If you’re looking to enhance your gardening skills or want to try a new and efficient method of growing vegetables, then “The Ultimate Guide to Growing Aquaponic Cucumbers” is a must-read. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover everything you need to know about successfully cultivating cucumbers using aquaponic systems. From understanding the basics of aquaponics to choosing the right cucumber variety and providing the optimal growing conditions, this article will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to grow healthy and abundant cucumbers in your own backyard. Say goodbye to traditional soil-based gardening methods and embark on an exciting journey of aquaponics with cucumbers as your star crop.
Choosing the Right Setup
Selecting the Aquaponic System
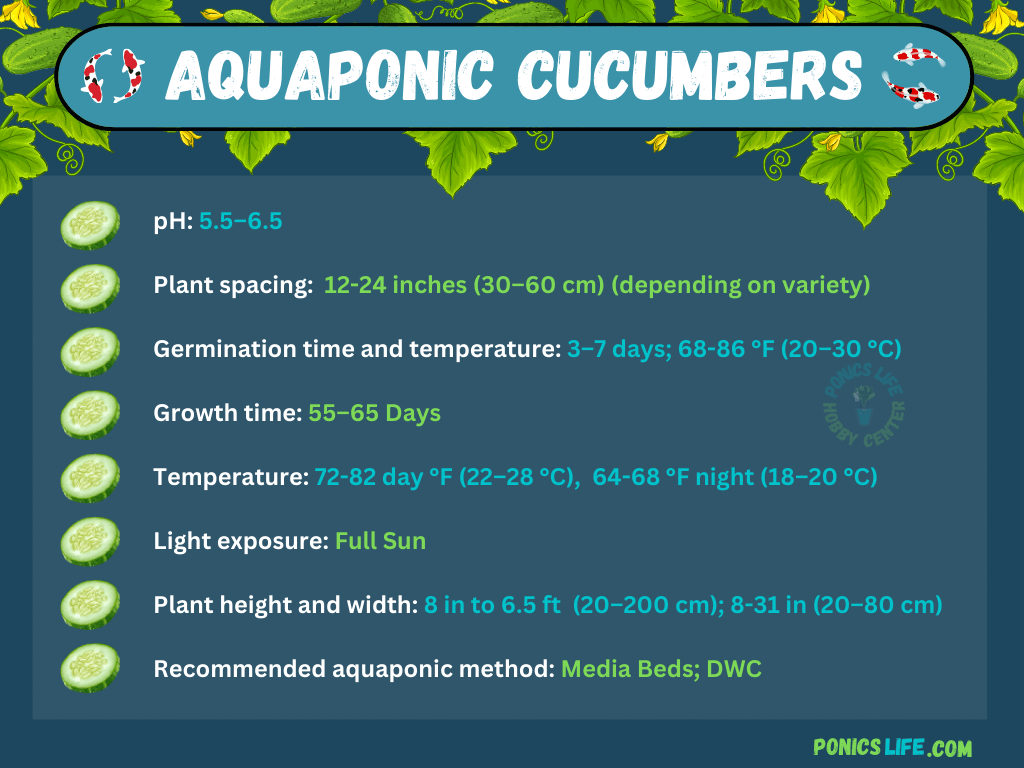
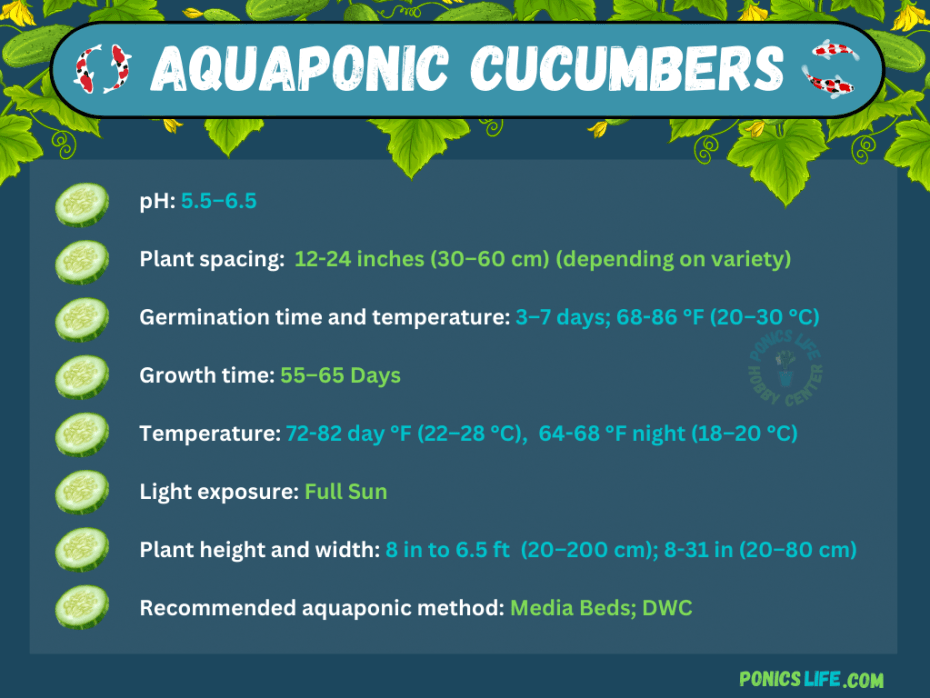
When it comes to growing cucumbers in an aquaponic system, selecting the right setup is crucial. There are various types of aquaponic systems available, such as media beds, nutrient film technique (NFT), and deep water culture (DWC). Each system has its own advantages and considerations.
Media beds are a popular choice for beginners as they are easy to manage and provide a good media for plant growth. NFT systems are ideal for smaller spaces, as they utilize a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over a sloped surface. DWC systems, on the other hand, involve suspending the plant’s roots directly in the nutrient solution.
Consider factors such as available space, your budget, and the level of maintenance you are willing to commit to when selecting your aquaponic system.
Determining the Size of the System
The size of your aquaponic system will depend on the amount of space you have available and the number of cucumbers you wish to grow. Cucumber plants require enough space to spread out their vines and produce an abundance of fruits. It’s important to ensure that your system can accommodate the growth of cucumber plants, both in terms of physical space and nutrient capacity.
Consider the maximum number of cucumber plants you want to grow and the available area in your aquaponic setup. Adequate spacing is vital to prevent overcrowding, which can lead to poor air circulation and increased susceptibility to diseases.
Setting up the Grow Bed
