Potato plants, a staple crop worldwide, rely on an optimal nutrient mix to thrive. In the pursuit of sustainable and eco-friendly gardening practices, gardeners have often wondered if eggshells, discarded treasures from the kitchen, can play a role in supporting potato growth. This article investigates whether eggshells hold potential as a natural fertilizing agent for potato plants and explores the scientific evidence behind this age-old gardening practice. By understanding the potential benefits of incorporating eggshells into potato cultivation, gardeners can make informed decisions to maximize their plants’ health and productivity.

Benefits of Using Eggshells for Potato Plants
1. Nutrient-Rich Soil Amendment
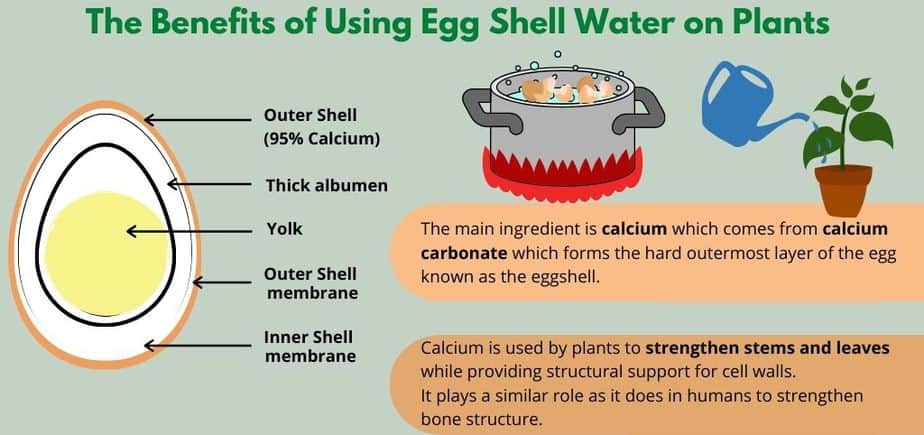
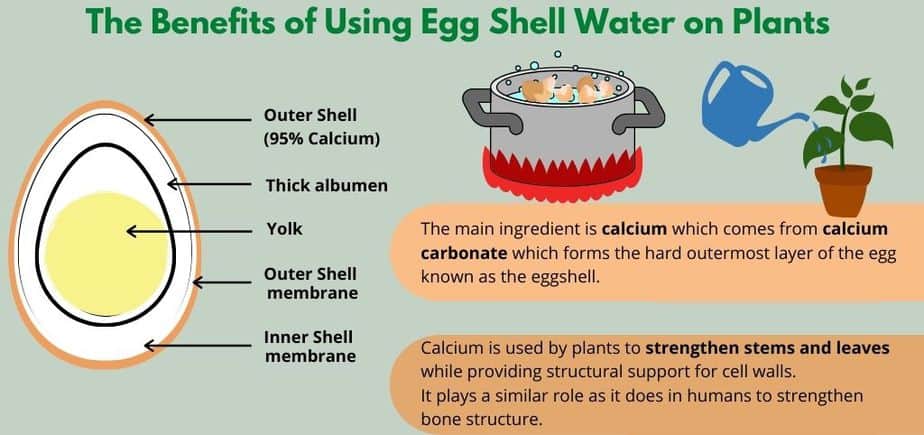
Eggshells are an excellent source of nutrients for potato plants. They contain essential elements such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, all of which are vital for healthy plant growth. When eggshells are crushed and incorporated into the soil, they release these nutrients gradually, providing a steady supply to the potato plants throughout their growth cycle. This nutrient-rich soil amendment can improve overall plant health, leading to increased yields.
2. Calcium Source
Calcium is an essential nutrient for potato plants, as it plays a crucial role in cell wall formation and overall plant structure. Eggshells are particularly beneficial as a calcium source because they contain a high concentration of this nutrient. By incorporating crushed eggshells into the soil, potato plants can absorb the calcium they need to develop strong roots, stems, and tubers. Adequate calcium levels can also reduce the risk of common disorders such as blossom end rot.
3. pH Regulation
Maintaining the optimal soil pH is crucial for the successful cultivation of potato plants. Eggshells can help regulate the pH levels of acidic soil. When eggshells decompose, they release calcium carbonate, a natural alkaline compound. This helps to neutralize the acidity in the soil and create a more favorable pH environment for potato plants. By using eggshells as a soil amendment, you can ensure that your potato plants have the ideal pH range for nutrient absorption and overall growth.
4. Pest Deterrent
Potato plants are susceptible to various pests, including slugs, snails, and cutworms. The sharp edges of crushed eggshells can act as a deterrent to these pests. When sprinkled around the base of potato plants, the jagged texture of the eggshells can discourage crawling insects from approaching and damaging the plants. This natural pest control method can help reduce the need for chemical pesticides and protect your potato plants from potential infestations.
