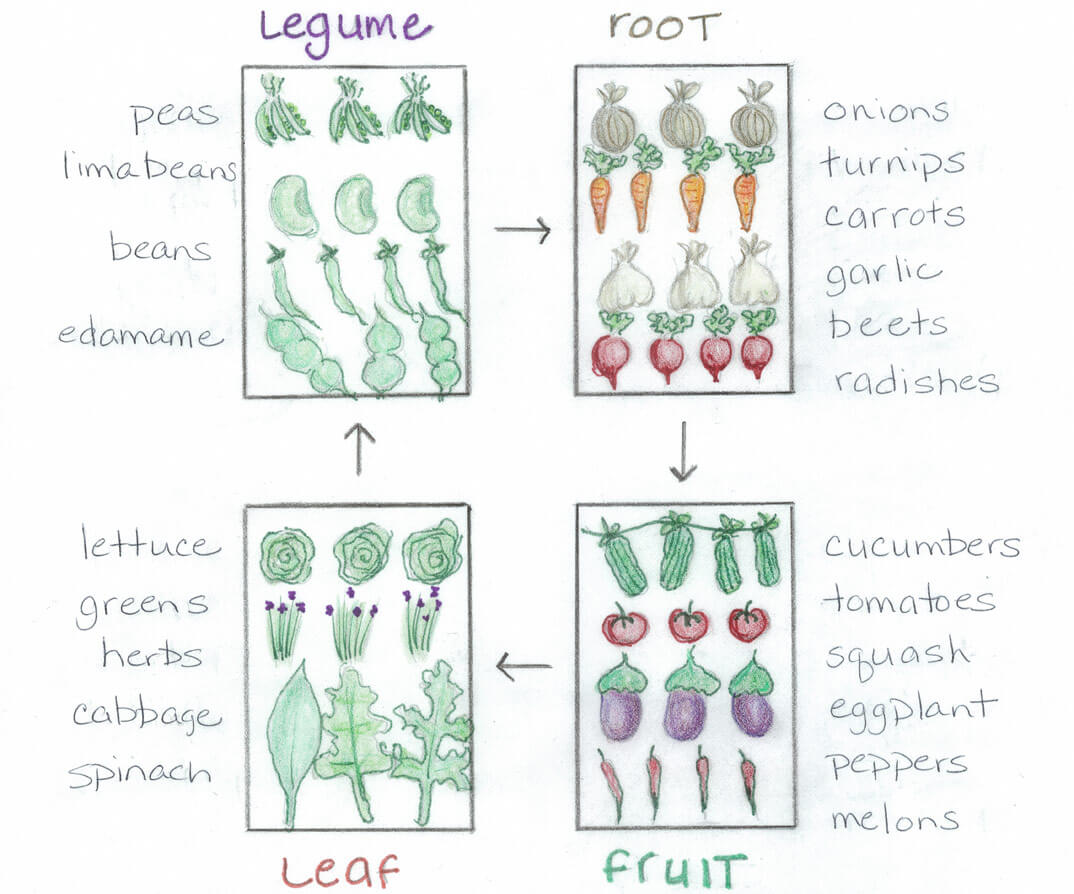
In the realm of gardening, the question of what to plant after successfully growing tomatoes often emerges as a perplexing dilemma. Once the tomato harvest is complete, there lies an ample stretch of land eagerly awaiting its next occupants. Meticulous consideration must be given to selecting the successor plants that will thrive in this post-tomato environment, ensuring a fruitful and harmonious garden. This article will delve into the various options available to gardeners, shedding light on the ideal crops that can follow the vibrant reign of tomatoes, leading to sustainable and bountiful yield rotations.

