When considering the cultivation of strawberries in Zone 9, it is imperative to comprehend the appropriate timing and factors involved in the planting process. This article aims to guide you through the intricacies of planting strawberries in Zone 9, highlighting the crucial elements such as temperature, soil conditions, and the recommended planting months. By following these guidelines, you can maximize the success of your strawberry crop and ensure a bountiful harvest in this particular region.

Factors to Consider
When deciding to plant strawberries in Zone 9, there are several factors that need to be taken into consideration. These factors will greatly impact the success and yield of your strawberry plants. The three main factors to consider are climate, soil conditions, and planting season.
Climate
The climate of Zone 9 is characterized by hot summers and mild winters. This climatic condition is favorable for growing strawberries. However, it is important to note that strawberries prefer slightly cooler temperatures, especially during the fruiting season. Therefore, it is essential to choose the right strawberry varieties that are suitable for Zone 9 and can tolerate the heat.
Soil Conditions
Soil plays a vital role in the growth and development of strawberry plants. Before planting, it is crucial to assess the soil conditions in your garden or chosen growing area. Conducting a soil test is highly recommended to determine the pH level, nutrient content, and overall health of the soil. Strawberries prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.8. If the soil test reveals any deficiencies or imbalances, appropriate amendments should be made to optimize the soil conditions for strawberry growth.
Planting Season
Choosing the right planting season is another crucial factor in successfully growing strawberries in Zone 9. In this zone, the ideal time to plant strawberries is in early spring after the last frost. This allows the plants to establish themselves before the summer heat sets in. However, it is important to note that strawberries are sensitive to extreme temperatures. Therefore, careful attention should be given to the weather conditions during the planting season to ensure the survival and growth of the plants.
Preparing the Soil
Before planting strawberries, it is vital to prepare the soil to provide an optimal growing environment for the plants. This involves soil testing, amending the soil, and creating raised beds.
Soil Testing
Soil testing is a critical step in preparing the soil for strawberry planting. By conducting a soil test, you can determine the pH level, nutrient deficiencies, and other factors that could affect the growth of strawberries. This information will guide you in making necessary amendments to the soil to create conditions that are conducive to strawberry growth.
Amending the Soil
Based on the results of the soil test, it may be necessary to amend the soil to optimize its composition for strawberry cultivation. Adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure can improve soil structure, drainage, and nutrient availability. Additionally, adjusting the pH level using lime or sulfur can ensure that the soil is within the preferred range for strawberries.
Creating Raised Beds
In Zone 9, where the climate can be hot and dry, creating raised beds can be beneficial for strawberry cultivation. Raised beds provide improved drainage, better aeration, and increased control over soil quality. By constructing raised beds, you can ensure that the soil retains adequate moisture while allowing excess water to drain away. This helps to prevent waterlogging and root rot, which are common issues in humid environments.

Choosing Strawberry Varieties
Selecting the right strawberry varieties is crucial for successful cultivation in Zone 9. There are three main types of strawberry varieties to consider: day-neutral, June-bearing, and everbearing varieties.
Day-Neutral Varieties
Day-neutral strawberry varieties are known for their ability to produce fruit continuously throughout the growing season, regardless of day length. These varieties are often favored in Zone 9 due to their tolerance for warmer temperatures. They can produce a steady supply of strawberries from spring until fall, allowing for an extended harvest period.
June-Bearing Varieties
June-bearing varieties are the most common type of strawberry plants. As the name suggests, they typically produce a single large crop in early summer, usually during the month of June. These varieties require a longer period of chilling hours to initiate flowering, making them more suitable for cooler climates. However, some June-bearing varieties have been bred to tolerate warmer climates, making them viable options for Zone 9.
Everbearing Varieties
Everbearing strawberry varieties are a hybrid of the day-neutral and June-bearing types. They generally produce two to three harvests per year – one in spring, one in late summer, and possibly another in fall. These varieties are versatile and can adapt well to various climatic conditions, including Zone 9. Their ability to bear fruit at different times throughout the growing season provides flexibility and ensures a more continuous supply of strawberries.
Obtaining Strawberry Plants
Once you have determined the suitable strawberry varieties for Zone 9, the next step is to obtain the strawberry plants. There are three common methods of obtaining strawberry plants: purchasing plants, growing from seeds, and propagating through runners.
Purchasing Plants
Purchasing strawberry plants from reputable nurseries or garden centers is a popular option for obtaining healthy and well-established plants. When purchasing plants, it is essential to choose disease-free varieties that are specifically recommended for Zone 9. This ensures that the plants are adapted to the local climate and have a higher chance of success.
Growing from Seeds
Growing strawberries from seeds is another option, although it requires more time and patience. Seeds can be sown indoors several weeks before the expected planting date in Zone 9. However, it is important to note that not all strawberry varieties produce true-to-type plants from seeds. Therefore, it is recommended to choose heirloom or open-pollinated varieties if you decide to grow strawberries from seeds.