5. Soil Structure Improvement
The physical structure of the soil plays a significant role in the growth and development of potato plants. Eggshells can contribute to improving soil structure by increasing its porosity and drainage capabilities. When incorporated into the soil, the granular texture of crushed eggshells helps to break up compacted soil, allowing for better root penetration and water movement. By improving soil structure, eggshells support healthy root development and overall plant vigor.
How to Prepare Eggshells for Potato Plants
1. Gather Eggshells
To prepare eggshells for potato plants, start by collecting eggshells from organic eggs. It is essential to use organic eggs to avoid any pesticide residues that may be present on the shells. Collect enough eggshells to provide an adequate amount of calcium and other nutrients for your potato plants.
2. Clean and Dry the Eggshells
Once you have gathered the eggshells, rinse them thoroughly under running water to remove any residue or dirt. It is important to ensure that the eggshells are clean before using them as a soil amendment. After rinsing, allow the eggshells to dry completely. You can air dry them or place them in a warm oven for a few minutes until they are dry and brittle.
3. Crush the Eggshells
To facilitate the gradual release of nutrients, crush the dried eggshells into small pieces. You can use a mortar and pestle or a food processor to break the eggshells into granules. Aim for small and uniform pieces to ensure easy incorporation into the soil.
4. Incorporate Crushed Eggshells into the Soil
Once the eggshells are crushed, sprinkle them evenly over the soil surface around the potato plants. Gently work the crushed eggshells into the top few inches of soil using a garden fork or a hand rake. Take care not to damage the plant roots during this process. Ideally, the crushed eggshells should be mixed thoroughly with the soil to ensure their nutrients are evenly distributed and readily available to the potato plants.

Tips for Using Eggshells Effectively
1. Use Organic Eggs
When collecting eggshells for potato plants, it is crucial to choose organic eggs. Organic eggs come from hens that are not treated with antibiotics or hormones and are fed an organic diet. This ensures that the eggshells are free from any harmful residues that could affect the health of your potato plants.
2. Crush the Eggshells into Small Pieces
To maximize the benefits of eggshells, it is important to crush them into small pieces. Smaller pieces decompose faster, allowing for a more gradual release of nutrients. Additionally, smaller particles are easier to incorporate into the soil, ensuring that the nutrients are evenly distributed.
3. Time the Application
Timing the application of crushed eggshells is essential for optimal results. It is best to incorporate the eggshells into the soil before planting the potato tubers. This allows the nutrients to be readily available to the developing plants from the beginning of their growth. However, if you didn’t apply the eggshells before planting, you can still incorporate them into the soil around the base of the plants during early growth stages.
4. Avoid Overapplication
While eggshells provide valuable nutrients, it is important not to overapply them. Excessive amounts of eggshells can contribute to an imbalance in the soil pH or cause nutrient deficiencies. Follow the recommended application rates and adjust accordingly based on soil test results. It is always best to err on the side of caution and start with a smaller amount, gradually increasing if necessary.
Studies and Research on Eggshells for Potato Plants
1. Study 1: Effects of Eggshell Powder on Potato Yield
In a study conducted by researchers at a renowned agricultural university, the effects of eggshell powder on potato yield were evaluated. The study found that the addition of eggshell powder to the soil significantly increased potato yields compared to the control group. The researchers attributed this yield increase to the calcium content in the eggshells, which positively influenced tuber development and overall plant health.
2. Study 2: Influence of Eggshell Incorporation on Soil pH Levels
Another study examined the impact of eggshell incorporation on soil pH levels. Researchers conducted soil analysis before and after the addition of crushed eggshells to potato plots. The results showed a significant increase in soil pH, indicating that eggshells effectively neutralized the soil acidity. The study concluded that eggshells can be used as a natural and cost-effective method to regulate soil pH for optimal potato growth.
3. Study 3: Comparison of Potato Growth with and without Eggshells
A comparative study was conducted to assess the growth and development of potato plants with and without eggshell incorporation. The researchers measured various growth parameters, including plant height, stem diameter, and tuber weight. The study revealed that the potato plants grown with eggshells had significantly greater growth and higher tuber yields compared to those grown without eggshells. This finding further supports the benefits of using eggshells as a soil amendment for potato plants.

Alternative Uses for Eggshells
1. Compost Material
Eggshells can be an excellent addition to a compost pile. Their calcium-rich composition helps balance the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in the compost, promoting decomposition and nutrient availability. Crushed eggshells also help to deter pests in the compost, such as slugs and snails. Simply crush the eggshells and mix them with other organic materials in the compost bin.
2. Pest Control in the Garden
In addition to deterring pests around potato plants, crushed eggshells can be used as a general pest control measure in the garden. Spread crushed eggshells around the base of plants susceptible to snail and slug damage, such as hostas or lettuce. The rough texture of the eggshells acts as a barrier, preventing these pests from reaching the plants.
