If you’ve always wondered how to grow Japanese cucumbers in your own backyard, look no further! In this ultimate guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about successfully cultivating these crisp and flavorful cucumbers. From selecting the right seeds to providing optimal growing conditions, we’ll walk you through all the steps to ensure a bountiful harvest of these popular cucumbers. So, grab your gardening gloves and get ready to embark on a rewarding journey of growing Japanese cucumbers from scratch.
Choosing the Right Variety
Determining the Japanese cucumber variety
When it comes to growing Japanese cucumbers, the first step is to determine which variety you want to grow. Japanese cucumbers are known for their slender shape, crisp texture, and mild flavor. There are several popular varieties to choose from, including the Kyuri, Shiomido, and Suyo Long. Take some time to research the characteristics of each variety and decide which one suits your preferences best.
Consideration of climate and available space
Another important factor to consider when choosing the right variety is the climate in your area and the space available for your cucumber plants. Different varieties have different temperature requirements, so it’s crucial to select a variety that can thrive in your specific climate. Additionally, Japanese cucumbers tend to have long vines, so consider the amount of space you have in your garden or the availability of trellises or stakes for vertical growth.
Selecting disease-resistant varieties
Diseases can pose a serious threat to cucumber plants, so selecting disease-resistant varieties is advisable. Look for varieties that are resistant to common cucumber diseases such as powdery mildew, downy mildew, and cucumber mosaic virus. This will help ensure that your plants stay healthy and productive throughout the growing season.
Preparing the Soil
Testing the soil pH
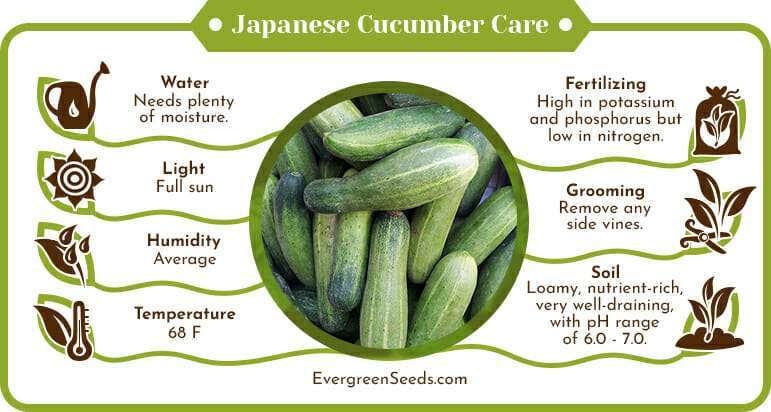
Before you start planting your Japanese cucumber seeds, it’s essential to test the pH of your soil. Cucumbers prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH ranging from 6.0 to 6.8. You can easily test the pH of your soil using a soil testing kit available at most gardening stores. If your soil’s pH is not within the recommended range, you can adjust it by adding amendments such as agricultural lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it.
Improving soil fertility
To ensure that your Japanese cucumber plants receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth, it’s essential to improve the fertility of your soil. Incorporating organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure into the soil before planting will help improve its structure, drainage, and nutrient-holding capacity. You can also consider adding a balanced fertilizer to provide additional nutrients that may be lacking in your soil.
Creating well-draining soil
Cucumbers thrive in well-draining soil, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot and other issues. To promote proper drainage, ensure that your garden bed has adequate slope or use raised beds. If your soil is heavy and has poor drainage, you can add organic matter or perlite to improve its structure. Proper drainage will allow excess water to flow away from the roots, preventing waterlogged conditions and promoting healthy growth.

Starting Seeds Indoors
Timing for starting cucumber seeds
Starting cucumber seeds indoors gives you a head start on the growing season, especially if you live in an area with a short growing season. The ideal time to start cucumber seeds indoors is about 2 to 4 weeks before the last expected frost date in your area. This will give the seeds enough time to develop into healthy seedlings before transplanting them outdoors.
Preparing seed trays and containers
When starting cucumber seeds indoors, you’ll need seed trays or containers to sow your seeds in. Ensure that the containers have drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Fill them with a good quality seed-starting mix, which is light, well-draining, and sterile. Moisten the mix before planting the seeds, ensuring it is evenly moist but not waterlogged.