Once you have selected your aquaponic system and determined its size, it’s time to set up the grow bed. The grow bed is where the cucumbers will be planted, and it plays a significant role in providing the necessary support and nutrients for optimal growth.
Use a high-quality planting medium, such as expanded clay pebbles or coconut coir, in the grow bed. This will provide a stable structure for the cucumber plants while allowing for proper water drainage and aeration.
Ensure that the grow bed is properly leveled and securely positioned within the aquaponic system. This will help prevent any imbalance or instability that could lead to issues down the line. Proper setup of the grow bed is essential for the success of your cucumber plants in the aquaponic system.
Selecting Cucumber Varieties
Understanding Different Cucumber Types
Before choosing cucumbers for your aquaponic system, it’s important to understand the different types available. There are mainly three types of cucumbers: slicing cucumbers, pickling cucumbers, and specialty cucumbers.
Slicing cucumbers are the most commonly grown variety and are often used in salads and sandwiches. They are usually larger in size, have a thick skin, and are ideal for fresh consumption.
Pickling cucumbers are smaller in size and have a thinner skin, making them perfect for pickling. They are often harvested when they are still small and firm.
Specialty cucumbers come in various shapes, sizes, and colors. They can be exotic and unique, such as lemon cucumbers or Armenian cucumbers. They add a touch of variety to your aquaponic garden.
Choosing Cucumbers for Aquaponics
When it comes to choosing cucumbers for your aquaponic system, there are certain factors to consider. Look for cucumber varieties that have been specifically bred for greenhouse or hydroponic cultivation. These varieties are usually more compact, disease-resistant, and adapt well to controlled environments.
Additionally, select cucumber varieties that have a shorter harvesting time, as this will allow you to enjoy a continuous harvest throughout the growing season. Check with local nurseries or seed suppliers to find cucumber varieties suitable for aquaponics.
Considering Climbing or Bush Varieties
Another consideration when selecting cucumber varieties for aquaponics is whether to choose climbing or bush varieties. Climbing cucumber varieties are ideal if you have limited space and want to maximize vertical growth. These varieties require trellising or a support system to train the vines upward.
