In the realm of botany, the process of pollination stands as an essential mechanism for plant reproduction. As curious minds seek answers to the mysteries of zucchini cultivation, a common query arises: do zucchini need to be pollinated? In this intellectual exploration, we shall uncover the intricate relationship between zucchini and pollination, shedding light on the vital role that this process plays in the growth and development of these versatile vegetables.

What is Pollination?
Definition of Pollination
Pollination is a crucial reproductive process in flowering plants, including zucchini (Cucurbita pepo). It involves the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organ (anther) to the female reproductive organ (stigma) of a flower. This transfer can occur within the same flower (self-pollination) or between different flowers (cross-pollination).
Types of Pollination
In the context of zucchini, both self-pollination and cross-pollination can occur. Self-pollination happens when the pollen from the anther is transferred to the stigma of the same flower. Cross-pollination, on the other hand, occurs when the pollen is transferred to the stigma of a different flower on the same or another plant.
Importance of Pollination
Pollination is vital for the reproduction and survival of many plant species, including zucchini. It is the process that leads to the formation of seeds, which are crucial for the next generation of plants. Additionally, pollination plays a significant role in increasing the genetic diversity of plant populations, promoting adaptation to changing environments, and ensuring the production of fruits and vegetables that we rely on for food.
Understanding Zucchini
Introduction to Zucchini
Zucchini, also known as courgette, is a popular summer squash that belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family. It is widely cultivated and consumed worldwide due to its mild flavor, versatility in culinary applications, and nutritional value. Zucchini plants are annuals that develop sprawling vines, producing an abundance of cylindrical-shaped fruits with green skin and tender flesh.
Growth and Reproduction of Zucchini
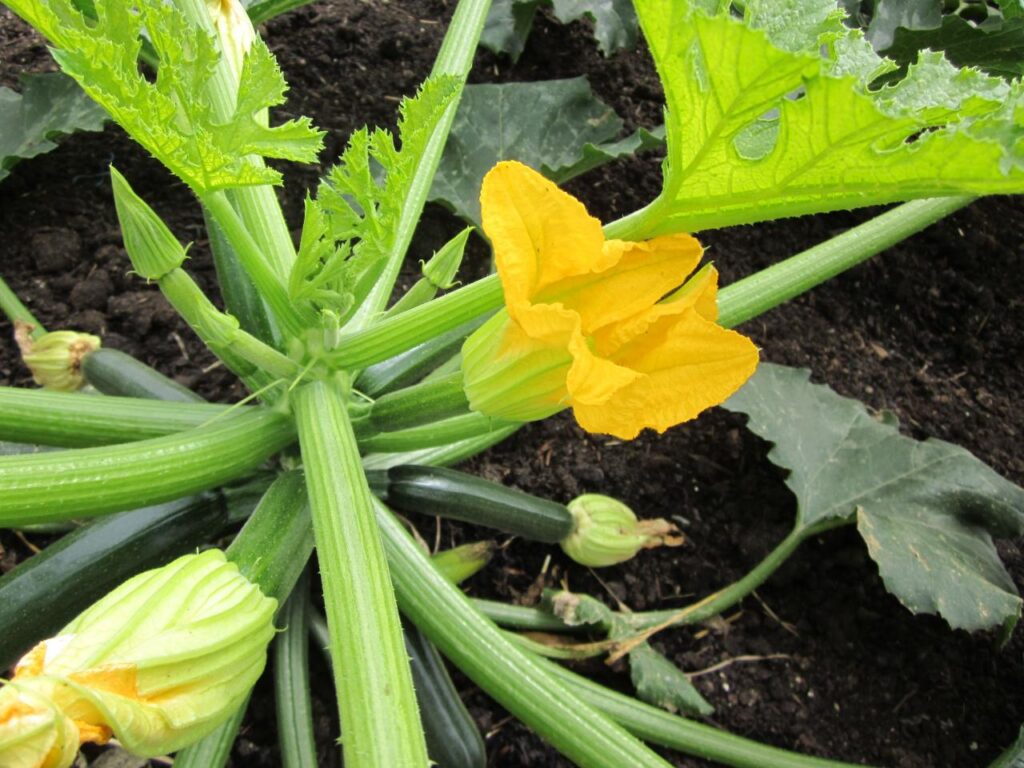
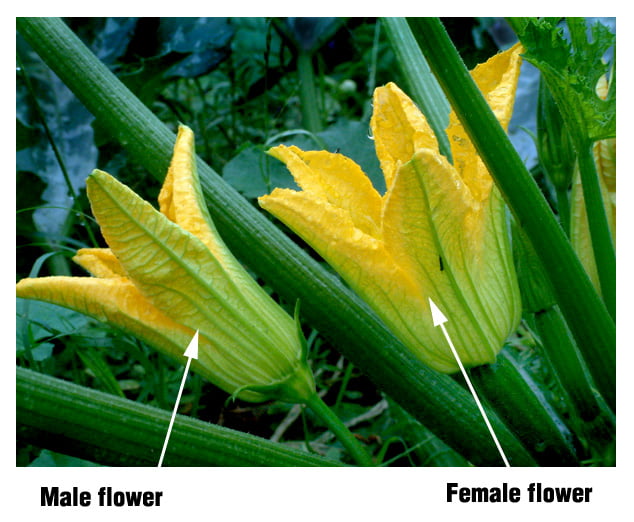
Like other plants, zucchini goes through a series of growth stages upon germination, including seedling, vegetative, flowering, and fruiting stages. During the flowering stage, zucchini produces both male and female flowers, essential for pollination and fruit set. The male flowers possess stamens, which produce pollen, while the female flowers have pistils, which contain the stigma, style, and ovary.
