So, you’ve got a green thumb and you’re itching to grow your own lettuce in the Lone Star State, huh? Well, look no further than this article for all the information you need on the best time to plant lettuce in Texas. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a newbie, timing is key when it comes to successful lettuce cultivation. With the ever-changing climate in Texas, knowing the ideal planting window can make all the difference in enjoying a bountiful harvest or watching your lettuce wilt away. So, grab your gardening gloves and let’s dig in!
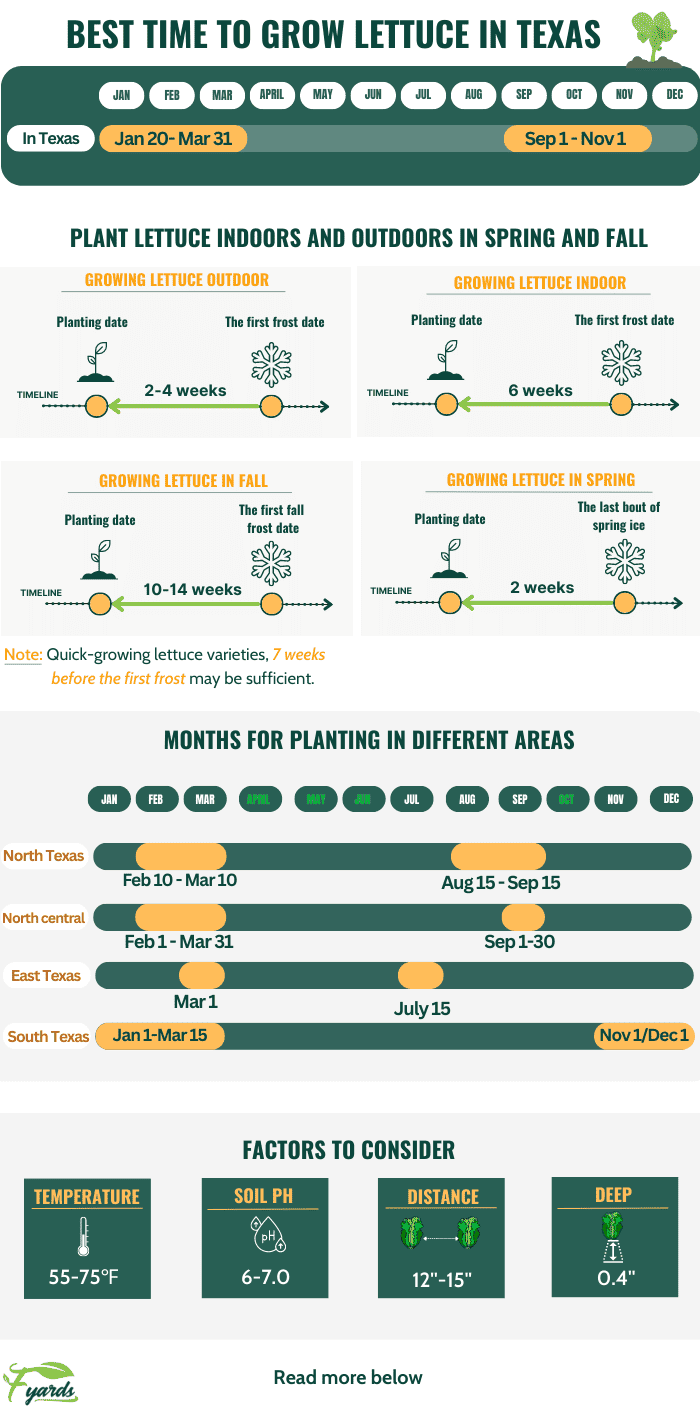
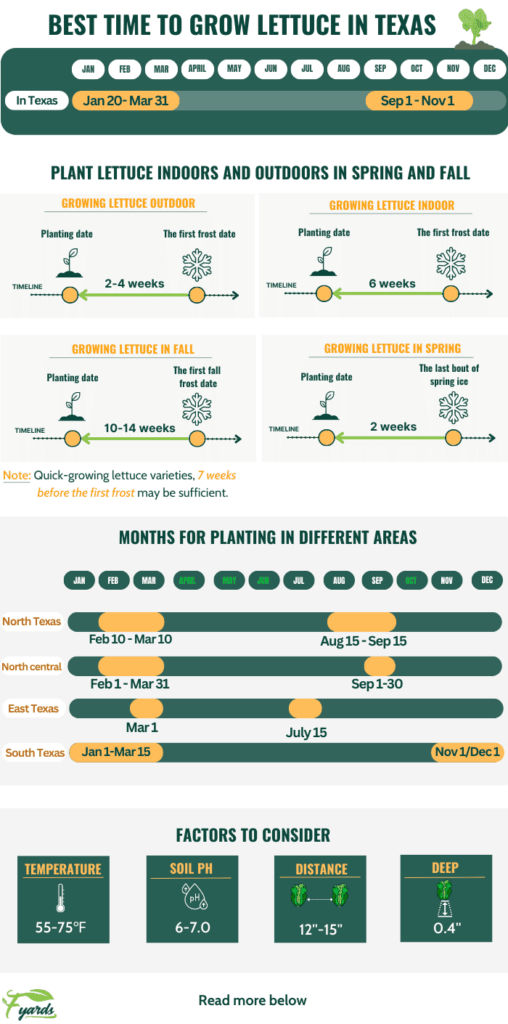
Best Time to Plant Lettuce in Texas
If you’re a lettuce lover and you live in Texas, you may be wondering when the best time to plant lettuce is in this sunny state. Factors such as climate and temperature, soil conditions, types of lettuce, preparing the garden bed, planting methods, watering and irrigation, and pest control all play a role in determining the ideal time to sow lettuce seeds or transplant seedlings. Let’s dive into each factor and explore the best practices for growing lettuce in Texas!
