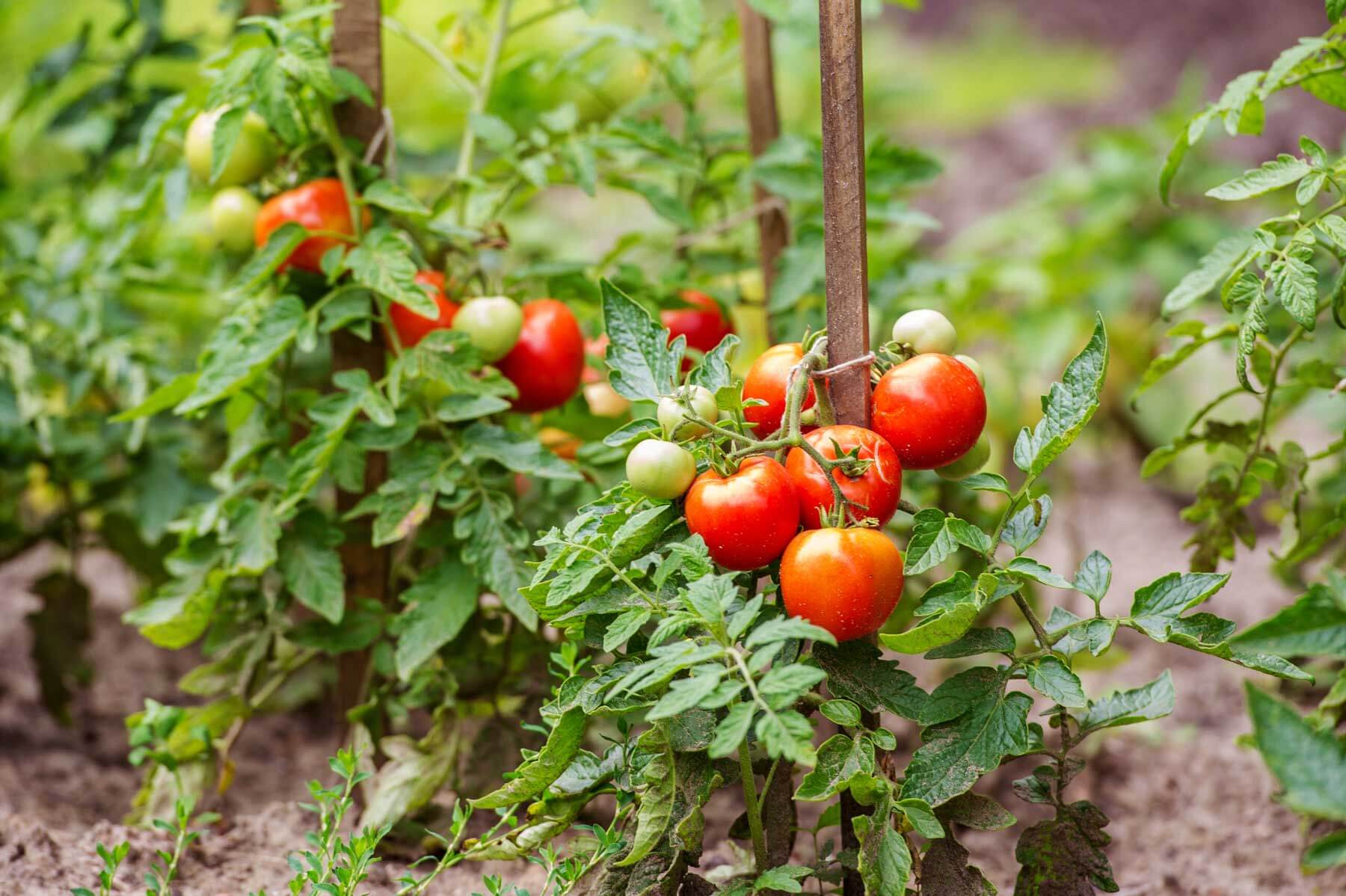
One of the most common questions that gardeners ponder is when their tomato plants will start yielding a bountiful harvest of ripe, juicy tomatoes. Aspiring green thumbs eagerly wait, wondering when their plants will finally bear fruits that can be transformed into mouthwatering dishes or enjoyed fresh off the vine. Understanding the factors that influence tomato plant growth and fruit production can help shed some light on this impatiently awaited phenomenon. From considering the variety of tomato plant to understanding the crucial role of environmental conditions, this article unravels the mysteries surrounding the long-awaited moment when your tomato plant finally grows those luscious red tomatoes.
