Apple tree cultivation is a worthwhile endeavor for those seeking to harvest their own delicious and nutritious fruit. However, it is crucial to understand the time and patience required for an apple tree to reach its full potential and begin bearing fruit. In this article, you will gain valuable insights into the timeline of apple tree growth and the various factors that influence the time it takes for an apple tree to produce apples. Understanding the intricate process will equip you with the knowledge necessary to nurture an apple tree and reap the rewards of a bountiful harvest.
Factors that affect the time taken for an apple tree to produce apples

Apple tree variety
The variety of the apple tree plays a crucial role in determining the time taken for it to start producing apples. Different apple varieties have varying growth and fruiting habits. Some varieties are early-season, meaning they produce fruit earlier in the year, while others are mid or late-season varieties and bear fruit later in the growing season. It is important to choose the right apple variety based on your desired harvest timeframe.
Environmental conditions
The environmental conditions where the apple tree is grown can significantly impact its fruiting timeline. Factors such as sunlight availability, temperature requirements, humidity levels, and wind exposure play a vital role in the growth and development of the tree. Apple trees require a sufficient amount of sunlight to produce energy through photosynthesis, which is essential for fruit production. Temperature extremes or inadequate humidity levels can hinder the tree’s ability to set fruit, impacting its overall fruiting timeline.

Climatic factors
Climatic factors also influence the time taken for an apple tree to bear fruit. Each apple variety has different chilling hour requirements, which is the number of hours the tree needs to be exposed to temperatures below a certain threshold during its dormant period. The suitable hardiness zones for a particular variety should be considered to ensure the tree can withstand the local climate. Frost and freeze events can damage the tree’s blossoms, potentially leading to a delay or absence of fruit production.
Soil type and fertility
The type and fertility of the soil in which the apple tree is planted directly impact its ability to produce apples. Well-drained soil is essential as excessive moisture can suffocate the roots and hinder nutrient uptake. Nutrient-rich soil is crucial for the tree’s overall health and fruit production. The soil’s pH level also plays a role, with most apple trees preferring a slightly acidic soil (pH range of 6.0 to 6.5). Soil amendments and organic matter can be added to enhance soil fertility, ensuring optimal conditions for apple production.