1. Climate and Temperature
Texas is known for its hot and dry climate, which can make it challenging to grow lettuce successfully. Lettuce thrives in cooler temperatures, ideally between 45°F and 75°F. When the temperature rises above 80°F, lettuce plants tend to bolt, meaning they send up flower stalks and prioritize seed production over leaf growth. To avoid this, it’s best to plant lettuce in Texas during the cooler seasons.
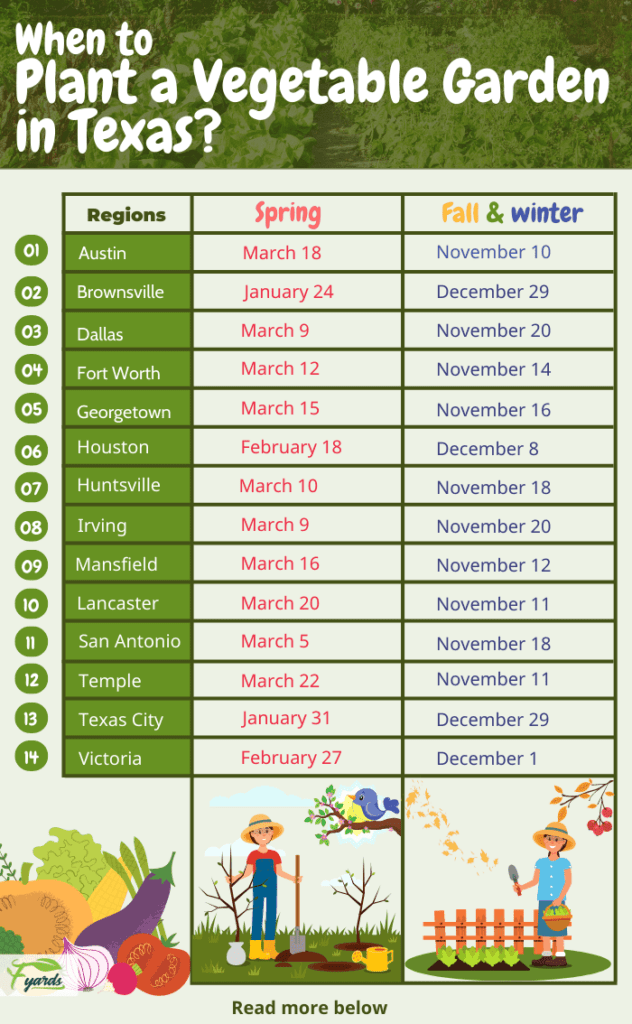
In Central and North Texas, planting lettuce in late winter or early spring is recommended. The average last frost date in these regions is typically around mid-March, signaling the beginning of the optimal planting period. In South Texas, where the climate is milder, you can push the planting window a bit further into spring, or even consider fall planting when temperatures cool down again.
