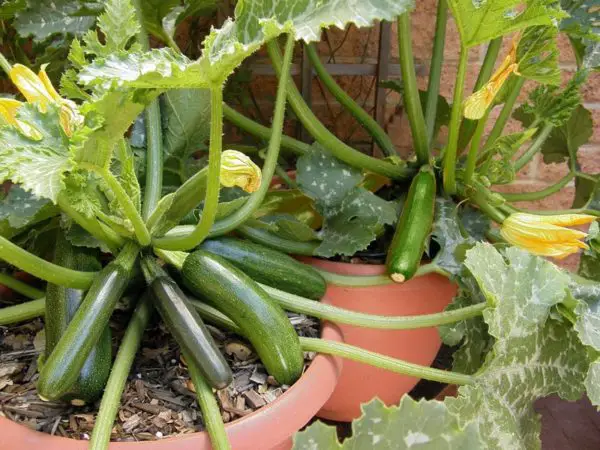
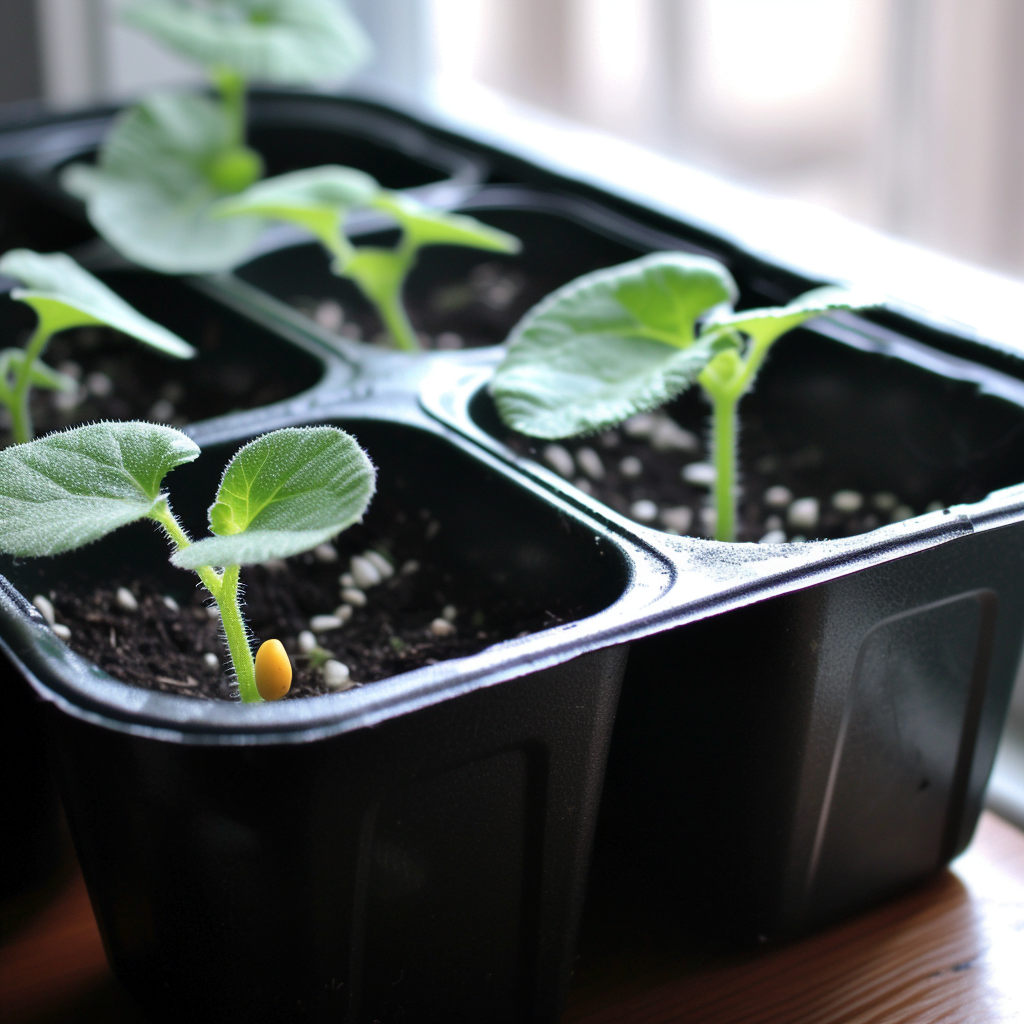
So, you’ve got that gardening bug and you’re itching to grow some zucchini, huh? Well, if you’re in Texas, you might be wondering when the best time is to plant this delicious vegetable. Lucky for you, we’ve got the answer. Texas weather can be a bit unpredictable, but with a little know-how, you can ensure a successful zucchini harvest. In this article, we’ll guide you through the optimal planting time, taking into consideration the climate and temperature variations across the Lone Star State. Get ready to dig in and discover the perfect time to kickstart your zucchini garden.
