Determining the right time to plant strawberries outdoors can be a crucial decision for any avid gardener. In order to ensure optimal growth and a bountiful harvest, it is vital to consider a variety of factors such as climate, soil temperature, and the specific variety of strawberries. By understanding these key elements, you can successfully navigate the delicate process of planting strawberries outside, ensuring a fruitful and satisfying gardening experience.

Factors to Consider
Climate
The climate in your region is a crucial factor to consider when determining the best time to plant strawberries. Strawberries thrive in temperate climates, with moderate temperatures that are neither too hot nor too cold. The ideal temperature range for strawberry growth is between 60 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit (15 to 27 degrees Celsius). Before planting, research the average temperatures and weather patterns in your area during the growing season to ensure that it aligns with the needs of strawberries.
Soil Temperature
Soil temperature plays a significant role in the success of strawberry plants. The soil should be consistently above 50 degrees Fahrenheit (10 degrees Celsius) for optimal root growth. If the soil temperature falls below this range, it can hinder the development of the plants. Use a soil thermometer to measure the temperature at a depth of about 4 inches (10 centimeters) before planting. This will help you determine whether the soil has reached the appropriate temperature for strawberry cultivation.
Frost Date
Another factor to consider is the average date of the last frost in your region. Strawberries are sensitive to frost, and planting them before the last frost can result in damage or even death of the plants. Research the frost date in your area and plan your planting accordingly. It is generally recommended to wait until after the last frost to ensure the safety of the plants. This will provide them with a better chance at establishing themselves before the arrival of cold temperatures.
Variety
Different strawberry varieties have different growth requirements and adaptability to various climates. Understanding the characteristics of different varieties can help you make an informed decision regarding the best variety for your region. Factors to consider when selecting a variety include the expected yield, taste, disease resistance, and the ability to tolerate your specific climate. Consult with local experts, such as agricultural extension offices or experienced growers, to determine the most suitable strawberry variety for your area.
Best Time to Plant
Spring Planting
Spring planting is the most common and recommended time to plant strawberries for most regions. It allows the plant to establish itself during the warm spring and summer months, which are ideal for growth. The exact timing of spring planting varies depending on climate and frost dates, but it generally occurs between March and May in the Northern Hemisphere. By planting in the spring, you give the strawberries ample time to develop a strong root system and prepare for fruit production.
Fall Planting
In certain regions with mild winters or specific climates, fall planting may be a viable option. Fall planting involves planting strawberries in late summer or early autumn, typically between August and September. The advantage of fall planting is that strawberry plants have time to establish themselves and develop a strong root system before winter sets in. However, avoid planting strawberries too late in the fall, as they need sufficient time to grow and acclimate to the new environment before the arrival of frost. Fall planting is generally not recommended in colder regions with harsh winters.

Preparing the Soil
Soil Testing
Before planting strawberries, it is crucial to assess the quality of your soil through soil testing. A soil test provides valuable information about the nutrient composition and pH level of the soil, enabling you to make necessary amendments for optimal growth. Contact your local agricultural extension office or a reputable soil testing laboratory to obtain a soil testing kit. Follow the instructions provided to collect a soil sample from your planting area and send it for analysis. The results will help you determine the specific nutrient deficiencies or imbalances in your soil, allowing you to address them before planting.
Amending the Soil
Based on the results of your soil test, you may need to amend the soil to create a suitable growing environment for strawberry plants. Common amendments include adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve soil structure and fertility. Adjusting the pH level may also be necessary, as strawberries prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. If the pH is too high or low, you can use agricultural lime or sulfur to bring it within the ideal range. By amending the soil before planting, you can provide the strawberries with the best possible growing conditions.
Planting Methods
Matted Row System
The matted row system is a popular planting method for strawberries that allows for efficient use of space and ease of maintenance. In this system, plants are spaced about 18 to 24 inches (45 to 61 centimeters) apart in rows, with multiple rows spaced approximately 3 to 4 feet (91 to 122 centimeters) apart. As the strawberry plants grow, they produce runners or stolons, which are long stems that form new daughter plants. These runners are allowed to root and develop into new plants, resulting in a dense matted row of strawberries. The matted row system facilitates easy access for weeding, watering, and harvesting.
