Strawberries, a beloved fruit adored for their luscious sweetness and vibrant red color, hold a special place in the hearts of many gardeners. However, there is a vital question that haunts both novice and experienced horticulturists alike: How deep should you plant strawberries? This seemingly simple query holds significant implications for the health and productivity of these delectable fruits. In this article, we will explore the optimal planting depth for strawberries, considering various factors that impact their growth and development. By delving into the depths of strawberry planting, you will gain valuable insights into ensuring the prosperity of these succulent berries in your own garden.
Factors to Consider
When considering how deep to plant strawberries, there are several factors that need to be taken into account. These include soil type, climate, and planting method. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in determining the ideal planting depth for strawberries.
Soil Type
Soil type is an important factor to consider when determining the planting depth for strawberries. Different soil types have different water-holding capacities and drainage properties. Sandy soils, for example, drain more quickly and require deeper planting to ensure proper moisture retention. On the other hand, heavier clay soils hold moisture for longer periods and may require shallower planting depths to prevent waterlogged roots. It is crucial to assess the soil type in your garden to determine the ideal planting depth for strawberries.
Climate
The climate in your region also plays a significant role in determining the planting depth for strawberries. Different climates have varying temperature ranges and frost patterns that can impact the root development and overall health of the strawberry plants. In colder climates, deeper planting is recommended to protect the plants from frost damage. In warmer climates, shallower planting may be necessary to prevent the roots from becoming too warm and potentially drying out. Consider the climate in your area when deciding on the planting depth for strawberries.
Planting Method