Zucchini Varieties
There are various zucchini varieties available, offering different characteristics in terms of size, shape, color, and flavor. Common zucchini varieties include the classic green zucchini, yellow zucchini, and heirloom varieties with unique attributes. Each variety may have its own specific requirements for pollination, growth, and fruit development.

The Role of Pollination in Zucchini
Zucchini and Pollination
Pollination is of utmost importance in the successful production of zucchini. As zucchini plants have separate male and female flowers, they require effective pollen transfer for fertilization to occur. Without pollination, zucchini fruit development would not take place, resulting in poor yield.
Importance of Pollination for Zucchini
Pollination plays a critical role in zucchini production by facilitating the development of viable seeds within the fruit. This process triggers hormonal changes that support fruit growth and regulates the production of auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins. These growth regulators influence cell division, elongation, and differentiation, leading to proper fruit development.
Effect of Lack of Pollination on Zucchini
Insufficient or unsuccessful pollination can significantly impact zucchini plants. Without adequate pollination, zucchini fruits may exhibit abnormalities, such as misshapen or underdeveloped fruit, reduced size, or even complete fruit drop. Inadequate pollination can also lead to reduced seed production and genetic diversity, negatively affecting the overall health and sustainability of zucchini populations.
How Zucchini are Pollinated
Zucchini and Natural Pollination
In their natural environment, zucchini plants rely on natural pollinators, mainly insects, to facilitate pollination. Bees, including honeybees, bumblebees, and solitary bees, are the most common pollinators of zucchini. These insects visit the male flowers, collect pollen on their bodies, and transfer it to the receptive stigma of female flowers as they forage for nectar and pollen.
Insects and Zucchini Pollination
Insects, particularly bees, play a crucial role in zucchini pollination. They carry out the transfer of pollen between flowers, enabling fertilization. The buzzing activity of bees helps dislodge pollen grains from the anthers and facilitate their deposition onto the stigmas of receptive female flowers. Therefore, it is essential to attract and maintain healthy populations of pollinating insects in zucchini-growing areas.
Wind Pollination and Zucchini
While zucchini flowers are primarily adapted for insect pollination, they can also undergo limited wind pollination. However, wind pollination alone is generally insufficient to ensure optimal fruit set and seed production in zucchini. The reliance on insect pollination is linked to the flowers’ structure, as they are specifically designed to attract and accommodate insect visitors.
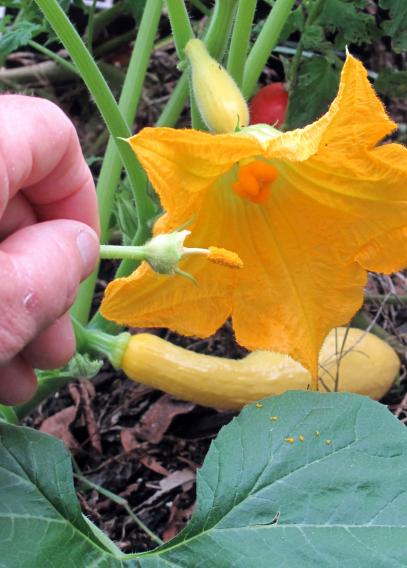
Hand Pollination of Zucchini
In cases where natural pollinators are scarce or when controlled pollination is desired, hand pollination can be employed. Hand pollination involves manually transferring pollen from the anthers of male flowers to the stigma of female flowers. This can be done using a small brush or by carefully removing the petals of the male flower and rubbing its stamen against the stigma of the female flower.

Factors Affecting Zucchini Pollination
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions significantly influence zucchini pollination. Factors such as temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind speed can affect insect activity and the availability of pollen. Extreme weather events, like heatwaves or heavy rains, can disrupt both flower production and the movement of pollinators, impacting pollination success.
Availability of Pollinators
The presence and abundance of pollinators in the area directly impact the effectiveness of pollination in zucchini. If there is a scarcity of pollinators due to habitat loss, pesticide use, or other factors, zucchini plants may experience reduced pollination and subsequent yield. Creating pollinator-friendly habitats and minimizing pesticide applications can help ensure a sufficient population of pollinators.