Propagating through Runners
Strawberries have a unique method of reproduction through runners. These runners are long stems that develop from the mother plant and produce new plantlets at their tips. This natural propagation method allows gardeners to obtain new strawberry plants for free. To propagate through runners, select healthy runners with well-formed plantlets and gently transplant them to new positions in the garden.
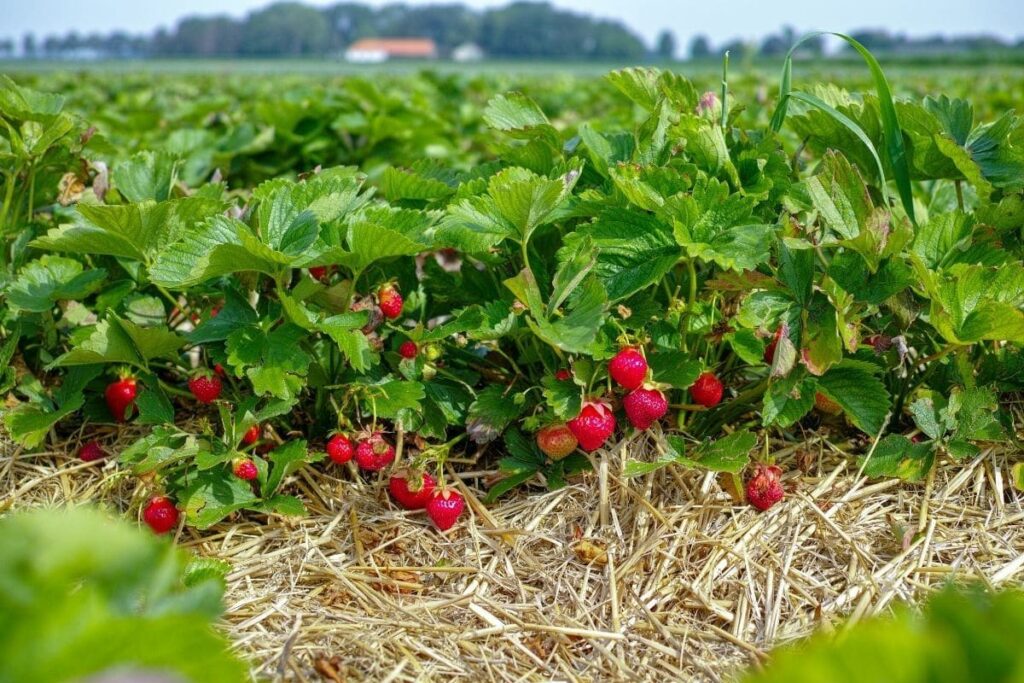
Planting Strawberries
Proper planting techniques are crucial for the establishment and growth of strawberry plants in Zone 9. Paying attention to site selection, spacing, and planting technique will greatly contribute to the success of your strawberry planting endeavors.
Site Selection
Choosing the right site for planting strawberries in Zone 9 is essential. Strawberries require a location that receives full sun for at least six hours a day. The site should also have well-drained soil to prevent waterlogging. Additionally, it is beneficial to select a location that offers protection from strong winds, as this can damage the delicate strawberry plants.
Spacing
Proper spacing between strawberry plants is important for ensuring healthy growth and optimal yield. In Zone 9, it is recommended to space your strawberry plants approximately 12 to 18 inches apart within the row, and maintain a distance of 2 to 3 feet between rows. Adequate spacing allows for proper air circulation, reduces the risk of disease, and provides sufficient room for the plants to spread as they grow.
Planting Technique
When planting strawberries in Zone 9, it is crucial to follow the correct planting technique. Start by preparing the soil by removing any weeds or grass. Next, dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the roots of the strawberry plant. Place the plant in the hole, ensuring that the crown (the point where the leaves emerge) is level with the soil surface. Gently fill the hole with soil, firming it around the roots. Water the newly planted strawberries thoroughly to settle the soil.
Caring for Strawberry Plants
Once your strawberry plants are properly planted, ongoing care is essential for their health and productivity. There are several key aspects to consider when caring for strawberry plants in Zone 9, including watering, mulching, fertilizing, weed control, and pest and disease management.
Watering
Proper watering is crucial for strawberry plants to thrive in Zone 9. While strawberries require consistent moisture, they are also susceptible to root rot if overwatered. Therefore, it is important to strike a balance and ensure that the plants receive adequate hydration without waterlogging their roots. Water deeply and thoroughly, focusing on the root zone, and avoid wetting the leaves to prevent fungal diseases.