The planting method you choose can also influence the ideal planting depth for strawberries. There are two primary methods for planting strawberries: bare root and container-grown plants. Bare root plants are dormant strawberry crowns without any soil. These should be planted relatively shallow, with the roots spread out and the crown sitting just above the soil surface. Container-grown plants, on the other hand, should be planted at the same depth they were growing in the container. Adjust the planting depth according to the chosen method to ensure optimal growth and establishment of the strawberry plants.
Recommended Planting Depth
Determining the ideal planting depth for strawberries is essential for their successful growth and development. While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, certain guidelines can be followed to ensure you are planting your strawberries at the optimal depth.
Determining Ideal Depth
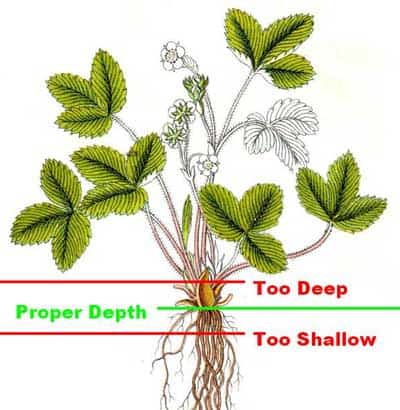
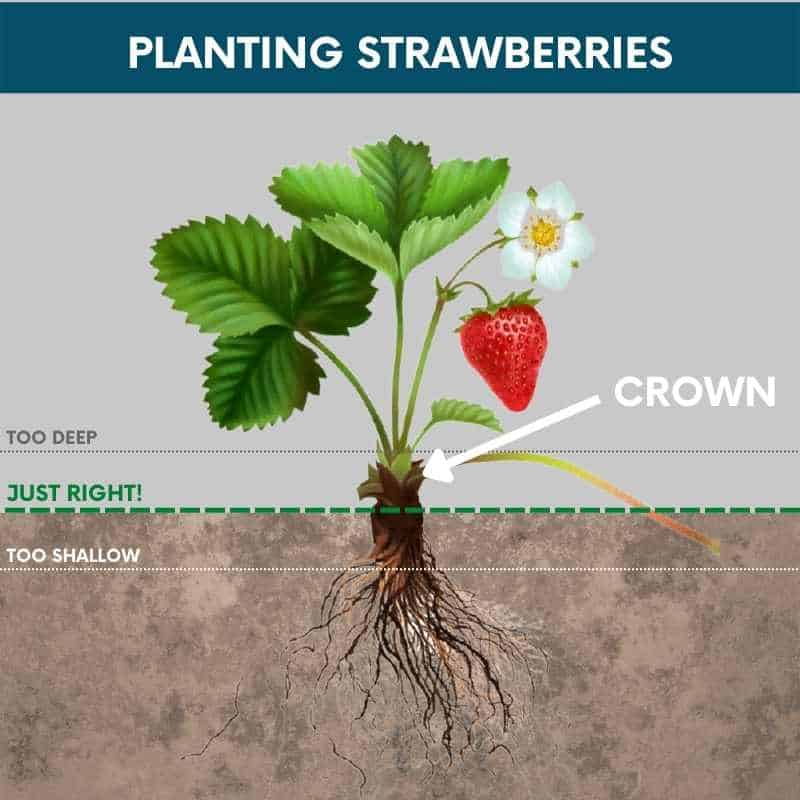
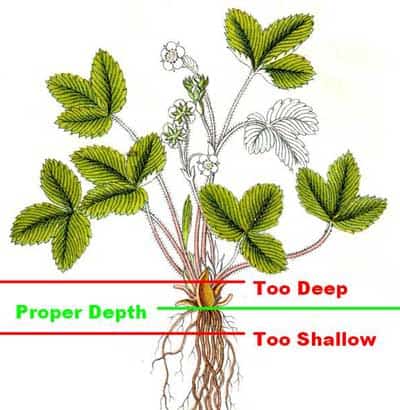
To determine the ideal planting depth for strawberries, it is best to observe the anatomy of the plant. Strawberries have a crown, which is the central part of the plant where the leaves emerge from. The roots grow from the crown and spread out into the soil. When planting, the crown should be positioned at soil level, neither too deep nor too shallow. This allows the roots to access moisture and nutrients while protecting the crown from direct exposure and potential rot.
Planting Depth Guidelines
As a general guideline, the planting depth for strawberries should be approximately one inch below the soil surface. This depth ensures that the crown is not buried too deeply, leading to rot, while also preventing it from sitting too high, causing dehydration and susceptibility to frost. Adjust the depth slightly depending on the specific soil type, climate, and planting method, but always aim for the crown to be at or slightly above soil level.
Effects of Incorrect Planting Depth
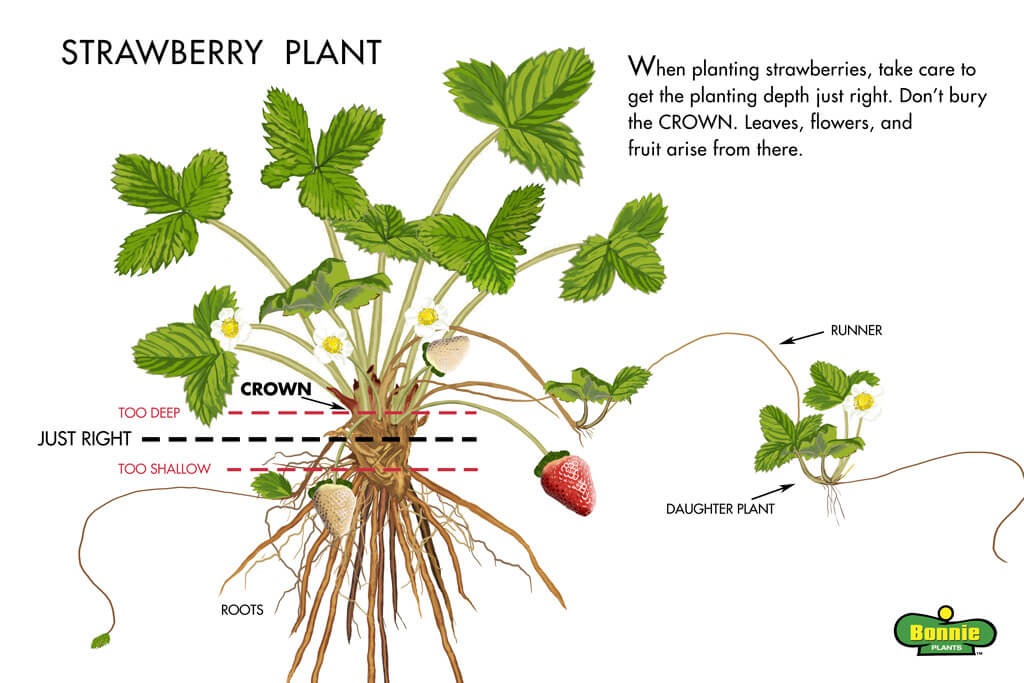
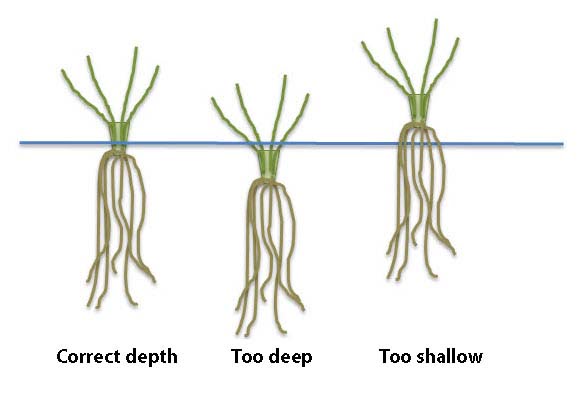
Planting strawberries at an incorrect depth can have detrimental effects on their growth and overall health. Whether the plants are planted too shallow or too deep, they can suffer from various problems that can hinder their productivity and survival.