Factors Affecting Tomato Plant Growth
Tomato plants require specific environmental conditions and care in order to grow and produce healthy tomatoes. There are several factors that significantly affect tomato plant growth:
| Growth Stage | Approximate Duration | Specific Care |
|---|---|---|
| Germination | 5-10 days | – Maintain moist, not soggy, soil. – Keep at steady warmth (70-80°F or 21-27°C). |
| Seedling Stage | 2-3 weeks | – Provide strong, direct light (sunlight or artificial). – Water regularly. |
| Vegetative Stage | 5-6 weeks | – Fertilize with a balanced nutrient mix. – Stake or trellis for support. – Regular watering and pruning of side shoots. |
| Flowering Stage | 1-2 weeks | – Ensure pollination (encourage beneficial insects, hand pollinate if necessary). – Avoid excess nitrogen to promote flowering over foliage. |
| Fruit Formation | 20-50 days (varies greatly by variety) | – Consistent watering (avoid fluctuations). – Sunlight is crucial for fruit ripening. – Harvest when fruit reaches desired ripeness. |
Sunlight
Sunlight is essential for the growth and development of tomato plants. Tomato plants require at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day to thrive. Sunlight provides the energy for photosynthesis, a process by which plants convert sunlight into energy to fuel growth. Insufficient sunlight can lead to weak and spindly plants, delayed flowering, and poor fruit production.
Temperature
Temperature plays a crucial role in tomato plant growth. Tomatoes prefer warm temperatures between 70°F (21°C) and 85°F (29°C). Cooler temperatures can slow down growth, while excessive heat can stress the plants and inhibit fruit production. It is important to choose the appropriate tomato varieties that are suited for the specific temperature range of your region.
Watering
Proper watering is essential for tomato plant growth. Tomato plants need consistent moisture to ensure the uptake of essential nutrients and maintain optimal cell function. Over-watering can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases, while under-watering can cause stress and stunted growth. It is important to water tomato plants thoroughly, allowing the soil to dry slightly between watering intervals to promote deep root development.
Soil
The quality of the soil significantly affects tomato plant growth and productivity. Tomatoes thrive in well-draining soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.8. The soil should be rich in organic matter and nutrients, providing a favorable environment for root growth and nutrient absorption. Regular soil testing can help identify any deficiencies and guide the appropriate amendments. Additionally, proper soil preparation, such as loosening the soil and removing weeds, is essential to create an optimal growing environment for tomatoes.
Fertilizer
Fertilizing tomato plants is crucial for providing the necessary nutrients for growth and fruit production. Tomatoes have specific nutrient requirements, with nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) being the main elements needed in varying quantities at different growth stages. Organic or synthetic fertilizers can be used, and it is important to follow the recommended application rates and timing to prevent over-fertilization and potential damage to the plants. Regular soil testing can help determine the nutrient needs of tomato plants and guide appropriate fertilizer applications.