Tree age and maturity
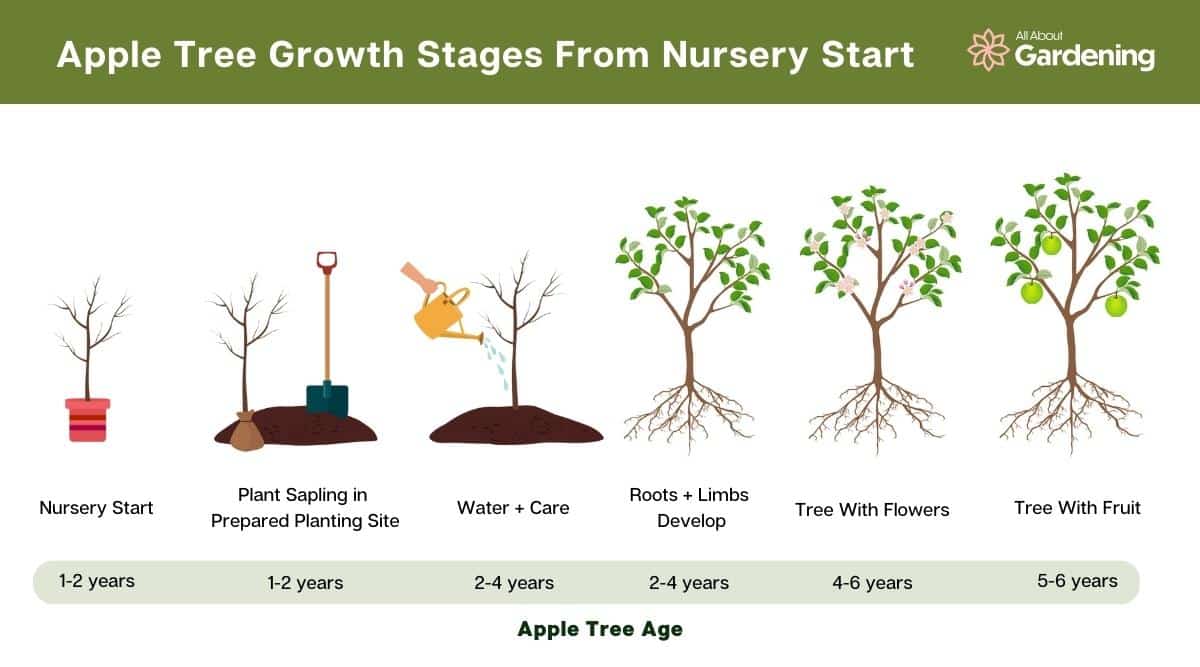
The age and maturity of an apple tree influence the time it takes for it to produce apples. During the establishment period, which typically lasts for the first three to five years after planting, apple trees focus on root and branch development rather than fruit production. Young trees usually take a few years before they start bearing fruit. As the tree matures, it goes through a phase of increased fruit production, reaching its peak production capacity. However, over time, apple trees may experience a decline in productivity, especially if they are not adequately cared for.
Pollination
Pollination is a critical factor affecting apple tree fruiting. Most apple trees are not self-pollinating, meaning they require a compatible pollinizer to transfer pollen from one flower to another. Cross-pollination between different apple varieties is often necessary for optimal fruit set. Bees and other pollinators play a vital role in the pollination process by transferring pollen from the male parts (anthers) of one flower to the female parts (stigma) of another flower. Without proper pollination, the apple tree may not produce fruit or only produce limited quantities.

Pruning and training
Pruning and training practices for apple trees have a significant impact on their fruiting timeline. Pruning is essential to remove dead or diseased branches, improve air circulation, and shape the tree for optimal fruit production. Different techniques, such as heading cuts and thinning cuts, are employed to encourage the growth of strong and productive branches. Training systems, like the central leader or espalier, are used to guide the tree’s growth pattern. Proper pruning and training promote an open canopy, which allows light penetration and increases the chances of fruit bud development.
Nutrition and fertilizer
Providing the apple tree with adequate nutrition is crucial for its growth and fruiting. Apple trees require essential nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese. Fertilizer application should be done based on soil test results to ensure the right balance of nutrients. Timing and frequency of fertilization vary depending on the tree’s needs and the specific fertilizer used. Deficiency symptoms, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth, should be monitored, and corrective measures, like targeted fertilizer applications or soil amendments, should be taken promptly.
Disease and pest control
Effective disease and pest control measures are vital for apple tree health and fruiting. Various diseases, including apple scab, powdery mildew, and fire blight, can significantly impact fruit production if left unchecked. Regular tree inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of disease or pest infestations. Timely application of appropriate treatments, such as fungicides or insecticides, can help prevent or manage these issues. Maintaining a healthy and disease-free tree is essential for consistent fruiting.
Tree health and overall care
Providing proper care and attention to the apple tree promotes its overall health and, in turn, fruitful production. Regular tree inspections allow for early detection of any issues, ensuring prompt intervention. Effective watering practices, such as deep and infrequent irrigation, prevent water stress and promote root development. Mulching around the base of the tree helps retain soil moisture, regulate soil temperature, and suppress weed growth. Protecting the tree from extreme weather events, such as high winds or hail, can prevent damage to blossoms or developing fruit.
In conclusion, several factors influence the time taken for an apple tree to produce apples. The variety of the tree, environmental conditions, climatic factors, soil type and fertility, tree age and maturity, pollination, pruning and training, nutrition and fertilizer, disease and pest control, and overall tree health are all interconnected and play important roles in determining the fruiting timeline. By understanding and managing these factors effectively, growers can optimize apple production and enjoy a bountiful harvest.