growing conditions and provide proper care. This includes ensuring appropriate temperature and moisture levels, as well as adequate sunlight exposure. Avoiding over-fertilization, excessive weed competition, and overcrowding can help minimize stress on the radish plants. Regularly monitoring plant health and promptly addressing any issues, such as nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations, can also help prevent stress-related damage to the roots.
Protective measures against mechanical pressure
Implementing protective measures is essential to safeguard radish roots against mechanical pressure and subsequent splitting. To prevent accidental trampling, it is advisable to mark or fence off radish beds to indicate their presence. Using lightweight, breathable garden fabric or mulch around the plants can provide a cushioning effect and protect the roots from mechanical pressure. When working in the garden, exercising caution and mindfulness around radish plants can help prevent unintentional damage. By taking appropriate protective measures, gardeners can minimize the risk of mechanical pressure-related splitting and preserve the health of radish roots.
Role of Growth Hormones
Understanding the role of growth hormones in plants
Growth hormones, also known as plant hormones or phytohormones, are chemical messengers that regulate various aspects of plant growth and development. These hormones are naturally produced by plants and control processes such as cell division, elongation, and differentiation. In radishes, growth hormones play a crucial role in root development and water regulation, which can directly impact their susceptibility to splitting.
How hormones contribute to radish growth and development
In radishes, growth hormones influence various aspects of growth and development, including root formation and enlargement. Auxins, a class of growth hormones, are essential for root initiation and elongation. By promoting cell division and elongation, auxins facilitate the development of a robust root system. Cytokinins, another group of hormones, contribute to the overall growth and vigor of the plant, affecting both shoots and roots. Proper hormone balance is crucial for healthy root development in radishes, as imbalances can lead to compromised root structures and increased susceptibility to splitting.
The relationship between hormonal imbalances and splitting
Imbalances in growth hormone levels can disrupt the delicate equilibrium necessary for healthy root development in radishes. Excessive or deficient levels of auxins or cytokinins can lead to abnormal root growth, weakened root tissues, and increased propensity for splitting. Hormonal imbalances can arise from various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental stressors, and nutrient deficiencies or excesses. By understanding the relationship between hormonal imbalances and splitting, growers can implement strategies to promote hormone balance and reduce the risk of splitting in radishes.
Managing growth hormones to prevent radish splitting
Managing growth hormones in radishes can help promote healthy root development and minimize the risk of splitting. Maintaining optimal nutrient levels, especially those related to hormone synthesis and metabolism, is crucial for hormone regulation. Providing a suitable growing environment, including consistent moisture levels and appropriate temperatures, can support hormone balance in radishes. Genetic selection of radish varieties that exhibit a natural balance of growth hormones and/or resistance to splitting can also be a useful strategy. By managing growth hormones, either through environmental control, nutrient management, or appropriate variety selection, gardeners can improve the overall health of radish roots and mitigate the risk of splitting.
In conclusion, radish splitting can occur due to various factors related to root growth, environmental conditions, watering practices, nutrient levels, disease and pest issues, harvesting and storage methods, cultivation techniques, mechanical pressure, and growth hormone imbalances. Understanding the role of roots in plant growth, the characteristics of different radish varieties, and the impact of environmental factors can help gardeners make informed decisions and prevent splitting. Implementing appropriate watering practices, nutrient management, and disease and pest control measures can further reduce the risk of splitting. Proper harvesting and storage techniques, careful cultivation, and protective measures against mechanical pressure can also contribute to preventing splitting. By considering the multifaceted factors influencing radish splitting and adopting proactive measures, growers can promote healthy radish growth and maximize the quality of their harvest.



