Strawberries, the delectable red fruit that bursts with sweetness, are a favorite amongst many gardeners. However, successfully growing these luscious berries requires careful planning and consideration of the optimal planting time. In this article, you will explore the ideal month for planting strawberries, unearthing the key factors that influence their successful growth and bountiful harvest. By understanding the nuances of strawberry cultivation, you will be equipped with the knowledge to embark on a fruitful gardening journey.

Factors to Consider Before Planting Strawberries
When considering planting strawberries, there are several important factors to take into account. These factors include climate and hardiness zones, soil conditions, variety selection, and site selection.
Climate and Hardiness Zones
Strawberries thrive in temperate climates, preferring cool winters and moderate summers. Before planting strawberries, it is essential to determine the hardiness zone of your region. The hardiness zone will determine the suitability of specific varieties and the optimal planting times. In colder regions, it is crucial to select varieties that can withstand frost and cold temperatures.
Soil Conditions
Strawberries require well-drained and fertile soil for optimal growth. Before planting, it is recommended to test the soil pH to determine if any adjustments are necessary. Strawberries prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. If the soil pH is outside this range, appropriate amendments can be made to achieve the desired pH level. Additionally, improving soil drainage and adding organic matter are critical to ensure the strawberries have the necessary nutrients and water availability.
Variety Selection
Choosing the right variety of strawberries is vital for successful cultivation. Varieties differ in terms of taste, yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to specific climates. Therefore, research the different varieties available in your region and select those that are most suitable for your climate and personal preferences. It is advisable to consult with local agricultural extension services or experienced growers for advice on the best strawberry varieties for your area.
Site Selection
Selecting an appropriate site for planting strawberries is crucial for their overall health and productivity. Ideally, the site should receive full sun exposure for at least six hours a day, as this enhances fruit production. Furthermore, the site should have good air circulation to minimize the risk of diseases. Avoid planting strawberries in areas prone to excessive wind or frost pockets, as these conditions can damage the plants. Additionally, consider the site’s proximity to a water source, as strawberries require consistent moisture throughout the growing season.
Best Months for Planting Strawberries
The best time to plant strawberries depends on the region and the desired crop harvest. Generally, strawberries are best planted in either the spring or fall, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Spring Planting
Spring planting is the most common method for starting a strawberry bed. This allows the plants to become fully established before the heat of summer arrives. The exact timing for spring planting varies depending on the region and the last frost date. However, it is generally recommended to plant strawberries in late winter to early spring, just as the ground starts to thaw and the temperatures begin to rise.
Fall Planting
In regions with milder climates, fall planting can be a viable option for growing strawberries. Fall planting allows the plants to establish a strong root system during the cooler months, enabling them to produce an abundant crop in the following spring. Fall planting is typically done from late summer to early fall, before the first frost.
Spring Planting
For those opting for spring planting, there are different periods within the spring season that are suitable for planting strawberries.
Late Winter to Early Spring
In regions with milder climates, late winter to early spring is an ideal time for planting strawberries. The soil has thawed, and the ground is workable. This period allows the plants to establish well before the arrival of warmer temperatures.
Mid-Spring
In most regions, mid-spring is considered the prime time for planting strawberries. By mid-spring, the risk of frost has significantly decreased, and the soil has warmed up enough to support vigorous plant growth. This is an opportune time to plant strawberries as they can take advantage of the longer daylight hours and warmer temperatures.
Late Spring
Late spring is the last chance to plant strawberries before the temperatures become too hot. Ideally, late spring planting should be done at least a few weeks before consistently high temperatures arrive. Planting in late spring allows the strawberries to establish themselves and produce a limited harvest before the intense summer heat sets in.
Fall Planting
Fall planting offers an alternative timeline for growing strawberries, particularly in regions with milder winter climates.
Late Summer to Early Fall
Fall planting generally occurs from late summer to early fall. This period allows the plants to establish their root systems before the onset of winter. The soil is still warm, providing optimal conditions for root development. Planting during this time ensures that the strawberries will be well-established and ready to produce a bountiful harvest in the following spring.
Mid-Fall
Mid-fall is another suitable period for fall planting strawberries. By mid-fall, the temperatures have cooled down, reducing the risk of heat stress on the plants. It is important to complete planting before the ground freezes to allow the plants to settle in and establish their roots.
Late Fall
Late fall planting should be approached with caution, as it is closer to the winter season. In regions with more severe winters, late fall planting may not be recommended, as the plants may not have enough time to establish strong root systems. However, in areas with mild winters, late fall planting can still be successful if proper winter protection measures are taken.