Shallow Planting
When strawberries are planted too shallow, the roots may dry out quickly, especially in warmer climates or during dry periods. Shallow planting exposes the crown to direct sunlight and air, which can lead to dehydration and ultimately plant death. Additionally, shallow planting may result in weak root development, leaving the plant vulnerable to diseases and pests. It is important, therefore, to ensure adequate soil coverage and proper planting depth to prevent these issues.
Deep Planting
On the other hand, planting strawberries too deep can have equally negative consequences. Deep planting can lead to poor root development, as the roots struggle to reach the surface for essential air and light exposure. Insufficient oxygen supply may cause root rot, and the plant may become weak and unproductive. Deep planting also increases the risk of the crown becoming waterlogged, further exacerbating the potential for root rot. Proper planting depth is crucial to avoid these complications and promote healthy strawberry growth.
Step-By-Step Planting Guide
To ensure successful planting and optimal growth of your strawberry plants, follow this step-by-step planting guide.
Preparation
Before planting strawberries, it is important to prepare the soil adequately. Start by removing any weeds or grass from the planting area. Loosen the soil with a garden fork or tiller to a depth of at least 6 inches to promote good root penetration and drainage. Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve soil fertility and structure.
Digging the Hole
Once the soil is prepared, dig a hole wide and deep enough to accommodate the plant’s roots comfortably. Make sure the hole is deep enough to position the crown at soil level or slightly above it. Roughly one inch below the soil surface is generally recommended, but adjust accordingly based on soil type, climate, and planting method.
Planting the Strawberry
Place the strawberry plant in the hole, spreading the roots out carefully and ensuring they are not bent or crowded. Position the crown at the appropriate depth, leaving it slightly above the soil level. Backfill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots to eliminate any air pockets. Avoid compacting the soil too tightly, as this can hinder root growth and water absorption.
Mulching
After planting the strawberry, it is beneficial to apply a layer of mulch around the plant. This helps to conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and maintain a more consistent soil temperature. Organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, is commonly used for strawberries. Apply a layer of mulch approximately 2-4 inches thick, ensuring it does not touch the crown. Mulching also helps to protect the berries from coming into contact with the soil, reducing the risk of diseases.
Additional Tips for Successful Planting
In addition to the proper planting depth, there are several other factors to consider to ensure successful strawberry planting and growth. These include variety selection, watering, and fertilization.
Variety Selection
Choose strawberry varieties that are well-suited to your specific climate and growing conditions. Some varieties are more tolerant of heat, while others are better adapted to cold climates. Consider factors such as disease resistance, fruit production, and flavor when selecting strawberry varieties.
Watering
Proper watering is crucial for the health and productivity of strawberry plants. Ensure the plants receive sufficient moisture, especially during dry periods. Use a drip irrigation system or water at the base of the plant to prevent excess moisture on the leaves, which can encourage fungal diseases. Aim to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged, allowing for good drainage to avoid root rot.
Fertilization
Strawberries benefit from regular fertilization to promote healthy growth and fruit production. Apply a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 or 14-14-14 formula, according to package instructions. Fertilize the plants when they are actively growing, typically in the spring and early summer. Avoid excessive fertilization, as this can lead to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of fruit production.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure the best possible outcome for your strawberry plants, it is important to avoid common planting mistakes that can hinder their growth and productivity.
