You’re in for a treat as we explore the seasonality of green grapes, those crisp and refreshing fruits that leave a burst of flavor in your mouth. Have you ever wondered when the perfect time is to indulge in these green gems? Look no further, as we unravel the answer to the age-old question: when are green grapes in season? Brace yourself for a journey through grape-growing regions and the peak times to savor these delicious fruits. Get ready to satisfy your cravings and embrace the sweet taste of nature’s bounty.

The Seasonality of Green Grapes
Green grapes are a delightful and refreshing fruit that many people enjoy. But have you ever wondered when exactly green grapes are in season? Understanding the timing of green grape seasonality is essential for both consumers and grape growers alike. In this article, we will delve into the various factors that influence the seasonality of green grapes, explore the different varieties of green grapes, and examine global and regional variations in grape seasonality. Additionally, we will discuss the impact of climate on green grape seasonality and the availability and market demand of these delicious fruits.
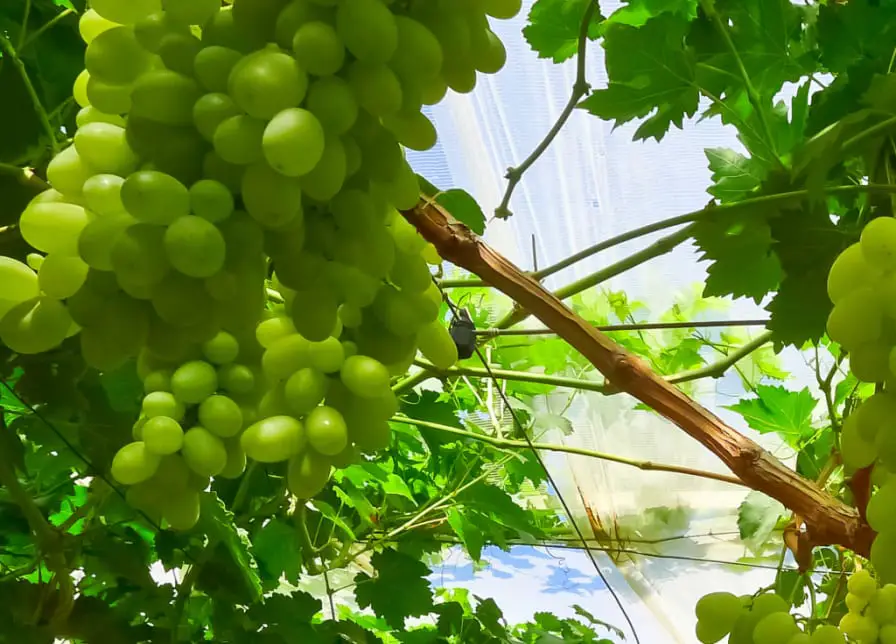

Understanding the Timing of Green Grapes
Classification of Grape Seasons
Grape seasons are typically classified into three categories: early season, mid-season, and late season. These classifications help grape growers and consumers understand when to expect the availability of different grape varieties. Each category has its own distinct characteristics and harvest times, allowing for a diverse selection of green grapes throughout the year.
Typical Months of Green Grape Harvest
In general, green grapes are harvested during the summer and early fall months. The exact months may vary depending on the specific grape variety and geographical location. However, it is common to find green grapes appearing in grocery stores and farmers’ markets from late spring to early autumn. This wide harvesting window ensures that green grapes are readily available for consumers during the warmer months when the demand for refreshing fruits tends to be higher.
Variations in Hereditary and Environmental Factors
The timing of green grape seasonality can be influenced by a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. Grape varieties have inherent characteristics that determine their growth and fruiting patterns. Some varieties naturally exhibit early or late season characteristics, while others fall into the mid-season category. Additionally, environmental factors such as temperature, sunlight, and climate conditions play a crucial role in determining the specific timing of green grape harvests.