Mulching
Mulching is highly beneficial for strawberries in Zone 9, providing several advantages. Mulch helps to conserve soil moisture, regulate soil temperature, suppress weed growth, and prevent soil erosion. Organic mulches such as straw or pine needles are commonly used for strawberries. Apply a layer of mulch around the plants, leaving a small space around the crown to promote air circulation and prevent crown rot.
Fertilizing
To promote healthy growth and fruit production, strawberry plants require proper fertilization. It is recommended to apply a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for strawberries in early spring, after the plants have started to grow. Additionally, a second application of fertilizer may be beneficial in late summer to provide the necessary nutrients for the plants to develop strong roots and flower buds. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and frequency.
Weed Control
Weed control is essential to prevent competition for resources and to maintain the overall health of strawberry plants. Before planting, remove any existing weeds or grass from the planting area. Once the plants are established, it is important to regularly inspect and remove weeds that may emerge. Avoid using chemical herbicides near strawberry plants, as they can harm the delicate roots and foliage. Instead, use a combination of hand-pulling, cultivating, or applying mulch to suppress weed growth.
Pest and Disease Management
Strawberry plants are susceptible to various pests and diseases, which can significantly impact their health and productivity. In Zone 9, common pests that affect strawberries include slugs, snails, aphids, and spider mites. Regular inspection and early detection are key to managing these pests. Implementing cultural practices such as removing weed hosts, maintaining clean garden areas, and practicing proper sanitation can help reduce pest populations. Additionally, organic pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or using insecticidal soaps, can be employed when necessary. As for diseases, common ones in Zone 9 include fungal infections like gray mold (Botrytis cinerea) and powdery mildew (Sphaerotheca macularis). Proper air circulation, adequate spacing, and regular removal of infected plant parts can help prevent and manage these diseases. Fungicidal sprays may also be used as a last resort if necessary, following the instructions on the product label.

Harvesting and Storing Strawberries
The moment you have been waiting for has finally arrived – the time to harvest your strawberries! Proper harvesting techniques and storage methods are crucial to ensure the highest quality and flavor of your freshly picked berries.
Determining Ripeness
Strawberries are ready to be harvested when they have fully ripened. The color of the strawberries should be uniformly red, indicating that they are fully matured and sweet. Avoid picking strawberries that are still partially green, as they will not ripen further after being picked.
Picking Techniques
To harvest strawberries, delicately hold the stem just above the berry and gently twist it off with your fingers. Avoid pulling or yanking the berry, as this can damage the plant and the fruit. If you prefer to use scissors or pruning shears for harvesting, make sure to sterilize them beforehand to prevent the spread of diseases.
Storage Tips
To maximize the shelf life of your harvested strawberries, it is important to handle them with care and store them properly. After harvesting, immediately place the strawberries in a cool location away from direct sunlight. Avoid washing the berries until just before consumption to prevent premature spoilage. If storing the strawberries in the refrigerator, place them in a breathable container or paper bag to maintain freshness. Consume the strawberries within a few days to enjoy their full flavor and sweetness.
Renovating Strawberry Beds
Over time, strawberry plants can become less productive and develop overcrowded beds. Renovating the strawberry beds is necessary to maintain the health and vigor of the plants. Renovation typically involves pruning and thinning the plants to promote new growth and improve overall productivity.
Renovation Timing
The ideal time to renovate strawberry beds in Zone 9 is immediately after the last harvest, typically in late summer or early fall. This allows the plants to recover and establish new runners before the arrival of cooler temperatures.
Pruning and Thinning
During renovation, it is important to remove any old or nonproductive strawberry plants. Cut back the foliage to a height of about 1 inch above the crown using sharp and clean pruning shears. This stimulates new growth and prevents the accumulation of pests and diseases. Additionally, thin the strawberry bed by removing excess runners and daughter plants. This helps to create adequate spacing and allows the remaining plants to receive sufficient nutrients and sunlight.
Renovation Techniques
After pruning and thinning, it is beneficial to further enhance the soil quality by incorporating organic matter into the bed. This can be done by top-dressing the bed with compost or well-rotted manure. Apply a layer of mulch to conserve moisture and suppress weed growth. Finally, irrigate the renovated strawberry bed thoroughly to ensure proper hydration of the plants and the newly amended soil.
In conclusion, growing strawberries in Zone 9 comes with unique considerations, including climate, soil conditions, and planting season. By carefully preparing the soil, choosing suitable strawberry varieties, obtaining healthy plants, and implementing proper planting techniques, you can establish a successful strawberry garden. Caring for the plants through regular watering, mulching, fertilizing, weed control, and pest and disease management is crucial for their longevity and productivity. Harvesting the strawberries at the right stage of ripeness and storing them properly ensures the enjoyment of fresh and delicious berries. Lastly, renovating strawberry beds when necessary maintains the health of the plants and promotes ongoing productivity. With a combination of knowledge and proper care, you can successfully grow and enjoy the luscious fruits of your strawberry plants in Zone 9.