Sowing and caring for seedlings
Sow the cucumber seeds about half an inch deep in the seed trays or containers. Keep the trays in a warm and bright location, such as near a south-facing window or under grow lights. Maintain a consistent temperature of around 70°F (21°C) to encourage germination. Keep the soil moist but not soggy, watering from below to avoid disturbing the seeds. Once the seedlings have emerged, provide them with adequate light, water and transplant them outdoors after the threat of frost has passed.
Direct Seeding in the Garden
Choosing an appropriate planting location
If you prefer to sow cucumber seeds directly in your garden, it’s important to choose a suitable planting location. Cucumbers love full sun, so select a spot that receives at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day. Ensure that the area has well-draining soil and is protected from strong winds, as they can damage the delicate cucumber vines.
Preparing the garden bed
Prepare the garden bed by removing any weeds or vegetation and loosening the soil with a garden fork or tiller. Incorporate organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve the soil’s fertility and structure. Smooth out the soil surface and create raised rows or hills if desired, as these can help improve drainage and provide better access for the cucumber vines.
Planting cucumber seeds directly
Sow the cucumber seeds directly in the prepared garden bed, planting them about half an inch deep and spacing them according to the specific variety’s recommendations. Cover the seeds with soil, gently firming it around them. Water the bed thoroughly, ensuring that the soil is evenly moist. As the seedlings emerge, thin them out if necessary to ensure adequate spacing for optimal growth.

Providing Proper Watering
Establishing appropriate watering schedule
Watering is crucial for the healthy growth of Japanese cucumber plants. Establishing an appropriate watering schedule is essential to avoid both overwatering and underwatering. Cucumber plants need consistent moisture, so water deeply but infrequently, ideally providing about 1 inch of water per week. However, adjust the frequency and amount based on the weather conditions and the moisture levels in the soil.
Using drip irrigation or a soaker hose
To ensure proper and efficient watering, consider using drip irrigation or a soaker hose. These watering methods deliver water directly to the plant roots, minimizing water wastage and reducing the risk of disease. They also help keep the foliage dry, which can prevent the spread of fungal diseases. Install the system early in the growing season, and regularly check to ensure that it is working correctly.
Avoiding waterlogged conditions
While adequate watering is essential for the health of Japanese cucumber plants, it’s crucial to avoid waterlogged conditions. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other issues. To prevent waterlogging, ensure that your soil has proper drainage and that excess water can flow freely away from the roots. Be mindful not to water too frequently, especially during periods of heavy rain or high humidity.
Implementing Mulching Techniques
Benefits of mulching
Mulching is a beneficial practice for growing Japanese cucumbers. Mulch helps conserve soil moisture, suppress weeds, and maintain more consistent soil temperatures. It also acts as a barrier between the soil and the fruit, preventing soil-borne diseases. In addition, mulch can help improve soil fertility as it breaks down over time.
Selecting the right mulch material
When it comes to selecting the right mulch material for your cucumber plants, there are several options to choose from. Organic mulches such as straw, shredded leaves, or grass clippings work well for cucumbers. These materials break down over time, adding organic matter to the soil. Avoid using synthetic mulches, as they can prevent water and air flow to the soil.
Applying and maintaining mulch
Apply a layer of mulch around the base of your cucumber plants, ensuring that the soil is covered but not piled up against the stems. Maintain a thickness of about 2 to 3 inches. Regularly check the mulch and replenish it as needed to ensure adequate coverage. Avoid allowing the mulch to come into direct contact with the cucumber vines, as this can create a moist environment and promote disease.

Supporting Cucumber Plants
Choosing suitable support structures
Supporting cucumber plants is important, especially when growing vining varieties. Choosing suitable support structures will help keep the vines off the ground, improve air circulation, and prevent the fruit from developing deformities. There are different options for supporting cucumber plants, such as trellises, stakes, or cages.
Using trellises or stakes
Trellises and stakes are popular choices for supporting cucumber plants. Trellises can be made of wood, wire, or even bamboo. They provide a vertical structure for the vines to climb on, saving space in the garden. Stakes are another option, where you tie the cucumber vines to individual stakes as they grow. Whichever method you choose, ensure that it is sturdy enough to support the weight of the plants and fruit.