Bush cucumber varieties, on the other hand, are more compact and do not require trellising. They are suitable for aquaponic systems with limited vertical space. However, keep in mind that bush varieties may not yield as many fruits as climbing varieties.
Consider your available space and the type of trellising or support you can provide before deciding on the cucumber variety for your aquaponic system.
Preparing the Environment
Providing Adequate Lighting
Lighting is essential for the healthy growth of cucumber plants in an aquaponic system. If you are growing cucumbers indoors or in a greenhouse, you will need to supplement natural light with artificial lighting.
Choose high-quality LED grow lights that provide a full spectrum of light to mimic natural sunlight. Position the lights at an appropriate distance from the plants to ensure they receive adequate light for photosynthesis.
It is recommended to provide cucumber plants with around 14-16 hours of light per day. This will promote healthy and vigorous growth, leading to higher yields.
Controlling Temperature and Humidity
Cucumber plants thrive in warm temperatures ranging from 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C). Maintaining a stable temperature within this range is crucial for optimal growth and fruit development.
Use a thermometer to monitor the temperature in your aquaponic system. Consider using a heater or ventilation system to regulate the temperature if necessary.
In addition to temperature, humidity levels also play a significant role in cucumber cultivation. Cucumber plants prefer a relative humidity of around 60-70%. However, be cautious of excessive humidity, as it can lead to the development of fungal diseases. Use a hygrometer to assess and control humidity levels, and consider using fans or dehumidifiers if needed.
Creating a Suitable Water Environment
Cucumber plants in an aquaponic system rely on a suitable water environment to receive their nutrients. The quality of water directly impacts plant growth and yield. Ensure that the water in your aquaponic system is free from contaminants, such as chlorine, chloramines, and heavy metals.
Use a water dechlorinator or a filtration system to remove any harmful substances from the water before introducing it into your system. Additionally, regularly monitor water parameters such as pH, ammonia, and nitrate levels to maintain a healthy water environment for your cucumber plants.
Starting with Seeds or Seedlings
Germinating Cucumber Seeds
You have two options when starting cucumber plants in your aquaponic system – germinating seeds or using seedlings. If you decide to germinate cucumber seeds, follow these steps:
- Fill a tray or small pots with a high-quality seed starting mix.
- Plant one or two cucumber seeds per pot, burying them approximately half an inch deep.
- Keep the soil consistently moist and maintain a temperature of around 75°F (24°C) for successful germination.
- After germination, thin out the weaker seedlings to allow the strongest ones to grow.
Transplanting Seedlings into the Aquaponic System
If you prefer to start with seedlings, you can purchase them from a local nursery or start your own indoor seedlings before transplanting them into the aquaponic system.
When transplanting cucumber seedlings, follow these steps:
- Make sure the seedlings have developed a strong root system and are at least three to four weeks old.
- Gently remove the seedlings from their pots, being careful not to damage the roots.
- Place each seedling into pre-dug holes in the grow bed, ensuring the roots are well-covered with the planting medium.
- Water the seedlings thoroughly after transplanting to help them settle into their new environment.
Caring for Young Cucumber Plants
After planting the cucumber seeds or transplanting the seedlings into the aquaponic system, it’s important to provide proper care to promote their healthy growth.
Ensure the young plants receive adequate light, water, and nutrients. Monitor the moisture level in the grow bed and water the plants whenever the top few inches of soil become dry. Be cautious not to overwater, as cucumbers can be susceptible to root rot in excessively wet conditions.
Regularly check for signs of pests or diseases and address any issues promptly. Implementing a regular preventive maintenance routine will help ensure the long-term health and productivity of your cucumber plants.

Providing Nutrients and Supplements
Understanding Cucumber Nutritional Needs
Cucumber plants have specific nutritional requirements to thrive and produce high-quality fruits. Understanding these needs is essential for providing the proper nutrients in your aquaponic system.
Cucumbers require a balanced nutrient solution that includes macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc. Ensure that your aquaponic system is capable of providing these essential nutrients through the fish waste and associated biological processes.
Feeding Cucumbers in an Aquaponic System
In an aquaponic system, the primary source of nutrients for cucumber plants is the fish waste produced by the fish in the system. The waste undergoes a natural breakdown process, converting ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates, which are essential for plant growth.
