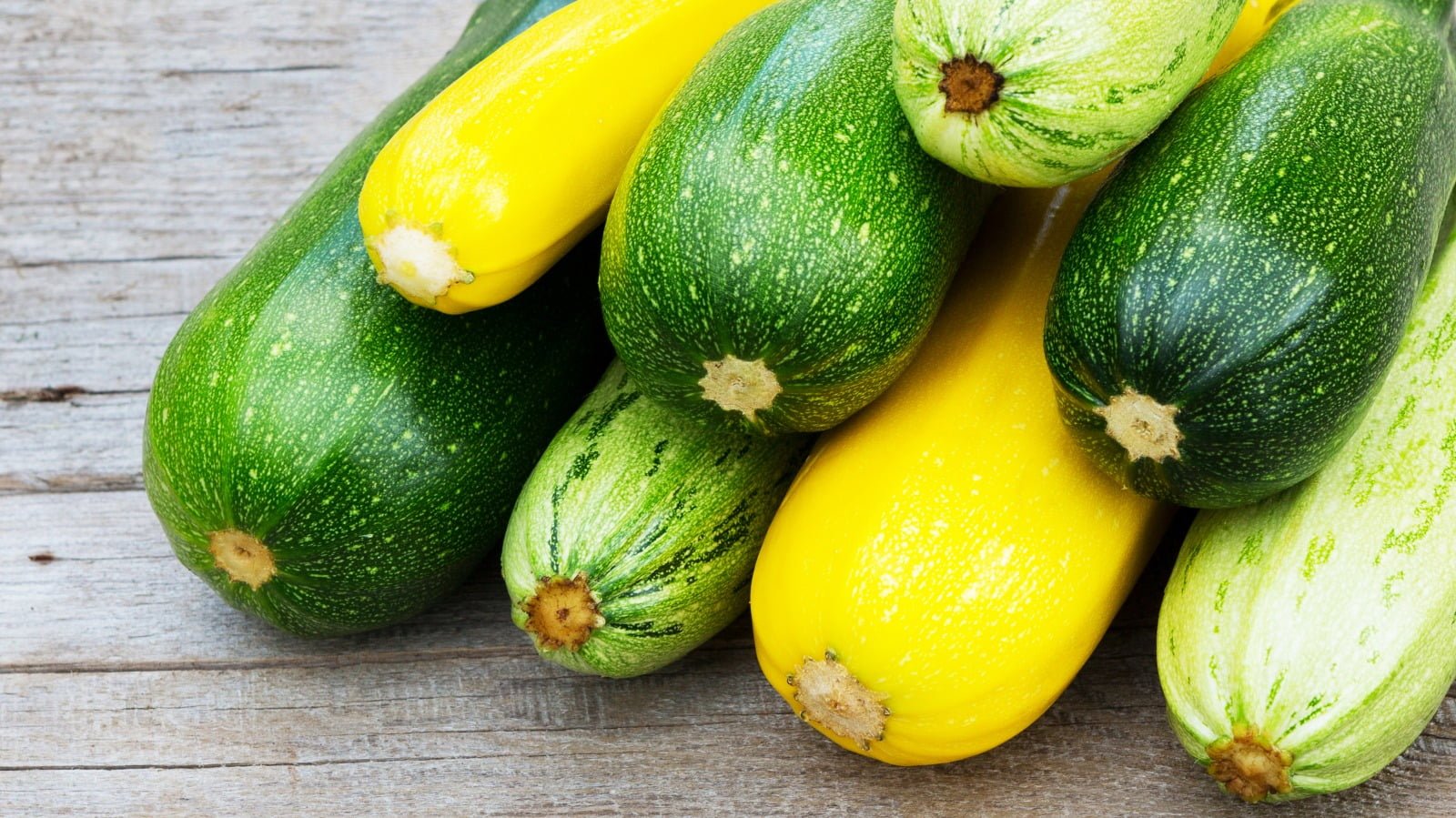
Let’s settle the age-old debate of zucchini versus squash once and for all. While many assume they are two completely different vegetables, the truth is that zucchini is actually a type of squash. However, what sets zucchini apart from its squashed siblings is its vibrant green color, smooth skin, and slightly sweeter flavor. Squashes, on the other hand, can come in a variety of colors and textures, ranging from yellow to pale green, with some varieties even having rough or warty skin. So, the next time you’re at the grocery store, remember that zucchini is just a special type of squash, but don’t be afraid to explore the wide world of squashes that await you!

