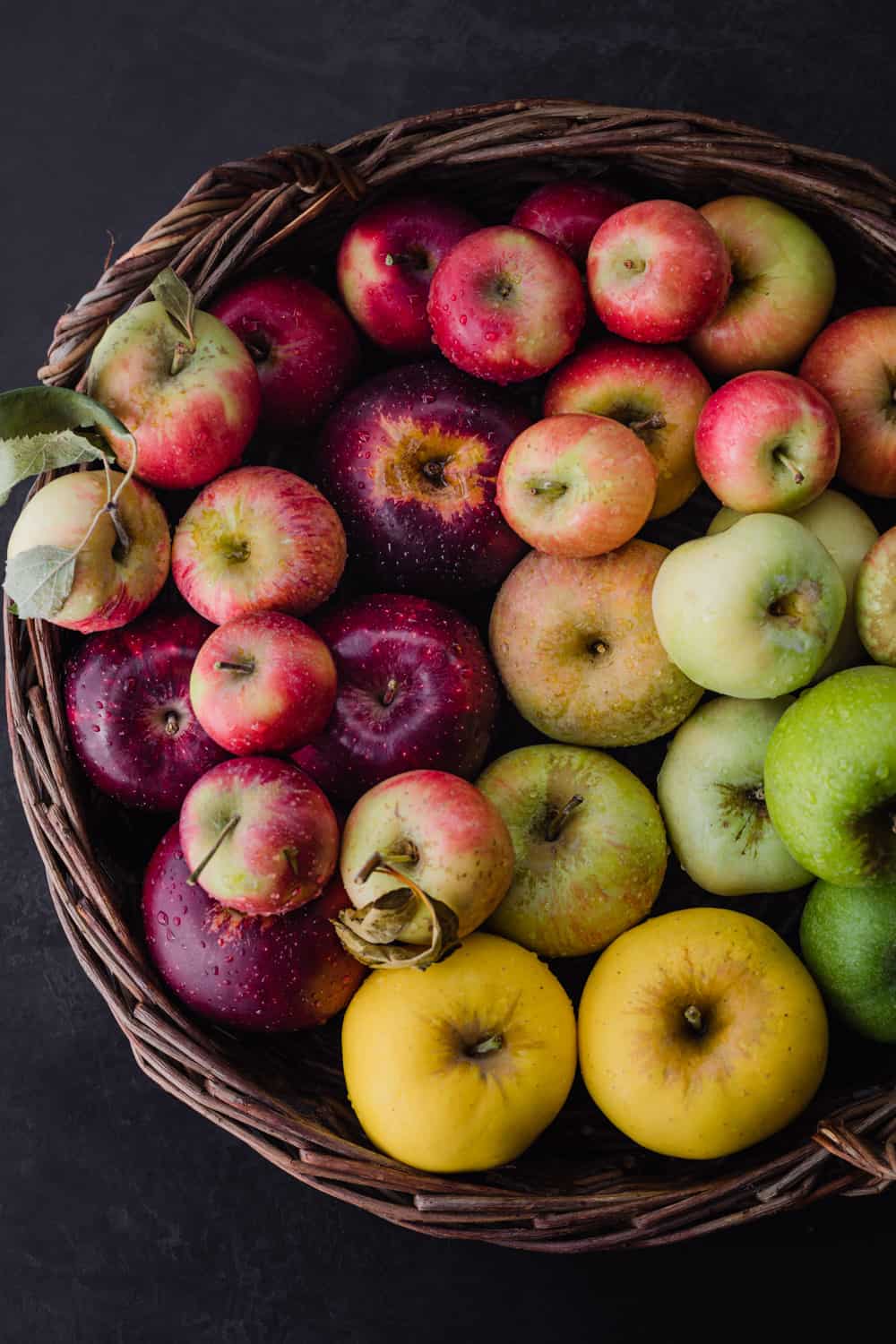
In this article, you will explore an intriguing topic that may seem simple at first glance: What color are apples? While it may appear straightforward, this question unravels a fascinating discussion encompassing various shades and hues that apples can possess. By exploring the wide spectrum of colors that apples can exhibit, you will gain a deeper appreciation for this common fruit and the diverse nature of its appearance. Prepare to delve into the captivating world of apple colors and discover the surprising range that exists beyond the initial assumption.
The Basics of Apples
Types of Apples
When it comes to apples, there are countless varieties to choose from. Each type has its own unique flavor, texture, and color. Some popular apple types include Granny Smith, Fuji, Gala, Honeycrisp, and Red Delicious. Each of these varieties offers a different taste experience, making them suitable for various culinary uses and personal preferences.