Factors to Consider when Planting Zucchini in Texas
If you’re considering planting zucchini in Texas, there are several important factors to take into account to ensure successful growth and a bountiful harvest. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key considerations when it comes to climate and weather, soil conditions, frost dates, variety selection, and planting timeline. By understanding and addressing these factors, you can enjoy a thriving zucchini garden regardless of where you are in Texas.
Climate and Weather
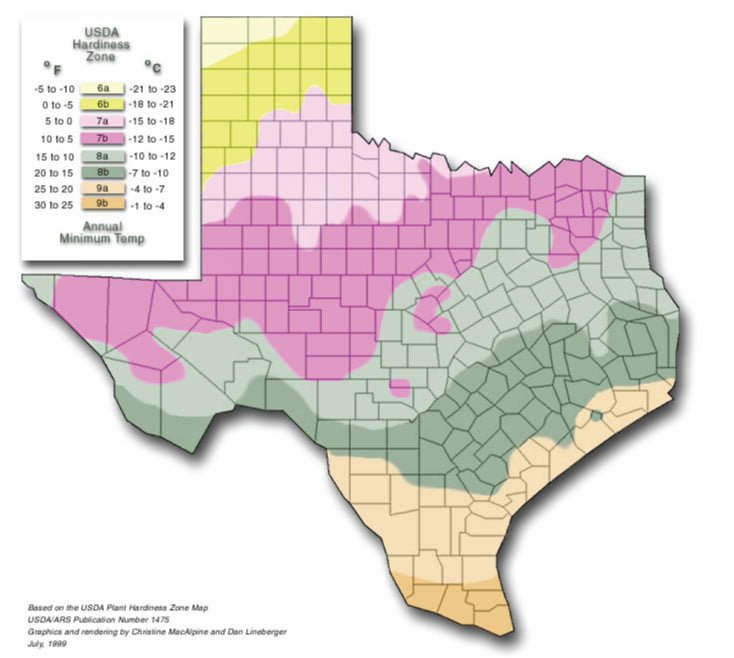
Understanding the climate and weather conditions in Texas is crucial when planning to grow zucchini. Texas has a diverse climate, ranging from arid regions in the west to humid areas in the east. The state is known for its long, hot summers and mild winters, factors that significantly influence zucchini growth.
Temperature Requirements
Zucchini plants thrive in warm temperatures, with an optimal range of 70 to 90 degrees Fahrenheit during the day. They are particularly sensitive to frost and cannot withstand freezing temperatures. Therefore, it is essential to monitor the weather conditions and avoid planting zucchini when frost is a possibility.
Sunlight Needs
Zucchini plants require plenty of sunlight to thrive. They should ideally receive a minimum of six to eight hours of direct sunlight each day. When selecting a planting location, ensure it offers ample exposure to sunlight, which is essential for plant growth, flower production, and fruit development.
Rainfall Considerations
While zucchini plants need consistent moisture, excessive rainfall can lead to problems such as root rot or fungal diseases. In Texas, where rainfall varies across different regions, it is crucial to monitor the amount of rainfall your zucchini plants receive. Consider implementing a watering schedule to maintain adequate moisture levels and prevent overwatering.
Soil Conditions
Proper soil conditions are essential for healthy zucchini plants. Understanding the soil type, pH levels, and preparing the soil adequately will contribute to a successful zucchini harvest.
Soil Type
Zucchini plants thrive in well-draining soil rich in organic matter. Sandy loam or loamy soil is considered ideal for optimal growth and development. If your soil is heavy clay, you can improve its drainage by mixing in organic matter and creating raised beds or mounds for planting.
Soil pH
The pH level of your soil also plays a crucial role in zucchini plant health. The ideal pH range for zucchini cultivation is between 6 and 7, which is slightly acidic to neutral. Conduct a soil test to determine the pH of your soil and make any necessary adjustments using appropriate amendments.
Soil Preparation
Before planting zucchini, it is important to prepare the soil properly. Remove weeds and debris from the planting area and incorporate organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve soil structure and fertility. Working the soil to a depth of at least 8 to 10 inches will ensure proper root development and access to nutrients.
Organic Matter
Adding organic matter to the soil provides essential nutrients, improves moisture retention, and enhances overall soil health. Compost, well-rotted manure, or other organic amendments can be incorporated into the soil during preparation to increase its organic matter content. This will promote optimal growth and productivity in zucchini plants.