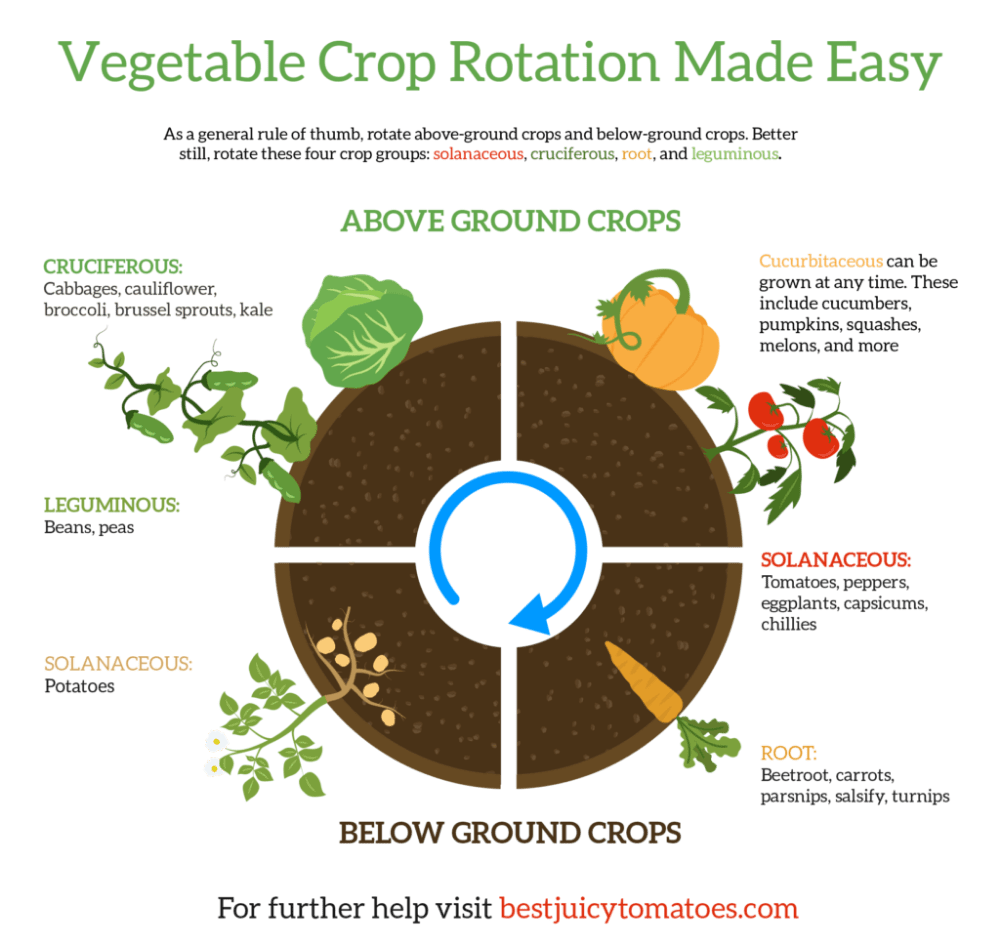
Rotation Crops
Rotation is a fundamental aspect of successful farming and gardening, and it holds particular significance in the cultivation of crops. Implementing a systematic rotation plan can offer numerous benefits, including improved soil health, enhanced pest and disease management, increased crop yield, and overall sustainability of the agricultural system. By carefully selecting rotation crops, you can effectively break the cycle of pests and diseases, rejuvenate the soil, and optimize the productivity of your garden or farm.
Why rotation is important
Rotation is essential because it disrupts the life cycles of pests and pathogens that target specific crops. Many pests and diseases have a limited range of host plants, and by rotating crops, you can reduce their prevalence and impact. Additionally, different plant species have varying nutrient requirements, and rotating crops helps ensure a more balanced nutrient utilization, preventing the depletion of specific elements in the soil. Moreover, rotating crops minimizes soil erosion, enhances water usage efficiency, and promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
Benefits of rotating crops
There are numerous advantages associated with a well-planned rotation system. One primary benefit is the reduction of pests and diseases. By rotating crops, you break the cycle of pests that thrive on a specific crop, reducing their populations and inhibiting their spread. This can significantly decrease the need for chemical pesticides and ultimately lead to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practice. Additionally, rotation can enhance soil structure and fertility. Certain crops have deep roots that penetrate the soil, improving its structure and reducing the risk of erosion. Furthermore, rotation can optimize nutrient availability, preventing the depletion of essential elements in the soil and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Crop rotation also aids in weed control, as the strategies used to combat weeds in one crop may not be as effective against different weed species, leading to a more diverse and resilient weed management system.
Rotation crops to consider
When planning your rotation scheme, it’s important to choose crops that have different nutrient requirements and are not susceptible to the same pests and diseases. Some recommended rotation crops include legumes, such as peas or beans, which fix nitrogen in the soil, nourishing subsequent crops. Brassicas, like broccoli or cabbage, are known for their ability to reduce soil-borne pests, making them excellent rotation options. Additionally, root crops such as carrots or beets can break up compacted soil and contribute to soil health. Including cover crops, like oats or clover, can provide excellent ground cover, suppress weeds, and add organic matter to the soil. Ultimately, the specific rotation crops you choose should reflect your climate, soil conditions, and personal preferences.