Apple Varieties
Apples come in a wide range of colors, sizes, and shapes. Different apple varieties have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Some apples have a tart or sour taste, while others are sweet or slightly tangy. Additionally, the texture can vary from soft and tender to crisp and firm. Identifying apple varieties is often done by considering their color, size, taste, and texture. This diverse array of apple varieties ensures that there is an apple to suit everyone’s taste.
Growing Conditions
Apples flourish under certain growing conditions. They require well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. Apples grow best in temperate climates with cold winters and moderate summers. The ideal temperature range for apple trees is between 60°F and 75°F (15°C and 24°C). Adequate sunlight exposure is crucial for the photosynthesis process that allows apple trees to produce energy and grow. Other factors such as moisture, wind, and altitude also play a role in the successful cultivation of apple trees.
The External Appearance
Color Perception
When it comes to perceiving the color of apples, our human eyes interpret the light reflected by the apple’s surface. Different wavelengths of light are absorbed and reflected, creating the perceived color. Our eyes are particularly sensitive to the colors red, green, and blue, which are the primary colors used in color perception and mixing.
Variations in Color
Apples showcase a wide range of colors, including red, green, yellow, and even variations within these hues. The specific color of an apple can differ depending on its variety, maturity level, and growing conditions. Variations in color can also be found within a single apple, with some areas appearing darker or lighter, adding visual interest to the fruit.
Ripeness Indicators
The color of an apple can serve as an important indicator of its ripeness. For example, green apples tend to be more tart and firm when they are not fully ripe, while red apples are often sweeter and juicier when allowed to fully mature. It is essential to pay attention to the color changes in apples to ensure they are enjoyed at their optimal flavor and texture.

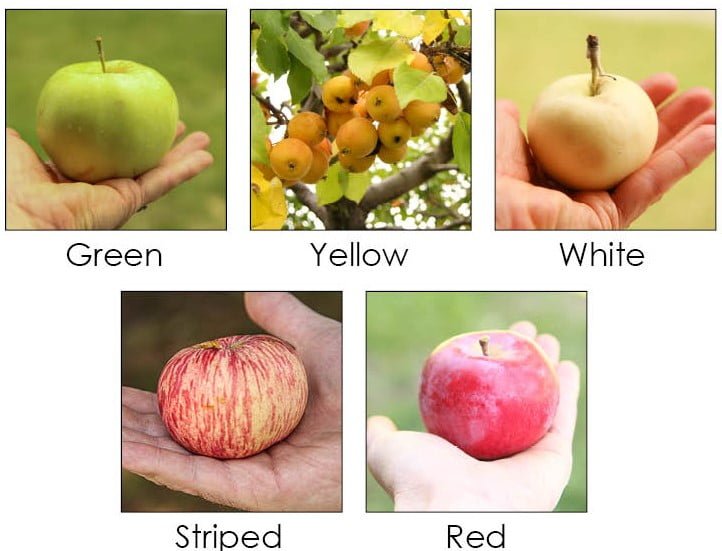
The Common Colors of Apples
Red
Red apples are often associated with sweetness and juiciness. This color is a result of pigments called anthocyanins, which give the apple its striking red hue. Some popular red apple varieties include Red Delicious, McIntosh, and Rome Beauty. These apples are often eaten fresh but can also be used in cooking and baking due to their balanced flavor profile.
Green
Green apples, such as Granny Smith, are known for their tartness and crisp texture. The color of these apples is attributed to the presence of chlorophyll, the same pigment found in plant leaves. Green apples are versatile and can be enjoyed both in sweet and savory dishes. Their refreshing tartness adds a delightful contrast to salads, pies, and sauces.
Yellow
Yellow apples, like Golden Delicious and Yellow Newtown Pippin, are often sweet and mildly tart. These apples get their yellow color from the pigments called carotenoids. Yellow apples are particularly popular for making applesauce and apple butter, as their slightly sweet taste enhances the overall flavor.
Other Colors
While red, green, and yellow are the most common apple colors, there are also apples with more unique hues. Some apples exhibit a pink or blush color, combining the sweetness of red apples with a delicate mellow flavor. Other apples may have a russet, or brown, coloration, which is caused by a buildup of cork cells. Apples with a rare blue or purple skin, such as the Purple Passion or Indigo Rose varieties, appeal to those seeking an unconventional apple experience.