Hill System
The hill system is another planting method commonly used for strawberries. In this system, plants are spaced about 12 to 18 inches (30 to 45 centimeters) apart in raised mounds or hills. The hills are typically 8 to 12 inches (20 to 30 centimeters) in height and 24 to 30 inches (61 to 76 centimeters) in width, created by adding soil or compost to the planting area. The benefit of the hill system is better airflow and drainage around the plants, reducing the risk of diseases. It also makes it easier to cover the plants with protective materials during inclement weather. However, the hill system requires more space compared to the matted row system.

Choosing Strawberry Plants
Bare Root Plants
Bare root plants are dormant strawberry plants that are usually sold without soil around their root systems. They are typically available for purchase during the spring planting season. Bare root plants are lightweight and easy to handle, making them a convenient option for planting. Before planting, soak the bare root plants in water for about 30 minutes to rehydrate the roots. Trim any damaged or excessively long roots and plant the strawberries at the recommended depth, ensuring that the crown is level with the soil surface. Bare root plants are an economical choice and have the potential to establish quickly and produce a good crop.
Potted Plants
Potted strawberry plants are sold in containers filled with soil or growing medium. They are available year-round and can be purchased from nurseries or garden centers. Potted plants are convenient because they are already established and ready for planting. When transplanting potted strawberry plants, carefully remove them from their containers, gently loosen the root ball if necessary, and plant them at the appropriate depth. Be cautious not to break or damage the roots during the transplanting process. Potted plants are an excellent option if you require instant results or if you missed the opportunity to plant bare root plants during the spring.
Runner Plants
Runner plants are the offspring of strawberry plants, produced through runners or stolons. They are small plants that develop along the runners and can be separated and replanted to establish new strawberry plants. Runner plants are an economical option as they can be obtained from existing strawberry plants or acquired from other gardeners. When using runner plants for propagation, allow them to root in pots or nursery beds until they grow sufficiently before transplanting them to their permanent location. This method requires patience, as runner plants take longer to establish and bear fruit compared to bare root or potted plants.
Planting Techniques