2. Soil Conditions
Lettuce prefers loose, well-draining soil with a slightly acidic pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Before planting lettuce, it’s important to prepare the soil properly to ensure optimal growth. Begin by removing any weeds or debris from the area where you plan to plant. This will give your lettuce plants the best chance of thriving without competition for resources.
Next, amend the soil to improve its texture and fertility. Adding organic matter such as compost or well-decomposed manure can significantly enhance the soil’s structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient content. Work the organic matter into the top few inches of soil to create a nutrient-rich bed for your lettuce plants.

Types of Lettuce to Plant
There are several popular lettuce varieties that can be grown in Texas, including leaf lettuce, romaine lettuce, and bibb lettuce. Each type has its own unique characteristics and growth requirements, so let’s take a closer look at each one:
1. Leaf Lettuce
Leaf lettuce is perhaps the most versatile and easiest type of lettuce to grow in Texas. It comes in a variety of colors and shapes, ranging from green to red and from frilly to smooth. Leaf lettuce can be sown throughout the growing season, allowing for a continuous harvest. This makes it a great choice for those who enjoy fresh salads year-round.
2. Romaine Lettuce
Romaine lettuce is known for its elongated leaves and crisp texture. It’s a popular choice for Caesar salads and other gourmet dishes. Romaine lettuce prefers cooler temperatures, so it’s best to plant it in early spring or fall in Texas. Keep in mind that it takes longer to mature compared to leaf lettuce, so plan accordingly.
3. Bibb Lettuce
Bibb lettuce, also known as butterhead lettuce, has tender leaves and a sweet flavor. It forms loose heads that resemble cabbages. Bibb lettuce prefers cooler temperatures, making it suitable for planting in early spring or fall in Texas. With its delicate texture and mild taste, it’s a favorite among salad enthusiasts.
Preparing the Garden Bed
Now that you’ve determined the best time to plant lettuce and chosen the appropriate lettuce variety for your Texas garden, it’s time to prepare the garden bed. Follow these steps to create an ideal growing environment for your lettuce:
1. Clearing the Area
Begin by clearing the area where you plan to plant lettuce. Remove any weeds, rocks, or debris that may interfere with the growth of your lettuce plants. Keeping the bed weed-free will reduce competition for nutrients and moisture.
2. Soil Preparation
Next, it’s time to prepare the soil. Loosen the top few inches of soil using a garden fork or a tiller. This will help create an aerated and well-draining bed for your lettuce plants. Once the soil is loosened, spread a layer of organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, on top of the bed. Work the organic matter into the soil using a rake or a garden fork.
3. Fertilizer Application
Lettuce plants have moderate fertility needs, so applying balanced organic or slow-release fertilizer before planting can provide a nutrient boost. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to determine the appropriate amount of fertilizer for your garden bed. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive leaf growth or nutrient imbalances.
Planting Lettuce
Now that your garden bed is ready, it’s time to start planting lettuce. There are three common methods for planting lettuce in Texas: direct seeding, transplanting, and using starter plants. Let’s explore each one:
1. Direct Seeding
Direct seeding involves sowing lettuce seeds directly into the garden bed. This method works well for leaf lettuce varieties that have a relatively short maturation time. Follow the seed packet instructions for spacing and depth, as this can vary depending on the lettuce variety.
2. Transplanting
Transplanting lettuce seedlings allows for quicker harvests and greater control over spacing. Start by sowing lettuce seeds indoors in cell trays or small pots about four to six weeks before the intended transplant date. Once the seedlings have developed a strong root system and their true leaves have emerged, they can be transplanted into the garden bed.