Cool Season Vegetables
What are cool season vegetables
Cool season vegetables are a diverse group of plants that thrive in cool temperatures and are typically planted in early spring or late summer. These vegetables are characterized by their ability to tolerate frost and their preference for cooler climates. They are a valuable addition to any garden, providing fresh produce during times when warm-season crops may struggle or not be available.
Examples of cool season vegetables
Some common examples of cool season vegetables include lettuce, spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and radishes. These leafy greens thrive in cooler temperatures and provide a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals. Other cool season favorites include broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage. These cruciferous vegetables not only withstand the cold but also offer an array of health benefits, including antioxidants and dietary fiber.
Herbs
Benefits of growing herbs
Growing herbs in your garden not only adds a burst of flavor to your culinary creations but also presents numerous benefits. Herbs are relatively low maintenance, making them an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced gardeners alike. Moreover, herbs are known for their aromatic qualities and can attract beneficial insects to your garden, helping to control pests naturally. They can also be used for medicinal purposes, as many herbs have historically been renowned for their healing properties.
Herbs to consider planting
There is a wide variety of herbs to consider planting in your garden. Some popular choices include basil, thyme, rosemary, sage, and oregano. These herbs are not only versatile in the culinary world but also attract pollinators, enhancing the biodiversity of your garden. Additionally, herbs like lavender and chamomile offer a calming fragrance and can be used for soothing teas or homemade aromatherapy products. Experimenting with different herbs will add depth and diversity to your garden while providing a fresh and sustainable source of flavor and wellness.
Root Vegetables
Benefits of growing root vegetables
Growing root vegetables can be a rewarding and flavorful endeavor. These vegetables are known for their ability to absorb nutrients deep within the soil, making them highly nutritious additions to any garden. Root vegetables also tend to be less demanding in terms of maintenance, requiring less space and often demonstrating resilience in adverse weather conditions. Additionally, the root systems of these plants help to improve soil structure by breaking up compacted soil, enhancing drainage, and preventing erosion.
Root vegetables to consider planting
When considering root vegetables for your garden, there are numerous options to choose from. Carrots are a classic choice, packed with vitamins and minerals, such as beta-carotene and vitamin K. Beets, known for their vibrant, earthy flavors, are rich in antioxidants and provide a host of health benefits. Radishes are a quick-growing option, able to thrive in cool temperatures and adding a peppery touch to salads and sandwiches. Other popular root vegetables include turnips, parsnips, and sweet potatoes, each offering unique flavors and textures to diversify your culinary repertoire.
Leafy Greens
Benefits of growing leafy greens
Growing leafy greens in your garden not only yields bountiful harvests but also boasts an array of health benefits. Leafy greens are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, making them a crucial component of a balanced diet. Growing your own leafy greens allows you to enjoy fresh and flavorful produce while minimizing exposure to pesticides and other harmful chemicals. Moreover, leafy greens are often easy to grow and can be a fantastic option, even for those with limited garden space.
Leafy greens to consider planting
When it comes to leafy greens, there is an abundance of options to consider planting. Lettuce, available in various varieties, is a staple in many gardens and provides the foundation for countless salads. Spinach, known for its dark green leaves and versatility, can be enjoyed fresh in salads or cooked in various dishes. Kale, a nutritional powerhouse, offers an abundance of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as calcium and iron, making it a top choice for health-conscious gardeners. Swiss chard, collard greens, and mustard greens are other excellent options that can add a burst of flavor and nutrition to your meals.
Legumes
Benefits of growing legumes
Legumes, a category that includes beans, peas, and lentils, bring numerous advantages to your garden and diet. These plants possess the unique ability to fix nitrogen from the air and convert it into a usable form for plants. This nitrogen fixation improves soil fertility and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, ultimately promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Legumes also contribute to crop rotation, as their root systems break up compacted soil and serve as excellent preceding crops for nitrogen-demanding plants. Additionally, legumes offer a valuable source of plant-based protein, making them an excellent addition to a balanced and sustainable diet.
Legumes to consider planting
There are numerous legumes to consider planting in your garden, each offering distinct flavors and nutritional benefits. Common bean varieties, such as snap beans, kidney beans, and black beans, are versatile and can be used in various dishes. Peas, including snow peas and sugar snap peas, are renowned for their delicate flavors and tender textures. Lentils, available in various colors, pack a protein punch and can be incorporated into soups, stews, or salads. These legumes provide both culinary diversity and environmental benefits, making them an excellent choice for your garden.