Exceptions to the Typical Planting Periods
While spring and fall are generally the optimal planting periods for strawberries, there are some exceptions to consider.
Mild-Winter Regions
In regions with mild winters and cooler summers, strawberries can be planted during the winter months. This is advantageous as it allows the plants to take advantage of the winter rainfall and cooler temperatures, which promote strong root development and minimize heat stress during fruit production. However, ensure that the soil is well-drained and protected from heavy rainfall to prevent waterlogging.
Winter Protection in Cold Regions
In colder regions where winter temperatures regularly drop below freezing, it is essential to provide adequate winter protection for strawberry plants. This can be achieved through the use of protective coverings such as straw, hay, or frost blankets. By incorporating these protective measures, strawberries can still be successfully grown in areas with harsh winter conditions.
Preparing the Soil for Strawberry Planting
Proper soil preparation is crucial for the successful establishment and growth of strawberry plants. The following steps should be taken to ensure the optimal soil conditions for strawberries.
Testing and Adjusting Soil pH
Before planting strawberries, it is essential to test the soil pH. Strawberries prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. If the soil pH is outside this range, the necessary adjustments should be made. Lime can be added to raise the pH if it is too acidic, while sulfur or peat moss can be incorporated to lower the pH if it is too alkaline.
Improving Soil Drainage
Strawberries require well-drained soil to prevent standing water, which can lead to root rot and other diseases. If the soil has poor drainage, it is advisable to amend it by adding organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or perlite. These amendments help improve soil structure, enhance drainage, and increase water-holding capacity.
Adding Organic Matter and Fertilizer
Incorporating organic matter into the soil before planting strawberries is beneficial for providing essential nutrients and improving soil fertility. Organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure should be spread evenly over the designated planting area. Additionally, a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for strawberries can be incorporated to provide the necessary nutrients for vigorous growth.
Propagating Strawberries
Strawberries can be propagated through two main methods: growing from seeds and growing from runners.
Growing From Seeds
Growing strawberries from seeds is a cost-effective method, but it requires patience and a longer timeframe for the plants to mature. To grow strawberries from seeds, start by selecting high-quality seeds and sowing them in seed trays or pots containing a well-draining seed-starting mix. Maintain consistent moisture and provide adequate light for seed germination. Once the seedlings have grown into robust plants, they can be transplanted into the desired planting location.
Growing From Runners
Growing strawberries from runners is a more common method as it allows for the production of genetically identical offspring. Runners are long stems that emerge from the mother plants and develop new plantlets at their tips. To propagate strawberries using runners, identify healthy mother plants and allow the runners to develop. Once the plantlets have established a root system, they can be carefully detached from the mother plant and transplanted into their final growing positions.
Planting Techniques for Strawberries
The two primary planting techniques for strawberries are bare-root planting and potted planting.
Bare-Root Planting
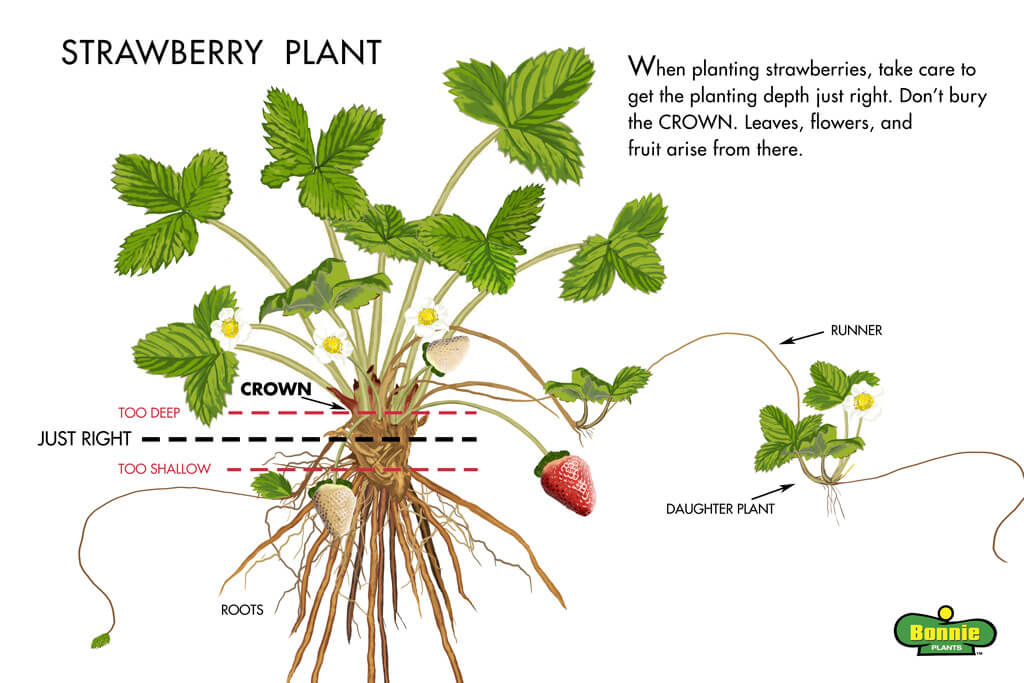
Bare-root planting is a common technique for planting strawberries. This involves planting dormant plants without any soil around their roots. To plant strawberries bare-root, prepare the planting area by removing weeds and loosening the soil. Dig a hole wide and deep enough to accommodate the roots without bending or crowding. Place the strawberry plant in the hole, ensuring that the soil is level with the crown. Gently fill in the hole and firm the soil around the roots. Water the newly planted strawberries thoroughly.