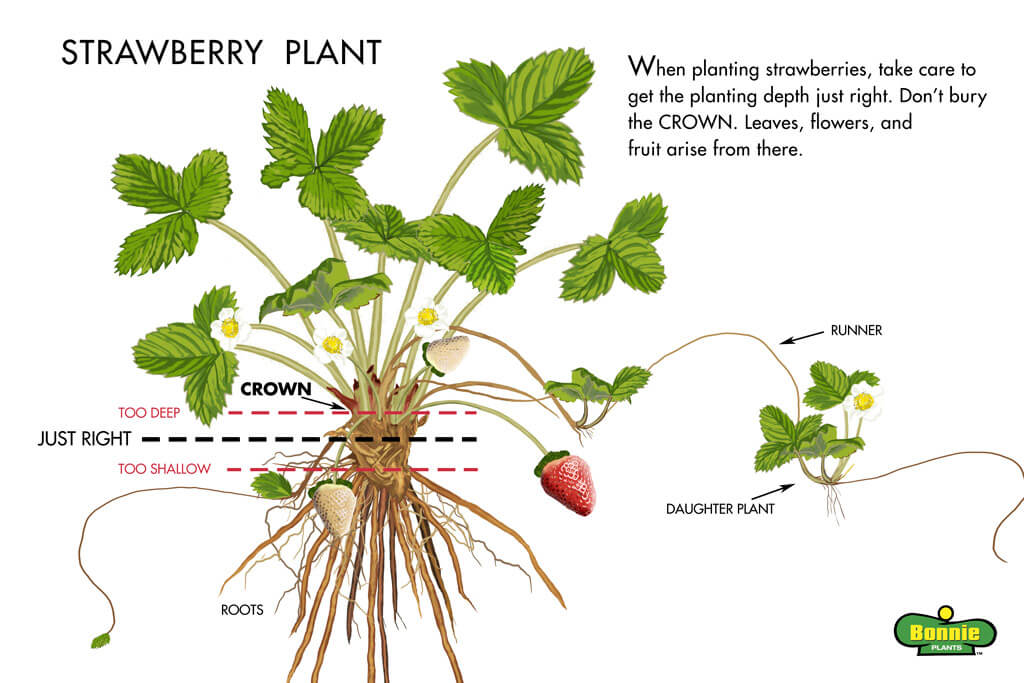
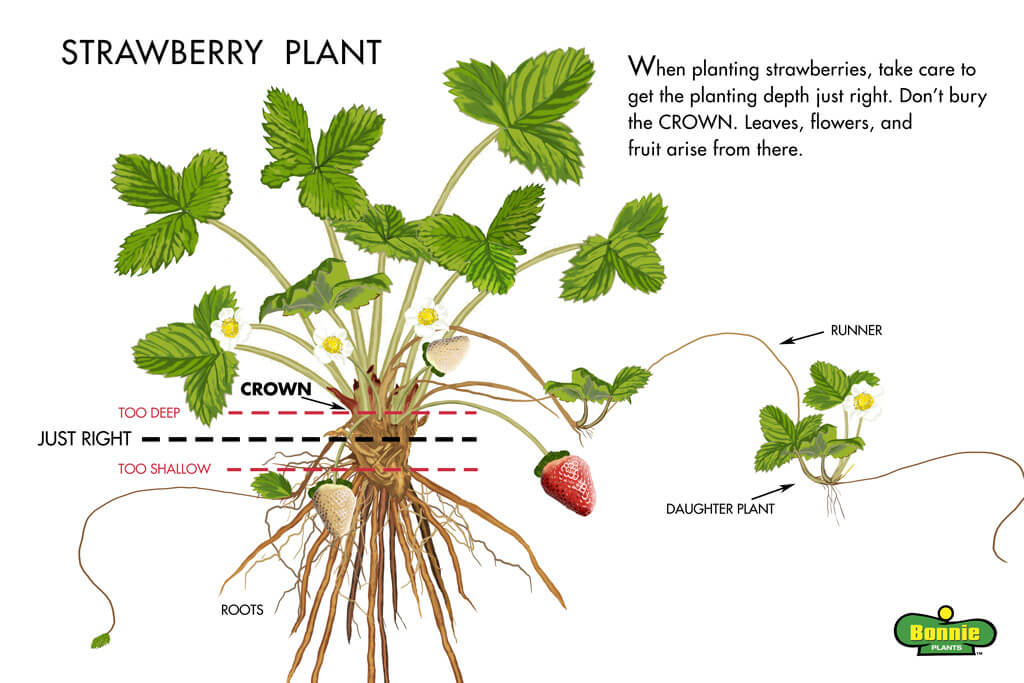
Planting Depth
Proper planting depth is essential for the successful establishment of strawberry plants. Planting too shallow or too deep can negatively impact the growth and performance of the plants. When planting bare root or potted strawberry plants, position them in the planting hole with the crown level or just above the soil surface. The crown is the junction where the roots meet the stem. Avoid burying the crown too deeply, as it may result in rotting or insufficient exposure to sunlight. Runner plants should also be planted at the same level as the original plant from which they were obtained.
Spacing
Strawberry plants require adequate spacing to ensure optimal growth and prevent overcrowding. Proper spacing allows good airflow, which reduces the risk of diseases and facilitates better sunlight exposure. When planting in the matted row system, strawberries should be spaced approximately 18 to 24 inches (45 to 61 centimeters) apart within the rows, with each row spaced 3 to 4 feet (91 to 122 centimeters) apart. In the hill system, plants are spaced about 12 to 18 inches (30 to 45 centimeters) apart within the hills. Follow the recommended spacing guidelines for your chosen planting method to maximize the productivity and health of your strawberry plants.
Watering
Proper watering is crucial during the early stages of strawberry growth to establish a strong root system. After planting, thoroughly water the strawberries to help settle the soil and eliminate air pockets around the roots. Subsequently, provide regular, deep waterings to keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Strawberries prefer consistent soil moisture, so monitor the moisture levels and adjust the watering frequency accordingly. However, be cautious not to overwater, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot and other issues. Mulching the soil around the plants can help retain moisture, reduce weed growth, and maintain more consistent soil moisture levels.

Maintenance and Care
Mulching
Mulching is a beneficial practice for strawberry plants as it offers numerous advantages. Applying a layer of mulch around the plants helps suppress weed growth, conserve soil moisture, regulate soil temperature, and prevent soil erosion. Organic mulches such as straw, pine needles, or wood chips are commonly used for strawberries. Apply the mulch after planting, once the soil has warmed and the plants have started to grow. Spread the mulch in a layer about 2 to 3 inches (5 to 7.5 centimeters) thick, making sure to keep it away from direct contact with the crowns of the plants.