Regularly monitor your system’s water parameters, including ammonia and nitrate levels, to ensure that the fish waste is being effectively converted and providing an adequate nutrient supply for the cucumber plants.
Supplementing with Fish Waste
If your aquaponic system does not produce enough fish waste to meet the cucumber plants’ nutritional needs, you can supplement with additional fish waste or organic fertilizers.
Consider adding worm castings or compost tea to provide an additional nutrient boost. These organic supplements can help enhance the soil fertility in the grow bed, promoting healthy cucumber growth.
However, be cautious not to overdo it with the supplemental nutrients, as excessive amounts can lead to nutrient imbalances and harm the cucumber plants. Regularly monitor the plant’s growth and water quality to ensure a balanced nutrient supply.
Maintaining Water Quality
Monitoring pH Levels
pH plays a crucial role in nutrient availability for cucumber plants. The optimal pH range for cucumber cultivation in aquaponics is typically between 6.0 and 6.8. This slightly acidic to neutral range ensures proper nutrient absorption and prevents any deficiencies or toxicities.
Regularly monitor the pH levels in your aquaponic system using a pH testing kit. If the pH deviates from the desired range, adjust it by adding pH-up or pH-down solutions, depending on the required correction.
Controlling Ammonia and Nitrate Levels
Ammonia and nitrate levels in the aquaponic system must be carefully monitored to ensure the overall health of the cucumber plants. High ammonia levels can be toxic to the plants, while adequate nitrate levels support healthy growth.
Regularly test the water for ammonia and nitrate levels using test kits. If ammonia concentrations are elevated, consider adjusting the fish stocking density or improving the biological filtration in the system. Nitrate levels should be regularly monitored to ensure a sufficient nutrient supply for the cucumber plants.
Regular Water Testing
Apart from pH, ammonia, and nitrate levels, it is essential to conduct regular water testing to maintain optimal water quality for cucumber plants. Test for other parameters such as dissolved oxygen levels, temperature, and conductivity.
By regularly testing the water, you can detect any potential imbalances or fluctuations that may impact plant growth. Promptly addressing these issues will help maintain a healthy growing environment for your cucumbers.

Pruning and Training Cucumber Plants
Managing Cucumber Canopy Growth
Cucumber plants have a vigorous growth habit and tend to develop large canopies. To ensure proper air circulation and sunlight penetration, it is important to manage the growth of the cucumber plants.
Regularly monitor the growth of the cucumber vines and trim off any excessive branches or foliage that obstructs airflow or shade neighboring plants. This will promote better ventilation and minimize the risk of disease development.
Pruning Excess Leaves and Suckers
Pruning excess leaves and suckers is an important practice to focus the plant’s energy towards fruit production. It helps to prevent overcrowding, improve airflow, and reduce the likelihood of disease spread.
Remove any yellowing or damaged leaves, as they may indicate a nutrient deficiency or pest infestation. Also, prune out any suckers, which are small shoots that grow in the leaf axils. Removing these suckers directs energy towards fruit development and improves the overall health of the cucumber plant.
Training Cucumbers to Climb or Trellis
If you have chosen climbing cucumber varieties, training them to climb a trellis or support system is essential. It not only saves space but also allows better air circulation around the plants.
Install a sturdy trellis or support structure in the aquaponic system and guide the cucumber vines to climb along it. You can use soft ties or plant clips to secure the vines to the trellis, ensuring they have enough support to grow vertically.
Prune any lateral branches that grow below the trellis, as they can compete for resources and hinder the upward growth of the cucumber plant. Training cucumbers to climb or trellis also makes harvesting easier and helps prevent the fruits from touching the ground.
Pest and Disease Management
Identifying Common Cucumber Pests
Cucumber plants can be susceptible to various pests that can hinder their growth and damage the fruits. Common pests that affect cucumber plants include aphids, cucumber beetles, spider mites, and whiteflies.
Regularly inspect your cucumber plants for signs of pest infestation, such as yellowing leaves, distorted growth, or visible insects. Early detection allows for prompt intervention, preventing pests from causing significant damage.
Preventing and Treating Pest Infestations
To prevent pest infestations, implement proper pest management strategies. Introduce beneficial insects, such as ladybugs or lacewings, which feed on common cucumber pests. Additionally, practicing good sanitation, removing debris from the aquaponic system, and regularly inspecting and cleaning the plants can help prevent pests from taking hold.