Appearance
Size
Both zucchini and squash belong to the same botanical family, but they do have some differences in appearance. When it comes to size, zucchinis are generally smaller compared to squash. Zucchinis are typically harvested when they are around 6 to 8 inches long and 2 inches in diameter, while squash can grow larger, reaching up to 12 inches in length and 3 inches in diameter.
Color
Another noticeable difference between zucchini and squash is the color. Zucchinis are usually dark green in color, with a smooth and glossy skin. On the other hand, squash can come in a variety of colors, ranging from yellow, green, and even a combination of both. This vibrant array of colors makes squash an eye-catching addition to any dish or garden.
Shape
In terms of shape, zucchinis and squash also differ. Zucchinis typically have a straight and cylindrical shape, with uniform thickness throughout. In contrast, squash can have various shapes, including round, scalloped, or even tubular. This diversity in shape adds an element of visual interest when incorporating squash into culinary creations.
Taste
Flavor
When it comes to flavor, zucchini and squash share some similarities. Both have a mild and slightly sweet taste, but zucchini tends to have a more subtle flavor compared to squash. Squash, especially the yellow varieties, can offer a slightly richer and nuttier flavor profile. Both are versatile ingredients and can easily absorb the flavors of other ingredients when cooked.
Texture
In terms of texture, zucchini and squash also differ slightly. Zucchini has a firm and slightly crunchy texture when raw, turning tender and soft when cooked. On the other hand, squash tends to have a denser and creamier texture, which holds up well in various cooking methods. The texture of squash adds a delightful creaminess and depth to dishes, making it a favorite among many culinary enthusiasts.
Nutritional Differences
Calories
In terms of calorie content, zucchini and squash are both low in calories, making them a great choice for those watching their calorie intake. A cup of raw sliced zucchini contains approximately 20 calories, while the same amount of yellow squash provides around 30 calories. These low-calorie counts make zucchini and squash excellent options for incorporating into weight management diets.
Carbohydrates
When it comes to carbohydrates, zucchini and squash are both considered low-carb vegetables. A cup of zucchini contains about 4 grams of carbohydrates, while yellow squash contains slightly higher, with approximately 7 grams of carbohydrates per cup. These low carbohydrate counts make zucchini and squash suitable for individuals following low-carb or keto diets.
Fiber
Zucchini and squash are both good sources of dietary fiber, which is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Zucchini contains about 2 grams of fiber per cup, while yellow squash provides approximately 3 grams of fiber in the same serving size. Including these vegetables in your diet can contribute to improved digestion and overall gut health.
Vitamins and Minerals
Both zucchini and squash are packed with essential vitamins and minerals. They are particularly rich in vitamins A and C, which are important for supporting immune function and promoting healthy skin. Additionally, zucchini and squash provide significant amounts of potassium, folate, and manganese. These nutrients are necessary for various bodily functions, including proper heart health, cell growth, and energy production.
Culinary Uses
Cooking Methods
Zucchini and squash are incredibly versatile vegetables that can be cooked in various ways to create delicious and healthy dishes. They can be enjoyed raw in salads or as crunchy additions to wraps and sandwiches. When cooked, zucchini and squash can be grilled, sautéed, roasted, or even spiralized to make vegetable noodles. They can also be used in stir-fries, soups, stews, and casseroles, adding depth and flavor to any culinary creation.
Recipes
The possibilities are endless when it comes to zucchini and squash recipes. Here are a few popular options to try:
Zucchini and Squash Stir-Fry: Sauté sliced zucchini and squash with garlic, ginger, and soy sauce for a quick and flavorful stir-fry. Serve it over steamed rice or alongside grilled protein for a complete meal.
Stuffed Zucchini Boats: Cut zucchinis in half lengthwise and hollow out the center. Fill the hollowed-out zucchinis with a mixture of cooked ground meat, vegetables, and cheese. Bake until the zucchinis are tender and the filling is golden and bubbly.
Summer Squash Casserole: Layer thinly sliced yellow squash, onions, and cheese in a baking dish. Top it off with a sprinkling of breadcrumbs and bake until golden and crispy. This comforting casserole is a crowd-pleaser and perfect for family gatherings.