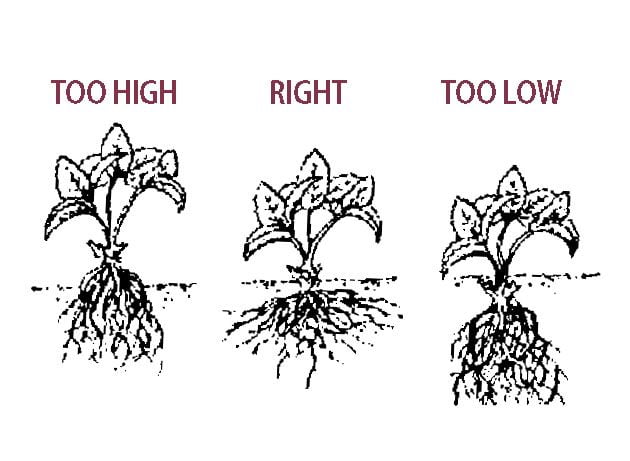
Planting Too Deep
As mentioned earlier, planting strawberries too deep can result in poor root development, restricted air and light exposure, and potential root rot. Always aim to position the crown at or slightly above soil level, ensuring the roots have access to the necessary resources for healthy growth.
Planting Too Shallow
Shallow planting is equally detrimental to strawberry plants. When planted too shallow, the roots may dry out quickly, leading to dehydration and plant death. Shallow planting also increases the risk of the crown becoming exposed to direct sunlight and air, which can further dehydrate the plant and cause damage.
Neglecting Soil Moisture
Failing to provide adequate soil moisture is another common mistake in strawberry planting. Strawberries require consistent moisture, especially during periods of hot weather or drought. Monitor the soil moisture levels regularly and adjust watering accordingly to maintain optimal hydration for the plants.
When to Plant Strawberries
Determining the appropriate time to plant strawberries is crucial for their successful establishment and growth. The timing may vary depending on the climate and specific recommendations for your region.
Spring Planting
In most regions, spring is the ideal time to plant strawberries. It allows the plants to become established before the summer heat and ensures they will produce fruits in the following season. Planting in early to mid-spring, after the threat of frost has passed, provides the best conditions for strawberry growth.
Fall Planting
In areas with mild winters, fall planting can be an excellent option for strawberries. Planting in late summer or early fall allows the plants to establish strong root systems during the cooler months, providing a head start for the following spring. Ensure that the strawberries have enough time to develop and enter dormancy before the arrival of freezing temperatures.
Overwintering Strawberries
In regions with cold winters, special care should be taken to protect strawberry plants during the dormant period. Proper overwintering techniques help ensure their survival and productivity in the following growing season.
Preparing for Winter
Before winter arrives, it is important to prepare strawberry plants for the cold temperatures. Remove any dead or diseased foliage from the plants to prevent the spread of diseases. It is also beneficial to trim the foliage to a height of around 2-3 inches, reducing the risk of frost damage. Clean up the planting area, removing any debris that could harbor pests or diseases over the winter.
Mulching for Protection
Mulching is a key technique for protecting strawberries during the winter months. Apply a layer of straw or other organic mulch around the plants to insulate the soil and protect the roots from freezing temperatures. The mulch should be applied to a thickness of 4-6 inches, ensuring complete coverage but leaving the crown exposed. Mulching helps regulate soil temperature and prevents frost heaving, where the freezing and thawing of soil can push plants out of the ground.
Tips for Potted Strawberry Plants
If you prefer to grow strawberries in containers, there are some specific considerations to keep in mind to ensure successful planting and optimal growth.
Planting Depth in Containers
When planting strawberries in containers, it is important to provide sufficient depth for root development. Ensure that the container is at least 8-12 inches deep to accommodate the roots and allow for proper nutrient and moisture uptake. Plant the strawberries at the same depth they were growing in the nursery container, positioning the crown slightly above the soil level.
Container Selection
Choose containers with adequate drainage holes to prevent waterlogging and ensure healthy root development. Use containers made from materials such as plastic or terracotta that provide good insulation and retain moisture. The size of the container should be suitable for the number of strawberry plants you wish to grow, allowing each plant enough space for proper growth and development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, determining the ideal planting depth for strawberries is crucial for their successful growth and fruit production. Factors such as soil type, climate, and planting method should be considered when deciding on the appropriate planting depth. Shallow planting can lead to dehydration and weak root development, while deep planting can cause root rot and poor oxygen supply. By following the recommended guidelines and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure optimal growth and productivity for your strawberry plants. With proper planting techniques, adequate moisture, and regular fertilization, you can enjoy a bountiful strawberry harvest in your garden or container.