Planting tomatoes too early can have detrimental effects on their growth and overall success. From potential frost damage to stunted growth, the consequences of premature planting can be significant. Timing is crucial when it comes to the planting of tomatoes, as they require warm soil and consistent temperatures to thrive. This article explores the potential risks and challenges that arise when tomatoes are planted too early, shedding light on the importance of proper planning and informed decision-making in the realm of gardening.

Effects of Planting Tomatoes Too Early
Damage from Cold Temperatures
Planting tomatoes too early can result in damage from cold temperatures. Tomatoes are warm-season crops that thrive in temperatures between 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit. When exposed to cold temperatures, especially below 50 degrees Fahrenheit, tomato plants may suffer from chilling injury. Chilling injury can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and even death of the plant. Additionally, the cold temperatures can inhibit the development of tomato plants, causing them to remain small and weak.
Stunted Growth
Another consequence of planting tomatoes too early is stunted growth. Tomatoes require warm soil temperatures for proper root development and nutrient uptake. When planted in cold soil, the roots struggle to grow and absorb essential water and nutrients. This can impede the overall growth of the plant, resulting in smaller and underdeveloped tomatoes. Stunted growth not only affects the size of the fruit but also reduces the plant’s ability to produce an abundant yield.
Reduced Fruit Production
Planting tomatoes too early can lead to reduced fruit production. The cold temperatures can affect the flowering process and hinder the ability of tomato plants to set fruits. Cold temperatures can disrupt the pollination process as they can decrease the activity of pollinators such as bees. Moreover, when tomato plants are exposed to stressors, such as cold temperatures, they may divert their energy towards survival rather than fruit production. Consequently, this can lead to a significant decrease in the number and quality of the tomatoes harvested.

Factors to Consider Before Planting Tomatoes
Last Frost Date
One crucial factor to consider before planting tomatoes is the last frost date in your area. The last frost date refers to the average date when frost is no longer expected to occur. This information is typically available from local agricultural extension services or gardening resources. Planting tomatoes before the last frost date greatly increases the risk of exposing them to cold temperatures and frost damage. It is essential to wait until after this date to ensure optimal growing conditions for your tomatoes.
Soil Temperature
Soil temperature is another vital factor to consider before planting tomatoes. Tomato seeds and seedlings require a specific range of soil temperature for optimal germination and growth. The ideal soil temperature for planting tomatoes is around 60 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit. If the soil is too cold, the seeds may not germinate, or if the seedlings are planted, they may exhibit slow growth and poor establishment. Testing the soil temperature with a soil thermometer can help determine if conditions are suitable for planting tomatoes.
Air Temperature
In addition to soil temperature, air temperature plays a significant role in the successful growth of tomatoes. Tomato plants thrive in warm climates and require consistent warm air temperatures to flourish. It is crucial to consider the projected air temperatures during the growing season. Planting tomatoes too early, when the air temperature is still cold, can lead to poor growth and reduced fruit production. Monitoring weather forecasts and waiting for consistently warm temperatures can help ensure the best conditions for your tomato plants.
Seedling Readiness
Before planting tomatoes, it is important to assess the readiness of the seedlings. Tomato seedlings need to be adequately developed and hardened off before being transplanted outdoors. Hardening off is the process of gradually exposing seedlings to outdoor conditions, including fluctuating temperatures, wind, and direct sunlight. This helps prepare the seedlings for the challenges they will face when planted in the garden. Planting inadequately hardened seedlings can increase their vulnerability to stress from cold temperatures and hinder their overall growth.

Signs of Tomato Stress from Early Planting
Wilting
One of the signs that tomato plants may exhibit as a result of early planting is wilting. Cold temperatures can impede the plant’s ability to take up water from the soil properly. Insufficient water uptake can lead to dehydration, causing the leaves and stems to wilt. Wilting is a defense mechanism employed by plants to reduce transpiration and conserve water. If you notice wilting in your tomato plants after early planting, it is crucial to provide them with adequate water and take steps to mitigate the impact of the early planting.
Yellowing Leaves
Yellowing leaves are another common sign of stress in tomato plants planted too early. Cold temperatures can hinder the plant’s ability to absorb essential nutrients from the soil. This nutrient deficiency often manifests as yellowing leaves, beginning from the bottom of the plant and progressing upwards. The yellowing of leaves, particularly between the veins, is indicative of a condition called chlorosis. Chlorosis affects the plant’s ability to carry out photosynthesis effectively, resulting in weakened growth and reduced fruit production.