Origin
Zucchini
Zucchini, scientifically known as Cucurbita pepo, is believed to have originated in Central and South America, where it has been cultivated for thousands of years. It was later introduced to Europe by Italian explorers in the 16th century, and from there, it spread to various parts of the world. Today, zucchini is widely grown and enjoyed in many cuisines, particularly in Mediterranean and American dishes.
Squash
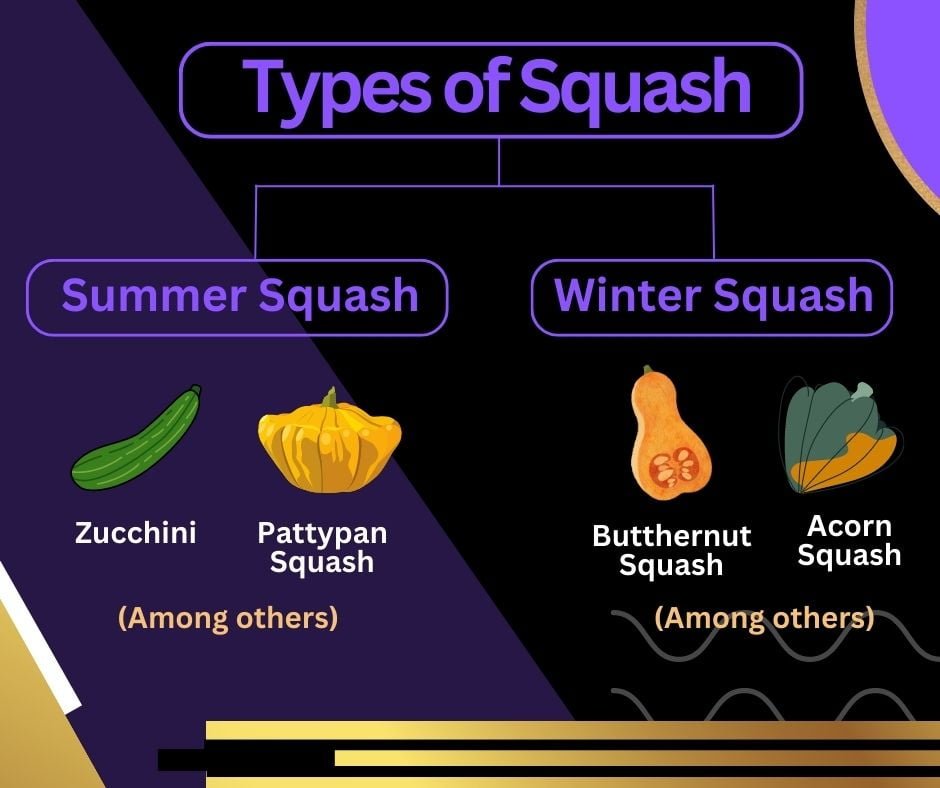
Squash is a broader term that encompasses various species, including zucchini. The term “squash” originated from the Native American word “askutasquash,” which means “eaten raw or uncooked.” Native Americans were the first to cultivate squash, and it quickly became a staple in their diet. Over time, different cultivars and varieties of squash were developed, each with unique characteristics and uses.
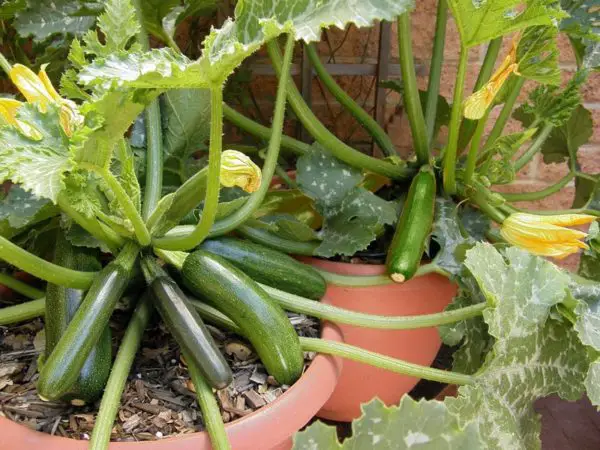
Cultivation
Growing Conditions
Both zucchini and squash thrive in warm climates and require well-drained soil, ample sunlight, and regular watering. They are annual plants and can be easily grown from seeds or transplants. It is advisable to start planting zucchini and squash after the last frost, as they are frost-sensitive. These vegetables are typically fast-growing, so it is essential to provide them with enough space to spread and grow.