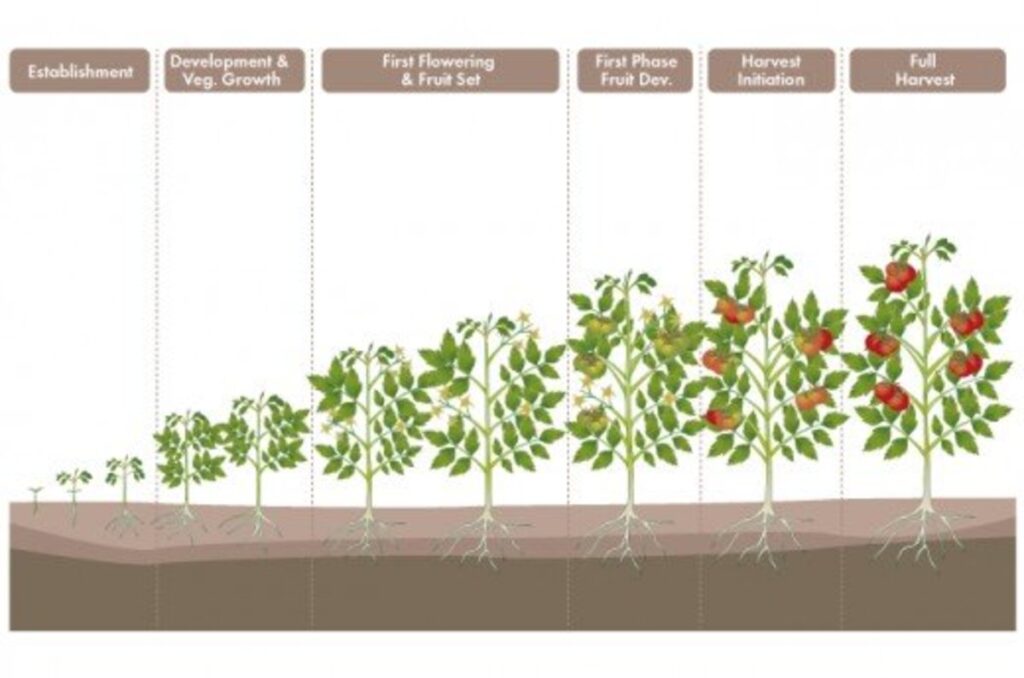
Stages of Tomato Plant Growth
Understanding the different stages of tomato plant growth is essential for providing appropriate care and maximizing yield. Tomato plants go through several distinct growth stages:
Germination
The germination stage is the beginning of a tomato plant’s life cycle. It starts when the seed absorbs water and swells, eventually leading to the emergence of the radicle, the first root of the plant. Factors that affect germination include seed quality, temperature, moisture levels, air supply, and light exposure.
Seedling Stage
The seedling stage occurs once the germinated seeds have developed into young plants with true leaves. At this stage, seedlings require specific care in terms of light intensity, temperature, watering, and possibly transplanting into larger containers. Providing adequate light and maintaining optimal temperature and moisture levels are crucial for healthy seedling growth.
Vegetative Stage
The vegetative stage is characterized by rapid vegetative growth, where the tomato plant develops an extensive root system and foliage. Care during this stage involves pruning to remove side shoots, fertilizing to provide necessary nutrients for growth, staking or trellising to support the plant, proper watering to maintain consistent moisture levels, and pest and disease control measures to protect the plant’s health.
Flowering Stage
The flowering stage is considered a critical phase in tomato growth, as it determines the potential fruit yield. Factors that influence flowering include pollination, environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, pruning to remove excessive foliage that may inhibit flower development, and adequate fertilization to ensure the availability of necessary nutrients for fruit formation.
Fruit Formation
After successful pollination, tomato flowers develop into fruit. The timeframe for fruit formation varies depending on the tomato variety and environmental conditions. Factors that influence fruit ripening include temperature, sunlight exposure, and the availability of water and nutrients. Harvesting should occur when the tomatoes reach the desired level of ripeness, which can vary depending on personal preference and intended use.
In conclusion, tomato plant growth is influenced by several factors, including sunlight, temperature, watering, soil quality, and fertilization. Understanding the different stages of tomato plant growth, from germination to fruit formation, allows for appropriate care and management. By providing optimal conditions and addressing specific requirements during each stage, gardeners can promote healthy tomato plant growth and maximize fruit production.