3. Spacing and Depth
Proper spacing is crucial for the healthy growth of lettuce plants. Consult the seed packet or nursery label for specific spacing guidelines, as different lettuce varieties have different requirements. Generally, leaf lettuce plants should be spaced about 6 to 12 inches apart, while romaine and bibb lettuce plants require around 12 to 18 inches of space.
When it comes to planting depth, lettuce seeds should be sown approximately 1/4 to 1/2 inch deep. Once planted, gently water the soil to ensure good seed-to-soil contact and promote germination.
Watering and Irrigation
Water is essential for lettuce growth, as it helps transport nutrients and keeps the plants hydrated. Lettuce plants prefer consistently moist soil but should never be waterlogged. Here are some important considerations for watering and irrigation:
1. Water Requirements
During the early stages of growth, lettuce plants have shallow root systems and require frequent, light waterings. As the plants mature, you can gradually reduce the frequency but increase the depth of watering. Aim to provide around 1 inch of water per week, either through rainfall or irrigation.
2. Irrigation Methods
Drip irrigation or soaker hoses are ideal for watering lettuce, as they deliver water directly to the soil without wetting the plant’s foliage excessively. Avoid overhead watering, as this can increase the risk of fungal diseases. Watering in the morning allows leaves to dry off during the day, reducing the chances of fungal infections.

Controlling Pests and Diseases
Just like any other crop, lettuce is susceptible to pests and diseases. By taking preventive measures and practicing good garden hygiene, you can minimize the risk of infestations and keep your lettuce plants healthy. Here are some common pests and preventative measures to consider:
1. Common Lettuce Pests
- Aphids: These small, sap-sucking insects can distort lettuce leaves and transmit viral diseases. Remove them manually or use organic insecticidal soap to control infestations.
- Slugs and Snails: These slimy pests can munch on lettuce leaves, leaving behind holes and slime trails. Use organic slug and snail baits or create barriers, such as copper tape, to protect your lettuce plants.
- Cabbage Worms: These green caterpillars love to feast on lettuce foliage. Hand-pick them off the plants or use organic caterpillar controls to keep them in check.
2. Preventative Measures
To prevent infestations, practice crop rotation by avoiding planting lettuce in the same location year after year. This reduces the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil. Additionally, remove any infested plant debris and weeds promptly to eliminate potential hiding spots for pests. Applying organic pest control methods, such as neem oil or companion planting with pest-repellent herbs like basil, can also help protect your lettuce plants.
Harvesting Lettuce
The joy of growing lettuce comes to fruition when it’s time to harvest your homegrown leaves or heads. Here’s what you need to know about the harvesting process:
1. Harvesting Time
Leaf lettuce can be harvested at any stage of growth, even when the leaves are small and tender. To harvest individual leaves, simply snip them off with scissors, leaving the plant’s center intact for continued growth. Alternatively, you can wait for the entire plant to reach maturity and harvest the entire head.
Romaine and bibb lettuce varieties are typically harvested when the heads reach full size and feel firm. Look for outer leaves that have begun to overlap or curl inward as indicators of maturity.
2. Picking Leaves vs. Cutting the Head
When harvesting leaf lettuce, it’s best to pick the outer leaves first, allowing the inner leaves to continue growing. This ensures a continuous supply of fresh leaves throughout the growing season. With romaine and bibb lettuce, you have the option to either harvest the entire head by cutting it at the base or pick individual leaves as needed.
3. Storage and Shelf-Life
Freshly harvested lettuce can be used immediately or stored in the refrigerator for future use. To extend the shelf life, wrap the leaves or heads loosely in a damp paper towel and place them in a plastic bag. Proper storage can help maintain their crispness and flavor for up to a week.
Now that you’re armed with the knowledge of the best time to plant lettuce in Texas, as well as the factors to consider, you’re ready to embark on your lettuce-growing journey. With attention to climate and temperature, soil conditions, proper garden bed preparation, planting methods, watering and irrigation, and pest control, you’ll be enjoying a bountiful harvest of fresh and delicious lettuce right from your own backyard. Happy gardening!