Harvesting
Both zucchini and squash can be harvested when they reach the desired size and color. For zucchini, it is best to harvest them when they are around 6 to 8 inches long, as they tend to become less tender and develop more seeds if left to grow larger. Squash varieties, however, can be harvested at different stages, depending on the preferred texture and flavor. Generally, squash is harvested when it is mature but still firm.
Storage
Zucchini and squash can be stored in a cool, dry place for a few days. To prolong their shelf life, it is recommended to store them in the vegetable compartment of the refrigerator. Placing them in a sealed plastic bag or wrapping them in a paper towel can help prevent moisture loss. It’s important to note that zucchini and squash are best consumed when fresh, as their flavor and texture may deteriorate over time.
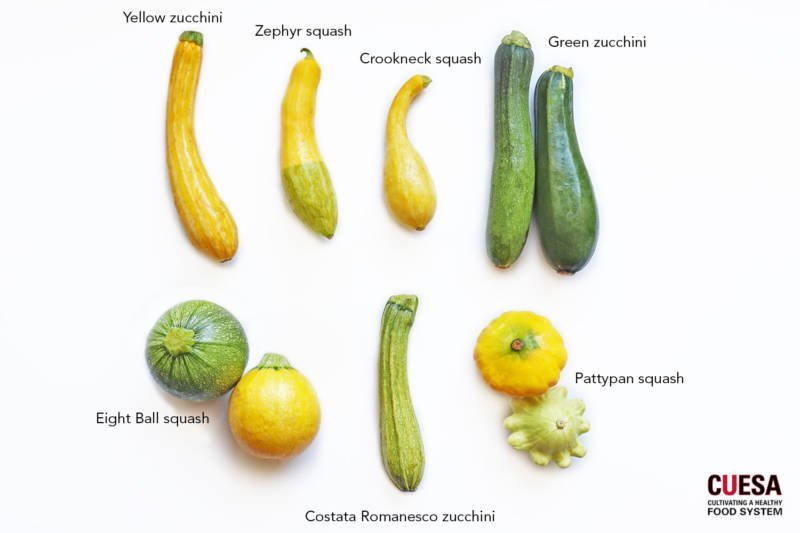

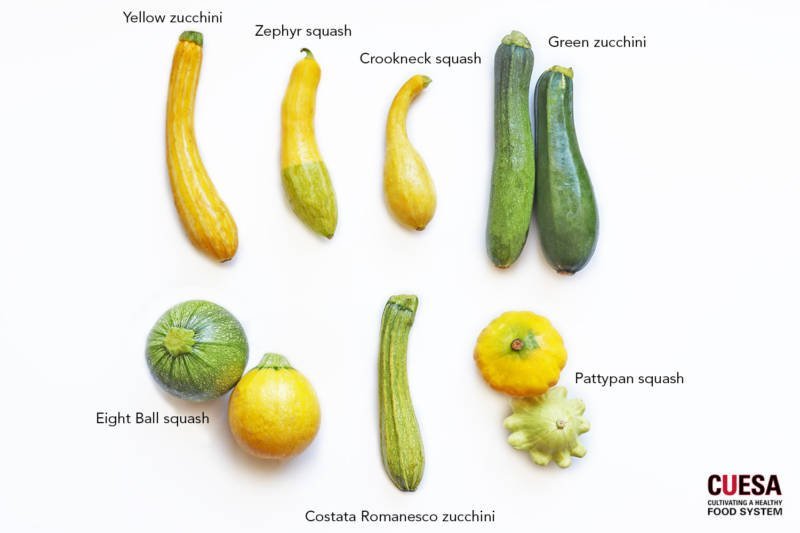
Popular Varieties
Zucchini Varieties
There are numerous zucchini varieties available, each with its own unique characteristics. Some popular zucchini varieties include:
Black Beauty: This variety boasts a deep green color and a classic zucchini flavor. It is one of the most commonly grown and widely available zucchini varieties.