3. Calcium Supplement for Animals
Eggshells can also serve as a calcium supplement for animals. Crushed eggshells can be added to the diet of birds, chickens, or reptiles to provide the necessary calcium for eggshell formation and bone health. Ensure that the eggshells are cleaned, dried, and crushed into small pieces before offering them to the animals.
Other Soil Amendments for Potato Plants
1. Compost
Compost is an excellent soil amendment for potato plants, as it enriches the soil with organic matter and essential nutrients. It improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and promotes overall soil health. Incorporate well-decomposed compost into the soil before planting or as a top dressing during the growing season.
2. Bone Meal
Bone meal is a natural source of phosphorus and calcium, both of which are essential for healthy potato growth. It promotes root development, flower and fruit production, and overall plant vigor. Mix bone meal into the soil at planting time or apply as a side dressing during the growing season.
3. Wood Ash
Wood ash is a rich source of potassium, which is vital for root and tuber development in potato plants. It also contains trace elements that contribute to plant health. However, wood ash should be used with caution, as excessive amounts can raise soil pH to alkaline levels. Apply wood ash sparingly, ensuring that the soil pH remains within the ideal range for potato cultivation.
4. Seaweed Extract
Seaweed extract is a natural soil amendment that provides essential nutrients and stimulates root growth in potato plants. It contains a wide range of micronutrients, including iron, manganese, and zinc. Seaweed extract can be applied as a foliar spray or incorporated into the soil during planting.
Common Potato Plant Problems
1. Potato Scab
Potato scab is a common disease that affects potato tubers, causing rough, corky lesions on their surface. It is primarily caused by certain species of soil-borne bacteria. To prevent potato scab, ensure that the soil is well-drained and avoid planting potatoes in acidic soil. Proper crop rotation can also help reduce the incidence of scab.
2. Late Blight
Late blight is a devastating disease caused by a fungus called Phytophthora infestans. It affects leaves, stems, and tubers, leading to rapid plant decay. To prevent late blight, plant disease-resistant potato varieties, provide adequate spacing between plants for good airflow, and practice proper irrigation techniques. Fungicides may also be necessary in severe cases.
3. Aphid Infestation
Aphids are small, sap-sucking insects that can cause significant damage to potato plants. They feed on the plant’s sap, weakening it and potentially transmitting viruses. To control aphid infestations, monitor plants regularly and remove any colonies by hand. Introducing beneficial insects such as ladybugs or using insecticidal soaps can also help manage aphid populations.
4. Nitrogen Deficiency
Nitrogen deficiency in potato plants is characterized by slow growth, stunted plants, and pale green or yellow leaves. It is a common problem in nitrogen-poor soils or when excessive rainfall leaches nitrogen from the soil. To address nitrogen deficiency, apply a balanced fertilizer with nitrogen, such as compost or well-decomposed manure. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of tuber development.
Preventive Measures for Healthy Potato Plants
1. Crop Rotation
To prevent the buildup of diseases and pests, practice crop rotation in your potato garden. Avoid planting potatoes or other members of the nightshade family, such as tomatoes or peppers, in the same spot for consecutive years. Rotate with unrelated crops to disrupt the life cycles of common potato pests and diseases.
2. Proper Irrigation
Proper irrigation is crucial for potato plants. They require consistent moisture throughout the growing season, but excessive water can lead to disease development or nutrient leaching. Water the plants deeply, ensuring that the soil is moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around the plants can help conserve soil moisture and reduce evaporation.
3. Hilling Soil
Hilling soil is a traditional practice in potato cultivation that involves mounding soil around the base of the growing plants. This technique promotes good tuber formation, prevents greening of the potatoes, and protects tubers from sunlight exposure. Hill the soil gradually as the plants grow, ensuring that only the top few leaves are exposed above the soil surface.
4. Timely Harvesting
Potatoes should be harvested at the right time to ensure optimal tuber quality and reduce the risk of storage diseases. Harvesting too early can result in small, immature tubers, while leaving them in the ground for too long can lead to over-maturity, which affects storage life. Follow the recommendations for the specific potato variety you are growing and harvest when the foliage begins to yellow and die back.

Conclusion
In conclusion, incorporating eggshells into your potato garden can offer numerous benefits for the plants. Eggshells provide essential nutrients, particularly calcium, that support healthy plant growth and development. They can regulate soil pH, deter pests, and improve soil structure. By following the proper techniques for preparing and applying eggshells, you can maximize their effectiveness as a soil amendment. Additionally, alternative uses for eggshells, such as composting or pest control, provide additional value. Consider using other soil amendments and implementing preventive measures to ensure healthy, productive potato plants. With proper care and attention, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious potatoes from your garden.