Slow Growth
Slow growth is a noticeable sign of stress in tomato plants that have been planted too early. Cold temperatures can severely inhibit the metabolic processes within the plant, including photosynthesis and nutrient uptake. As a result, the growth rate of the plant slows down considerably. The plant may appear smaller and weak, with thin stems and poor foliage development. Slow growth can have long-lasting effects on the overall health and productivity of the tomato plant, making it crucial to take steps to mitigate the impact of early planting.
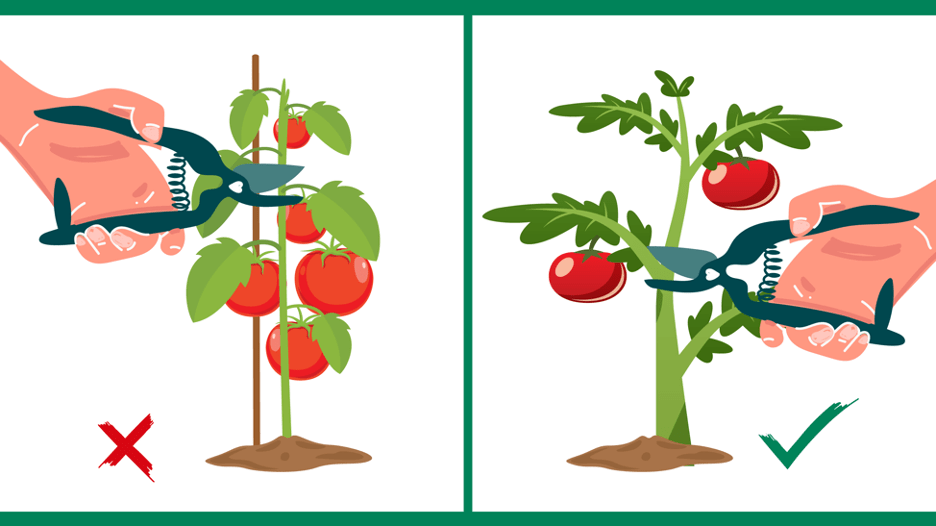
Steps to Mitigate the Impact of Early Planting
Provide Frost Protection
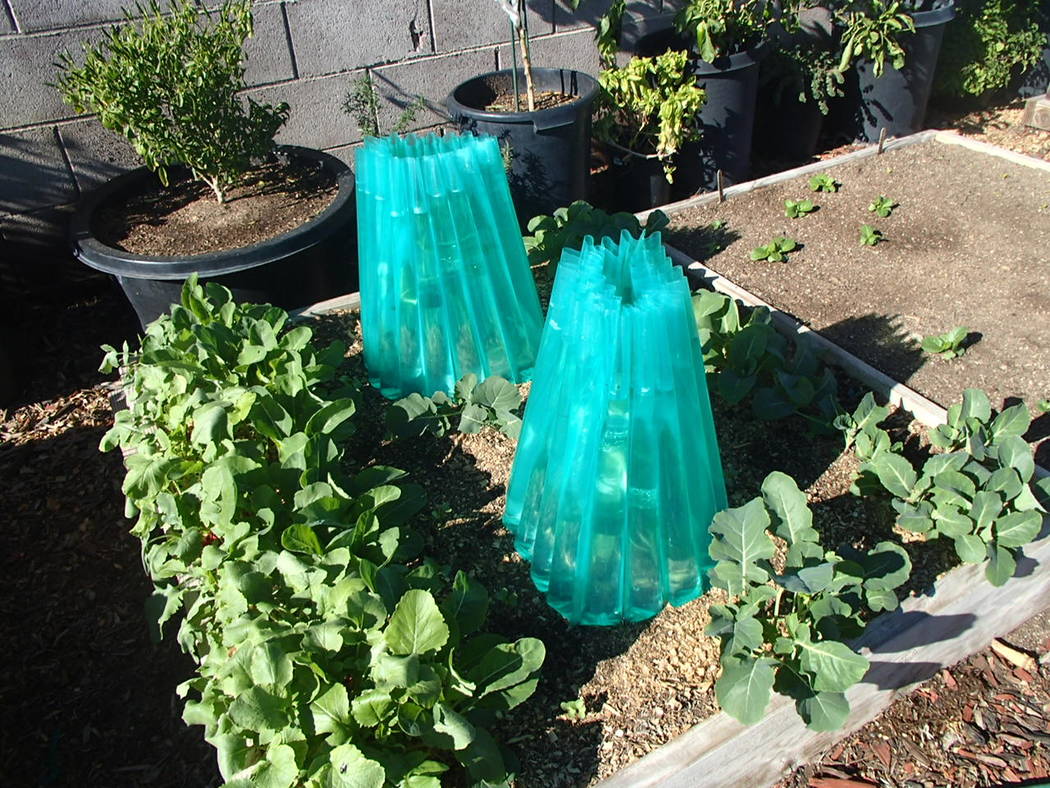
To mitigate the impact of early planting and protect your tomato plants from frost damage, it is essential to provide frost protection. Various techniques can be employed, such as covering the plants with cloths or using individual plant coverings. These protective coverings act as insulators and help trap heat around the plants, preventing frost from damaging their delicate tissues. Additionally, using mulch around the base of the plants can help regulate soil temperature and provide insulation, further protecting them from cold temperatures.