If an infestation occurs, there are various organic pest control methods available. These include using insecticidal soaps, neem oil, or homemade botanical sprays. It’s important to carefully follow the instructions provided by the chosen pest control method to ensure effective treatment while minimizing any negative impact on the aquaponic system.
Dealing with Cucumber Diseases
Cucumber plants are prone to certain diseases, such as powdery mildew, downy mildew, and bacterial wilt. These diseases can significantly impact the health and productivity of your cucumber plants if left untreated.
To prevent diseases, ensure proper air circulation and ventilation in the aquaponic system. Avoid wetting the foliage when watering to minimize the chances of fungal infections. Providing adequate spacing between plants and practicing good hygiene can also help minimize disease incidence.
If diseases do occur, promptly remove and dispose of infected plant parts to prevent further spread. Utilize organic fungicides or disease-resistant cucumber varieties, if available, to mitigate the effects of diseases and maintain the health of your cucumber plants.

Harvesting and Storage
Determining When Cucumbers are Ready for Harvest
Cucumbers are typically ready for harvest when they reach the desired size and color specific to the variety you are growing. Refer to the seed packet or variety description for specific indications of readiness.
Generally, slicing cucumbers are harvested when they are about 6-8 inches long and have a vibrant green color. Pickling cucumbers are harvested when they are small, firm, and have a uniform size. It’s important to harvest cucumbers promptly when they are mature but not overripe to ensure the best flavor and texture.
Properly Harvesting Cucumbers
To harvest cucumbers, use a sharp knife or shears to cut them from the plant, rather than pulling or twisting. This helps prevent damage to the vines and ensures a clean cut. Be gentle when handling the fruits to avoid bruising or injuring them.
Check the plants regularly, as cucumbers tend to grow rapidly once they start developing. Harvest cucumbers frequently to encourage continuous production throughout the growing season.
Storing Cucumbers for Longevity
Cucumbers are best enjoyed fresh, soon after harvest when they are at their peak flavor and crispness. However, if you have an abundant harvest and want to store cucumbers for longer, proper storage is essential.
Wash and dry the cucumbers before storing them. Wrap them individually in paper towels or place them in a perforated plastic bag to maintain optimal humidity levels. Store the cucumbers in the refrigerator, preferably in the crisper drawer, at a temperature between 45°F to 50°F (7°C to 10°C).
Avoid storing cucumbers alongside fruits like apples or tomatoes, as they produce ethylene gas that can accelerate the ripening process of cucumbers. With proper storage, cucumbers can stay fresh for up to a week.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing Nutrient Deficiencies
Nutrient deficiencies can occur in an aquaponic system, impacting the growth and health of cucumber plants. Monitor the plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or abnormal leaf discoloration.
Address nutrient deficiencies by adjusting the aquaponic system’s nutrient levels. Consider supplementing with organic fertilizers or adjusting the fish feeding rate to provide additional nutrients to the plants. Regular water testing can help identify any nutrient imbalances and guide the necessary adjustments.
Resolving pH Imbalances
pH imbalances can affect the availability of nutrients to cucumber plants in an aquaponic system. If the pH is too high or too low, it can lead to plant stress and hinder growth.
To resolve pH imbalances, adjust the water’s acidity or alkalinity by adding pH-up or pH-down solutions, respectively. Regularly monitor and maintain the pH within the recommended range for cucumber cultivation in aquaponics (6.0 to 6.8) to ensure optimal nutrient uptake.
Dealing with Stunted Growth
If you notice stunted growth in your cucumber plants, it could be due to various factors. Insufficient lighting, inadequate nutrient supply, or poor water quality are common causes of stunted growth.
Ensure that the cucumber plants receive sufficient light, adjust nutrient levels if needed, and regularly monitor water quality parameters. Additionally, check for potential pest or disease issues that may be affecting plant growth. Identifying the underlying cause will help you address the specific issue leading to stunted growth in your cucumber plants.
By following these guidelines and implementing proper care practices, you can successfully grow cucumbers in your aquaponic system. Enjoy the fresh and flavorful cucumbers harvested from your thriving aquaponic garden!