Golden Zucchini: As the name suggests, this variety has a vibrant golden-yellow color. It tends to have a slightly sweeter flavor compared to green zucchinis.
Magda: Magda zucchini is a pale green variety with a milder flavor. It is prized for its tender texture and is well-suited for grilling or roasting.
Squash Varieties
Similar to zucchini, squash also comes in a variety of types, each with its own unique characteristics. Some popular squash varieties include:
Yellow Crookneck: This variety has a distinctive curved neck and bright yellow skin. It has a rich, buttery flavor and creamy texture, making it perfect for sautéing or roasting.
Pattypan: Pattypan squash, also known as scallop squash, is characterized by its round, scalloped edges. It comes in various colors, including yellow, green, and white. Pattypan squash has a delicate flavor and can be stuffed, grilled, or baked.
Butternut: Butternut squash is a winter squash known for its sweet, nutty flavor and dense flesh. It is often used in soups, stews, and baked goods, and its distinctive shape makes it easy to recognize.
Health Benefits
Weight Management
Zucchini and squash are naturally low in calories and high in water content, making them excellent choices for weight management. Incorporating these vegetables into your diet can help you feel full and satisfied while consuming fewer calories. Their high fiber content also aids in digestion and can contribute to a healthy weight.
Digestive Health
Both zucchini and squash are excellent sources of dietary fiber, which helps promote a healthy digestive system. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. Including these vegetables in your diet can support optimal gut health and prevent digestive issues.
Heart Health
Zucchini and squash are nutrient-dense vegetables that contribute to heart health. Their high potassium content helps regulate blood pressure and maintain proper heart function. Additionally, the presence of vitamins A and C in these vegetables provides antioxidant benefits that help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Eye Health
Zucchini and squash contain important antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which are beneficial for eye health. These antioxidants help protect the eyes against oxidative stress and age-related macular degeneration. Including these vegetables in your diet can support overall eye health and maintain good vision.
Availability and Seasonality
Fresh
Zucchini and squash are widely available in grocery stores and farmer’s markets, especially during the summer months. They are considered warm-season vegetables and are most plentiful from late spring to early fall. Fresh zucchini and squash should be firm, with smooth skin and vibrant color. It is always best to choose organic or locally grown options for optimal freshness and taste.
Frozen
If fresh zucchini and squash are not readily available, frozen options can be a convenient alternative. Frozen zucchini and squash are usually harvested and packed at peak ripeness, preserving their nutritional value and flavor. They can be found in the frozen vegetable section of most grocery stores and can be used as a substitute in various recipes.
Canned
Canned zucchini and squash can be found in some grocery stores, typically in the canned vegetable aisle. While canned options may not offer the same texture as fresh or frozen alternatives, they can still be used in a variety of dishes. It’s important to check the label for any added preservatives or sodium and choose options with minimal processing.
Preparation Tips
Washing and Cleaning
Before preparing zucchini and squash, it is important to wash them thoroughly under cool running water. This helps remove any dirt, debris, or residual pesticides that may be present on the skin. It is advisable to use a vegetable brush to gently scrub the surface, especially if the skin is rough or bumpy.
Peeling
Whether or not to peel zucchini and squash is a matter of personal preference and recipe requirements. The skin of zucchini is edible and contains additional nutrients, so it can be left on for added texture and color. However, if you prefer a milder taste or need a more uniform appearance, peeling the skin is a viable option. Squash, on the other hand, generally has a tougher skin that is typically removed before cooking.
Slicing and Dicing
To slice zucchini and squash, start by trimming off the ends using a sharp knife. Depending on the recipe, you can slice them into rounds, half-moons, or julienne strips. For dicing, cut the zucchini or squash into uniform-sized pieces. This allows for even cooking and an appealing presentation in dishes such as stir-fries or soups.
In conclusion, while zucchini and squash may share some similarities in appearance and taste, they also have distinct characteristics that set them apart. From their different sizes and colors to their unique nutritional profiles and culinary uses, zucchini and squash offer a wealth of options for delicious and healthy meals. Whether roasted, grilled, or added to your favorite recipes, these versatile vegetables are sure to enhance any dish, providing flavor, texture, and a dose of nutritional goodness. So, next time you’re at the grocery store or planning your garden, consider adding some zucchini and squash to your shopping list or planting bed – your taste buds and body will thank you!