Frost Dates
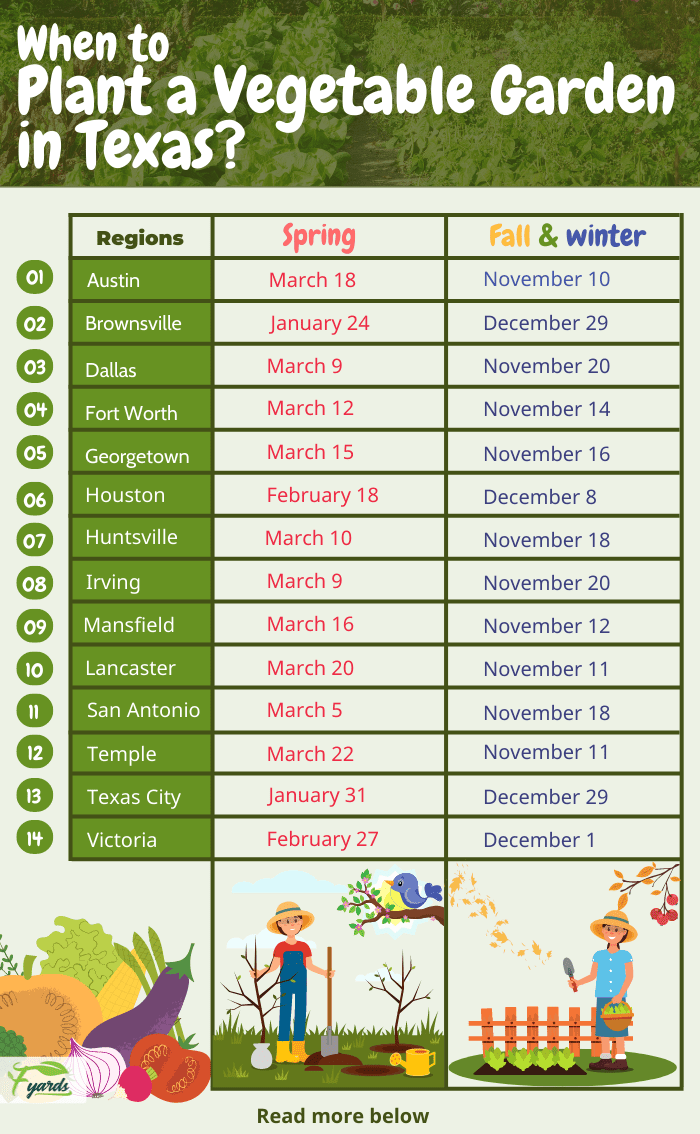
Understanding the frost dates in Texas is crucial for successful zucchini cultivation. Frost can damage or kill zucchini plants, so it is important to know the last frost date in spring and the first frost date in fall.
Last Frost Date
The last frost date in Texas generally varies depending on the specific region. In most areas of Texas, the last frost date occurs between late February and late March. However, it is advisable to consult with your local agricultural extension office or refer to a reliable gardening resource for the most accurate information relevant to your specific location.
First Frost Date
Similarly, the first frost date in Texas varies across different regions. In the majority of areas, the first frost typically occurs between late November and early December. Again, it is recommended to consult a local agricultural extension office or gardening resource to determine the specific first frost date for your location.
Effect on Zucchini Plants
Zucchini plants are highly sensitive to frost and cannot withstand freezing temperatures. Even a slight frost can damage the leaves and stems of the plants, ultimately reducing their productivity. To protect your zucchini plants from frost, it is important to time your plantings accordingly and provide sufficient shelter or cover during colder periods.
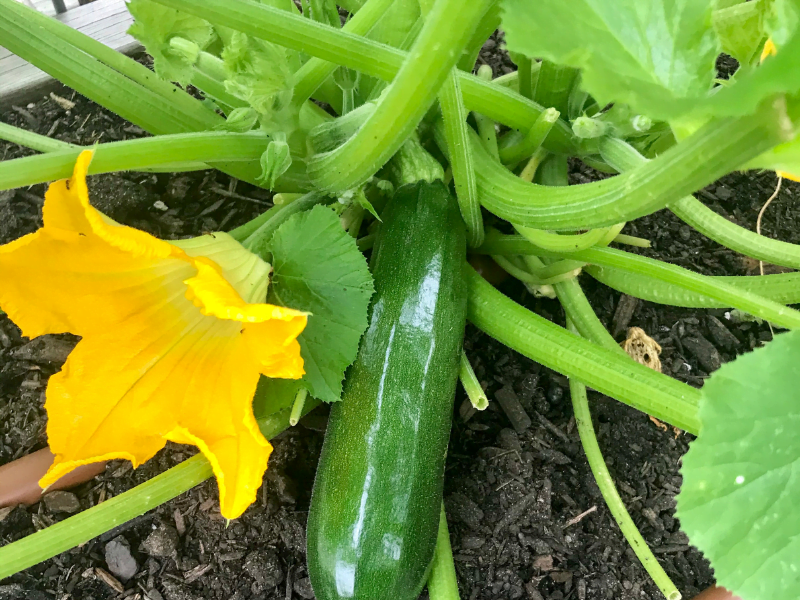

Variety Selection
Selecting the right zucchini variety is essential for successful growth and reliable harvests. Factors such as maturity time, disease resistance, and personal preferences should be taken into account.