Potted Planting
Potted planting involves transplanting strawberries that are grown in containers. This method provides a more established plant with a developed root system. To plant strawberries from pots, dig a hole slightly larger than the size of the container. Remove the strawberry plant from the pot, being careful to avoid damaging the roots. Place the plant in the hole, making sure that the crown is level with the soil surface. Backfill the hole with soil, ensuring that the plant is secure. Water the potted strawberries generously to settle the soil and promote root establishment.
Caring for Strawberries After Planting
After planting, proper care is essential to ensure the healthy growth and productivity of strawberries. The following practices should be implemented to care for strawberries after planting.
Watering
Strawberries require consistent moisture throughout the growing season. Adequate watering helps the plants establish and develop strong root systems. Water strawberries deeply and regularly, ensuring that the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overhead watering to minimize the risk of foliar diseases. Mulching can also help retain soil moisture and reduce the frequency of watering.
Mulching
Mulching is an essential practice for strawberry care. Applying a layer of organic mulch around the plants helps conserve soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and maintain even soil temperature. Suitable mulch materials include straw, wood chips, or pine needles. Apply a layer of mulch about 2 to 3 inches thick, ensuring that the crowns of the plants are not covered.
Fertilizing
Regular fertilization is crucial for promoting healthy growth and fruit production in strawberries. Apply a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for strawberries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Fertilizer can be applied in early spring, during the growing season, and after each harvest. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit production.
Weed and Pest Control
Weed control is essential to prevent competition for nutrients and moisture. Regularly inspect the strawberry beds and remove any weeds promptly. Mulching can also help suppress weed growth. Additionally, monitor the plants for pests such as aphids, slugs, or snails. If necessary, employ appropriate pest control measures such as applying organic insecticides or employing biological control methods.
Harvesting Strawberries
Determining the optimal time for harvesting strawberries is crucial to achieve maximum flavor and sweetness. The following aspects should be considered when harvesting strawberries.
Determining Ripeness
Strawberries are ripe and ready for harvest when they have reached their full color and size. Ripe strawberries will have a bright red color and a glossy appearance. The fruits should be firm and have a sweet fragrance. Gently touch the strawberries to assess their ripeness; they should feel plump and yield slightly to pressure without being mushy.
Picking Techniques
To pick strawberries, hold the stem above the fruit to avoid bruising or damaging the delicate berries. Use a sharp pair of scissors or garden shears to cut the stem about a 1/2 inch above the fruit. Alternatively, the strawberry can be gently twisted to detach it from the stem. Avoid pulling or tugging the fruit, as this can damage both the berries and the plant.
Storage and Preservation
To maximize the shelf life of harvested strawberries, it is important to handle and store them properly. Immediately after harvest, gently wash the strawberries to remove any dirt or debris. Do not wash strawberries until just before consuming as excessive moisture can promote spoilage. Store the strawberries in a cool, well-ventilated area or in the refrigerator. If necessary, strawberries can also be preserved through freezing, canning, or making jams and preserves.
In conclusion, successfully growing strawberries requires careful consideration of several factors, including climate, soil conditions, variety selection, and site selection. Planting in the optimal months, either in spring or fall, is crucial for healthy plant establishment and abundant fruit production. Proper soil preparation, propagation techniques, and planting methods are essential for ensuring the successful growth of strawberries. After planting, providing consistent care in terms of regular watering, mulching, fertilizing, and weed and pest control is necessary. Finally, harvesting strawberries at the optimal ripeness and storing or preserving them appropriately will ensure the enjoyment of delicious, homegrown strawberries.