Monitor Soil Moisture
Proper soil moisture management is crucial when planting tomatoes early. It is important to monitor the soil moisture levels regularly and ensure the plants receive adequate water. Cold temperatures can slow down the evaporation rate, leading to waterlogged or excessively dry conditions. Both of these extremes can stress the plants and hinder their growth. Regularly check the moisture content of the soil by touching it or using a moisture meter, and water as needed to maintain a moist but not waterlogged soil environment.
Provide Adequate Nutrition
To mitigate the impact of early planting, providing adequate nutrition to your tomato plants is essential. Cold temperatures can impede the plant’s ability to take up nutrients from the soil, so supplementing with fertilizers can help overcome these deficiencies. Use a balanced fertilizer that contains essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This will ensure that the plants have the necessary resources for growth and development. Additionally, incorporating organic matter, such as compost, into the soil can enhance its nutrient content and provide the plants with a nutrient-rich environment.
Prune Excess Growth
Pruning excess growth is an effective step to mitigate the impact of early planting. Cold temperatures can cause tomato plants to develop excessive vegetative growth, diverting energy away from fruit production. Regular pruning, especially of suckers and unnecessary foliage, helps redirect the plant’s energy towards fruit development and stimulates better air circulation, reducing the risk of diseases. Pruning also helps manage the overall size and shape of the plant, making it more manageable and facilitating proper light penetration.

Benefits of Planting Tomatoes at the Right Time
Optimal Growth and Development
Planting tomatoes at the right time offers several benefits, including optimal growth and development. When tomatoes are planted when the soil and air temperatures are favorable, the plants can establish strong root systems, enabling them to access water and nutrients efficiently. This sets the stage for healthy growth and robust plant development throughout the season. Proper growth and development increase the plant’s ability to withstand stressors, resist diseases, and produce a bountiful harvest of flavorful tomatoes.
Increased Fruit Yield
One of the key advantages of planting tomatoes at the right time is increased fruit yield. When tomatoes are planted in optimal conditions, they can focus their energy on flower production and successful pollination. This leads to a higher fruit set and ultimately a greater yield. Additionally, planting at the right time allows for proper fruit development without the hindrance of stressors such as cold temperatures. This results in larger, juicier, and more flavorful tomatoes that are more enjoyable to harvest and consume.
Pest and Disease Resistance
Planting tomatoes at the appropriate time enhances their resistance to pests and diseases. Cold temperatures can weaken tomato plants and make them more susceptible to attacks from pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and cutworms. Additionally, stresses caused by early planting can compromise the plant’s defense mechanisms, making it more vulnerable to diseases like early blight or powdery mildew. By planting at the right time, when temperatures are optimal, tomato plants are better equipped to handle these challenges and exhibit stronger defense mechanisms against pests and diseases.
In conclusion, planting tomatoes too early can have detrimental effects on the plants’ growth, fruit production, and overall health. It is crucial to consider factors such as the last frost date, soil and air temperatures, and seedling readiness before planting tomatoes. Signs of stress from early planting include wilting, yellowing leaves, and slow growth. Steps can be taken to mitigate the impact of early planting, including providing frost protection, monitoring soil moisture, providing adequate nutrition, and pruning excess growth. By planting tomatoes at the right time, optimal growth and development, increased fruit yield, and enhanced pest and disease resistance can be achieved.