Fruits
Benefits of growing fruits
Growing fruits in your garden not only provides a fresh and delicious harvest but also brings numerous benefits to your overall gardening experience. Fruits offer an array of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, contributing to a healthy and balanced diet. By cultivating your own fruits, you have control over the cultivation methods, reducing your exposure to harmful pesticides and ensuring the freshness and quality of the produce. Moreover, fruit trees and plants can enhance the aesthetics of your garden, providing beautiful blooms and foliage throughout the growing season.
Fruits to consider planting
When selecting fruits to plant in your garden, it’s important to consider your climate and available space. Some popular fruit options include apples, which come in a variety of flavors and can be stored for extended periods, and berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, which offer sweetness and vibrancy. Citrus fruits, like lemons, oranges, and grapefruits, thrive in warmer climates and add a touch of freshness to your garden. With proper care and maintenance, your fruit trees and plants can provide you with a bountiful harvest year after year.
Cover Crops
Benefits of cover crops
Cover crops, also referred to as green manure, offer various benefits in the realm of gardening and farming. When planted during periods of fallow or between cash crops, cover crops prevent soil erosion, reduce weed growth, and improve soil health. These crops act as protective covers, shielding the soil from wind, rain, and intense sunlight, thereby optimizing moisture retention. In addition to their protective capabilities, cover crops can add valuable organic matter to the soil upon incorporation, enhancing its fertility and structure.
Types of cover crops to consider
The selection of cover crops depends on several factors, including climate, soil type, and the specific goals of your rotation scheme. Leguminous cover crops, such as clovers or vetch, fix atmospheric nitrogen and increase soil fertility. Grass cover crops, such as ryegrass or oats, offer excellent erosion control and weed suppression. Brassica cover crops, like mustard or rapeseed, may suppress soil-borne pathogens and nematodes, contributing to pest and disease management. Ultimately, the choice of cover crops should align with your rotation objectives and the unique characteristics of your soil.
Flowers
Benefits of growing flowers
Integrating flowers into your garden not only enhances its visual appeal but also provides numerous benefits for the overall ecosystem. Flowers act as pollinator magnets, attracting bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects that aid in pollination, promoting fruit and seed production. The presence of flowers can also deter pests, as some varieties release natural compounds that repel harmful insects. Moreover, flowers contribute to biodiversity, fostering a welcoming environment for a wide range of wildlife, from birds to beneficial predatory insects.
Flowers to consider planting
When selecting flowers for your garden, it’s wise to choose varieties that are both visually appealing and beneficial to the surrounding ecosystem. Sunflowers are renowned for their vibrant blooms and their ability to attract pollinators, making them an excellent choice. Marigolds, with their bright colors and distinct scent, can repel pests and serve as a natural pest control option. Lavender, known for its soothing aroma, attracts pollinators and enhances the diversity of your garden. Other options to consider include cosmos, zinnias, and native wildflowers, each offering unique benefits and aesthetics to your outdoor space.
Green Manure Crops
What are green manure crops
Green manure crops, also known as cover crops, serve the dual purpose of improving soil fertility while providing ground cover. These crops are typically planted during fallow periods or as part of a rotation scheme, adding organic matter to the soil upon incorporation. By using green manure crops, you can enhance soil structure, increase nutrient availability, and promote overall soil health, contributing to the long-term sustainability of your garden or farm.
Benefits of green manure crops
Green manure crops offer an array of benefits for soil health and fertility. When incorporated into the soil, these crops break down, adding valuable organic matter that improves soil structure, aeration, and water-holding capacity. As the organic matter decomposes, it releases essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, making them readily available for subsequent crops. Green manure crops also suppress weed growth, preventing the establishment of unwanted plants and reducing the need for herbicides. By utilizing green manure crops, you can enhance the long-term productivity and sustainability of your agricultural system.
With careful planning and consideration, incorporating rotation crops, cool season vegetables, herbs, root vegetables, leafy greens, legumes, fruits, cover crops, flowers, and green manure crops into your garden or farm can yield a multitude of benefits. From improved soil fertility and structure to enhanced pest and disease management, these diverse crops offer a range of advantages. By diversifying your plantings and implementing a thoughtful rotation scheme, you can optimize the health and productivity of your garden or farm while enjoying a diverse and bountiful harvest.