The Science Behind Apple Colors
Pigments in Apples
The different colors of apples are a result of various pigments present in the fruit’s skin and flesh. These pigments absorb and reflect different wavelengths of light, creating the colors that we see. The three primary pigments involved in apple coloration are anthocyanins, chlorophyll, and carotenoids.
Anthocyanins
Anthocyanins are responsible for the red, pink, and purple colors found in apples. These pigments are water-soluble flavonoids that develop during the later stages of apple ripening. Anthocyanins accumulate in the apple’s skin and can play a role in providing health benefits to consumers.
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for a plant’s green color, is also present in apples. When apples are unripe, chlorophyll masks other pigments. As the apple matures, the breakdown of chlorophyll allows other pigments, such as anthocyanins or carotenoids, to become more visible.
Carotenoids
Carotenoids are pigments responsible for the yellow, orange, and brown colors in apples. These pigments are lipid-soluble compounds that accumulate in the fruit’s skin and flesh. Carotenoids contribute to the nutritional value of apples and have antioxidant properties.
Genetic Factors
The combination and concentration of different pigments in apples are determined by genetic factors. Specific apple varieties are genetically programmed to produce certain pigments, resulting in the characteristic colors associated with each variety. These variations in genetic makeup account for the diverse range of colors observed among different apple types.

Factors Influencing Apple Color
Varietal Differences
Each apple variety has its own genetic makeup, which dictates the pigments and colors present in the fruit. Therefore, the color of an apple is primarily influenced by its variety. Varietal differences contribute to the wide array of colors seen in apples, providing consumers with diverse options when it comes to taste, texture, and appearance.
Growing Conditions
The conditions in which apple trees are grown can impact the fruit’s color. Factors such as soil composition, nutrient levels, and moisture content can influence the intensity and vibrancy of an apple’s color. Additionally, apple trees may exhibit variations in color depending on the specific geographic location they are cultivated in.
Temperature
Temperature plays a crucial role in apple color development. Cooler temperatures during apple growth can lead to higher anthocyanin production, resulting in more vibrant red or purple colors. On the other hand, warmer temperatures may hinder anthocyanin formation and result in paler hues.
Sunlight
Sunlight is essential for apple tree health and fruit development. Adequate exposure to sunlight promotes photosynthesis, allowing the apple tree to produce energy. Sunlight also affects apple coloration by facilitating the synthesis of pigments such as chlorophyll and anthocyanins. Insufficient sunlight may result in less intense colors or uneven pigmentation.
Harvesting Time
The timing of apple harvesting can impact color development. Some apple varieties are typically picked when they are still green but will develop their final coloration during storage. Other varieties are harvested when they have reached their full color potential. Harvesting apples at the right time ensures optimal color, taste, and texture.
Nutritional Benefits of Apple Colors
Health Benefits
Apples, regardless of their specific color, offer numerous health benefits. They are a great source of dietary fiber, which promotes digestive health and helps maintain regular bowel movements. Apples also contain essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall well-being. Regular consumption of apples has been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain types of cancer.
Antioxidant Content
Apples are rich in antioxidants, which play a vital role in scavenging harmful free radicals in the body. The different pigments present in apples, such as anthocyanins and carotenoids, contribute to their antioxidant content. These antioxidants help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and may have anti-inflammatory properties.
Phytochemicals
Apples contain a variety of phytochemicals, which are natural compounds found in plant-based foods. These compounds are known to have potential health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Phytochemicals, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, can vary in concentration depending on the apple’s color and variety, contributing to the overall nutritional value of the fruit.
Vitamin Content
Apples are a good source of essential vitamins, including vitamin C and vitamin A. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production. Vitamin A is important for eye health and plays a role in maintaining healthy skin. The specific content of these vitamins may vary depending on the apple variety and its color.

Culinary Uses and Preferences
Apple Uses in Cooking
Apples have long been a favorite ingredient in countless culinary creations. They can be used in both sweet and savory dishes, providing a unique flavor and texture. Apples can be baked into pies, crumbles, and cakes, adding natural sweetness and moisture. They are also commonly used in salads, sauces, and chutneys, offering a refreshing and tangy element to balance other flavors. Apples can even be pressed into juice or fermented into cider, showcasing their versatility in the culinary world.
Color Preference in Apple Selection
The color of apples can influence consumer preferences when it comes to selecting and purchasing them. Some individuals may have a personal preference for a particular color due to associa