Male and Female Flowers in Zucchini
The relative abundance and synchrony of male and female flowers in zucchini can affect pollination success. If the number of male flowers significantly outweighs the female flowers, pollen may be wasted, leading to reduced fruit set. Conversely, an insufficient number of male flowers can result in limited pollen availability for proper fertilization. Achieving a balanced ratio of male to female flowers is crucial for optimal pollination.
Timing of Zucchini Pollination
The timing of pollination is critical for zucchini fruits’ successful development. Female flowers are typically receptive for only one day, during which pollination must occur for fruit set to take place. Adequate overlap between male and female flower availability is essential for successful pollination. If there is a delay in pollination, the female flowers may shrivel and drop off before setting fruit.
Promoting Pollination in Zucchini
Providing a Pollinator-Friendly Environment
Creating a pollinator-friendly environment is crucial for promoting effective pollination in zucchini. This can be achieved by planting diverse flowering plants that attract and support pollinators. Providing a continuous supply of nectar and pollen sources throughout the growing season ensures the presence of pollinators when zucchini flowers begin to bloom.
Attracting Bees and Other Pollinators
Bees, especially honeybees, are highly efficient pollinators for zucchini. To attract bees to zucchini gardens, include flowers known to be attractive to bees, such as lavender, borage, and sunflowers. Providing suitable nest sites, such as bee boxes or undisturbed areas, can also encourage nesting and population growth of native pollinators.
Avoiding Pesticide Use
Pesticides, particularly insecticides, can have harmful effects on pollinators and disrupt natural pollination processes. To promote pollination in zucchini, it is important to minimize or avoid pesticide use, especially when the plants are flowering. If pest control is necessary, opt for organic or biological pest management approaches that are less harmful to pollinators.
Hand Pollination Techniques
Hand pollination can be employed to ensure pollination in zucchini, especially when there is a lack of natural pollinators or controlled breeding is desired. As mentioned before, carefully transferring pollen from male to female flowers using a small brush or by hand can be an effective technique. This method allows for precise control over the pollination process, ensuring optimal fruit set.

Common Pollination Problems in Zucchini
Lack of Pollinators
Insufficient pollinator populations can lead to poor pollination in zucchini. This can be caused by habitat loss, pesticide use, disease outbreaks, or other factors that negatively impact pollinator health and abundance. Addressing these issues through habitat restoration, reduced pesticide usage, and conservation efforts can help mitigate the lack of pollinators.
Poor Weather Conditions
Unfavorable weather conditions, such as prolonged rain, extreme heat, or high winds, can negatively affect zucchini pollination. These conditions can deter pollinator activity and disrupt the transfer of pollen. Employing techniques such as providing windbreaks, shading, or using protective covers can help mitigate the impact of adverse weather on pollination.
Diseases Affecting Pollination
Certain diseases and infections can directly or indirectly impact zucchini pollination. For example, viral infections can cause deformities in zucchini flowers, hindering pollination. Fungal diseases, such as powdery mildew, can also affect flower health and reduce the attractiveness to pollinators. Implementing appropriate disease management strategies, including cultural practices and disease-resistant cultivars, can help minimize the impact of diseases on pollination.
Identifying Pollination Issues
To address pollination problems effectively, it is crucial to identify the specific issues affecting zucchini plants. Observing the presence and behavior of pollinators, assessing flower quality and abundance, and evaluating fruit set can help pinpoint the underlying causes of poor pollination. Monitoring and record-keeping are essential tools to track and address any ongoing pollination issues.
Improving Zucchini Yield through Pollination
Increased Fruit Set
Effective pollination directly contributes to increased fruit set in zucchini plants. Proper transfer of pollen ensures that the female flowers are fertilized, leading to the development of healthy fruits. Inadequate pollination can result in a reduced number of fruits, lower crop yields, and economic losses for growers. Enhancing pollination through various techniques can help maximize fruit set and overall yield.
Better Fruit Quality and Size
Pollination has a significant impact on the quality and size of zucchini fruits. When successful pollination occurs, it triggers the production of hormones that regulate fruit growth, resulting in well-formed, uniformly sized fruits. Proper pollination also promotes the development of seeds within the fruit, contributing to better texture, flavor, and overall market value of zucchini.
Higher Crop Yield
By ensuring adequate pollination, zucchini growers can expect higher crop yields. Successful pollination leads to improved fruit set, increased fruit size, and enhanced fruit quality, which directly translates to higher yields. By implementing strategies to promote effective pollination, growers can optimize their zucchini production and achieve sustainable crop yields.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pollination is indispensable for zucchini. The intricate process of transferring pollen between male and female flowers enables successful fertilization, fruit set, and subsequent seed production. Natural pollinators, such as bees, play a vital role in facilitating pollination, but environmental factors, availability of pollinators, and timing are key considerations. By understanding the importance of pollination in zucchini and implementing strategies to promote effective pollination, growers can optimize yield, fruit quality, and overall productivity of this beloved summer squash.