Fertilizing
Regular fertilization is essential to provide the necessary nutrients for strawberry plants to grow and produce abundant fruit. Before planting, incorporate a balanced fertilizer or compost into the soil according to the recommendations from your soil test. Additionally, during the growing season, supplemental fertilization may be required to sustain the plants. Use a slow-release fertilizer or apply liquid fertilizer every 4 to 6 weeks, following the package instructions for dosage and frequency. Remember to water the plants after fertilizing to ensure proper nutrient absorption. Monitor the plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies or excesses and adjust the fertilization accordingly.
Weeding
Weed control is essential for the health and productivity of strawberry plants. Weeds compete with strawberries for nutrients, water, and sunlight, hindering their growth and fruit production. Regularly inspect the planting area and remove any weeds promptly to prevent them from establishing and spreading. Hand weeding is the preferred method for strawberries, as it minimizes the risk of damaging the shallow root system. Avoid using herbicides near strawberry plants, as they can harm the strawberries or contaminate the fruit. Mulching the soil with organic materials can also help suppress weed growth and reduce the need for frequent weeding.
Pest Control
Strawberries are susceptible to various pests, including aphids, slugs, snails, spider mites, and strawberry root weevils. Regular monitoring is essential to detect and identify any pest activity early on. Integrated pest management (IPM) practices are recommended for effective and environmentally friendly pest control. IPM includes techniques such as handpicking pests, applying organic insecticides or biological controls, and promoting beneficial insects as natural predators. Avoid using chemical pesticides, especially during the bloom period, as they can harm pollinators and contaminate the fruit. Timely intervention and proper pest management strategies are crucial to protect your strawberry plants and ensure a healthy harvest.
Harvesting and Storing
When to Harvest
Knowing when to harvest strawberries is crucial to ensure optimal flavor and quality. Strawberries should be harvested when they are fully ripe, with vibrant color and a sweet aroma. The exact timing of harvest depends on the variety and growing conditions. It is recommended to taste a few berries from different parts of the plant to assess their flavor and determine the ideal harvesting time. Gently pick the strawberries, taking care not to damage the fruit or the plants. Regular harvesting promotes continuous fruit production and prevents overripening or spoilage.
Storage Options
Strawberries are best enjoyed fresh, but if you have an excess harvest or want to extend the shelf life, there are several storage options available. If storing strawberries in the refrigerator, promptly remove any damaged or overripe berries to prevent the spread of mold. Place the strawberries in a shallow container lined with paper towels to absorb excess moisture. Alternatively, you can freeze strawberries for long-term storage. Wash and hull the berries, then spread them in a single layer on a baking sheet and freeze until firm. Transfer the frozen strawberries to airtight containers or freezer bags for storage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Neglecting Soil Preparation
Failure to properly prepare the soil before planting can lead to nutrient deficiencies, poor drainage, and overall suboptimal growing conditions for strawberries. Take the time to conduct a soil test and amend the soil based on the results. By addressing any soil deficiencies or imbalances, you provide the strawberry plants with the necessary nutrients and promote healthy growth.
Overcrowding Plants
Planting strawberries too close together can result in overcrowding, which restricts airflow and increases the risk of diseases. Follow the recommended spacing guidelines for your chosen planting method to allow each plant to receive adequate sunlight, airflow, and room for growth. Remember to consider the potential spread of runner plants when determining the spacing.
Improper Watering
Proper watering is crucial for establishing healthy strawberry plants, but overwatering or underwatering can harm their growth. Strive for consistent soil moisture by watering deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. Avoid overwatering, as excessive moisture can cause root rot and other issues. Monitor the soil moisture levels regularly and adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
Conclusion
By considering various factors such as climate, soil temperature, frost date, and variety, you can determine the best time to plant strawberries outside. Adequate soil preparation, planting methods, and spacing contribute to successful growth and yield. Careful selection of strawberry plants, planting techniques, and proper maintenance ensure healthy plants and ample fruit production. Harvest strawberries when fully ripe and consider storing options for any excess harvest. By avoiding common mistakes and following best practices, you can enjoy the fruits of your labor and savor the delectable taste of homegrown strawberries.