Choosing the Appropriate Zucchini Variety
When choosing a zucchini variety, consider factors such as the space available, preferred flavor and texture, and cooking or usage preferences. Popular zucchini varieties include “Black Beauty,” “Golden zucchini,” and “Yellow Crookneck.” Research the characteristics of each variety and select the one that suits your gardening goals and taste preferences.
Determining Maturity Time
Different zucchini varieties have varying maturity times. Some zucchini plants produce fruits within 40 to 50 days from planting, while others may take up to 70 days. Consider the length of your growing season and select a zucchini variety that will have sufficient time to mature and produce ample harvests.
Hybrid vs. Heirloom Varieties
Hybrid zucchini varieties are bred to exhibit specific traits, such as disease resistance, improved yield, or specific fruit characteristics. Heirloom varieties, on the other hand, are open-pollinated and have been passed down through generations, offering unique flavors and traits. Decide whether you prefer the reliability of hybrid varieties or the historical significance and distinct qualities of heirloom varieties.
Planting Timeline
Understanding the planting timeline for zucchini in Texas is crucial to ensure optimal growth and maximize yield. Depending on the region and the desired harvest times, zucchini can be planted in early spring, mid-to-late spring, or during the fall season.
Early Spring Plantings
For early spring plantings, prepare the garden bed by removing weeds and debris. Start zucchini seeds indoors approximately four to six weeks before the last frost date. Use individual seedling pots filled with seed-starting mix, and keep them in a warm and well-lit area. Once the danger of frost has passed, transplant the seedlings to the garden bed, ensuring proper spacing of at least 3 feet between plants.
Mid-to-Late Spring Plantings
Mid-to-late spring plantings involve direct seeding zucchini into the garden bed once the soil has warmed up and the danger of frost has passed. Prepare the soil by removing weeds and improving its structure with organic matter. Make small mounds or hills with a spacing of about 3 to 4 feet between them. Plant the zucchini seeds in the hills, following the recommended planting depth provided on the seed packet. Water the newly planted seeds gently but thoroughly, ensuring the soil remains consistently moist during germination.
Fall Plantings
Fall plantings can extend the zucchini harvest into the cooler months. Begin by preparing the garden bed as you would for mid-to-late spring plantings. However, fall plantings may require starting the seeds indoors a few weeks earlier to ensure they are ready for transplantation once the soil has cooled down. Consider using protective measures such as row covers or cold frames to shield the plants from early fall frosts and extend the harvest season.
Harvesting Zucchini
Knowing when to harvest your zucchini is crucial to enjoy the best flavor and texture. It is important to recognize the signs of maturity, utilize appropriate harvesting techniques, and ensure regular harvesting throughout the growing season.
Recognizing Maturity
Zucchini is best harvested when the fruits are still young and tender, typically when they reach 6 to 8 inches in length. Larger, overripe zucchinis can become tough and less flavorful. Regularly monitor the fruits and harvest them promptly to encourage continuous fruit production.
Harvesting Techniques
To harvest zucchini, gently grasp the fruit near its base and twist it gently until it breaks away from the stem. Avoid using excessive force, as it may damage the plant or neighboring fruits. Utilize a sharp knife or garden scissors if necessary, but be careful not to injure the plant in the process.
Regular Harvesting
Regularly harvesting zucchini is essential to keep the plants productive. As soon as you notice a mature fruit, promptly harvest it. This encourages the plant to continue producing new flowers and fruits throughout the growing season. Regular harvesting not only ensures a consistent supply of fresh zucchini but also reduces the risk of overripe fruits or overgrown plants.
In conclusion, successful zucchini cultivation in Texas requires careful consideration of various factors such as climate and weather, soil conditions, frost dates, variety selection, and the planting timeline. By understanding the specific needs of zucchini plants and implementing appropriate practices, you can enjoy a thriving zucchini garden and relish in the abundant harvests. Happy zucchini gardening!