Training cucumber vines
As the cucumber vines grow, gently guide them towards the support structure. Use twine or soft ties to secure the vines loosely to the trellis or stakes. Regularly check the plants and adjust the ties as needed. Training the vines not only helps keep them organized and off the ground but also encourages better air circulation, reducing the risk of diseases.
Fertilizing Japanese Cucumbers
Understanding cucumber nutrient requirements
To ensure healthy growth and high yields, it’s important to understand the nutrient requirements of Japanese cucumbers. Cucumbers are heavy feeders, meaning they require ample nutrients throughout the growing season. They need a balanced supply of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients such as calcium and magnesium.
Applying organic or balanced fertilizer
There are two primary options for fertilizing Japanese cucumbers: organic fertilizers and balanced fertilizers. Organic options include compost, well-rotted manure, and other natural amendments that provide slow-release nutrients. Balanced fertilizers, both organic and synthetic, contain a mix of macronutrients and micronutrients. They can be applied either as a granular fertilizer scattered around the plants or as a liquid fertilizer for foliar feeding.
Frequency and timing of fertilization
The frequency and timing of fertilization depend on the specific needs of your cucumber plants and the type of fertilizer used. Generally, it’s recommended to apply fertilizer at planting time and then every 4 to 6 weeks throughout the growing season. However, be mindful not to over-fertilize, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit production. Always follow the recommended application rates provided on the fertilizer packaging.

Controlling Pests and Diseases
Identifying common cucumber pests
Cucumber plants can be susceptible to various pests, including aphids, cucumber beetles, and spider mites. Look for signs of infestation such as yellowing leaves, holes in the foliage, or sticky residue on the leaves. Early identification is key to preventing pests from causing significant damage to your plants.
Implementing organic pest control methods
When it comes to controlling pests in a natural and eco-friendly manner, there are several options to consider. One method is using companion planting, where certain plants are grown alongside cucumbers to repel pests or attract beneficial insects. Introducing biological controls such as ladybugs or predatory insects can also help manage pest populations. Regularly inspect your plants and remove any pests you spot by hand or using a strong jet of water.
Prevention and management of diseases
Preventing and managing diseases is crucial for the success of your Japanese cucumber plants. To prevent the spread of diseases, ensure that your plants have proper airflow by providing adequate spacing and support. Water the plants at ground level to avoid wetting the foliage, as this can encourage disease development. Be vigilant for signs of common cucumber diseases such as powdery mildew or downy mildew, and promptly treat them with appropriate organic fungicides if necessary.
Harvesting and Storage
Determining cucumber maturity
Knowing when to harvest your Japanese cucumbers is essential to ensure optimal flavor and texture. Most Japanese cucumber varieties are ready for harvest when they reach about 6 to 8 inches in length. However, the specific maturity guidelines may vary for different varieties, so refer to the seed packet or variety information for accurate harvesting instructions. Cucumbers that are overripe may become bitter or develop tough skin.
Proper harvest techniques
To harvest your cucumbers, use a pair of sharp garden shears or scissors to cut the fruit from the vine, leaving a small portion of the stem attached. Avoid twisting or pulling the cucumbers from the plant, as this can damage the vines. Harvest regularly to encourage continuous fruit production and prevent overcrowding.
Storage options and tips
Freshly harvested Japanese cucumbers can be enjoyed immediately or stored for a short period. If you plan on using them soon, store them in the refrigerator crisper drawer to maintain their crispness and freshness. If you have a surplus of cucumbers, consider pickling or preserving them to extend their shelf life. Alternatively, you can freeze sliced cucumbers for adding to smoothies or using in cooking later on.
Growing Japanese cucumbers can be a rewarding experience. By choosing the right variety, preparing the soil, starting seeds indoors or directly in the garden, providing proper watering, implementing mulching techniques, supporting the plants, fertilizing appropriately, controlling pests and diseases, and harvesting and storing the cucumbers correctly, you can ensure a successful and bountiful harvest. Enjoy the process and savor the delicious and refreshing taste of homegrown Japanese cucumbers!