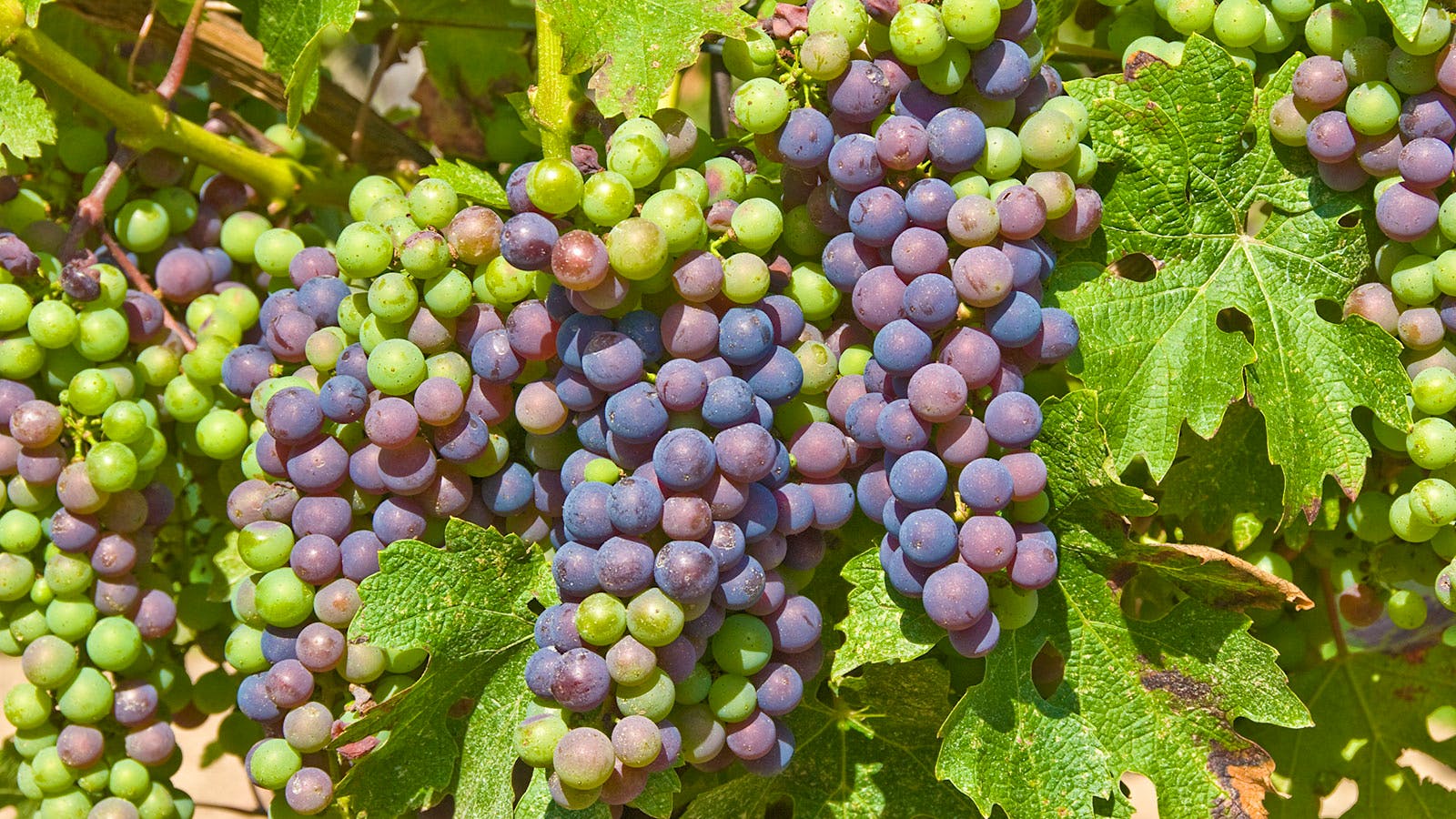
Factors Influencing Grape Seasonality
Climate Conditions
Climate conditions play a significant role in grape seasonality. Green grapes thrive in moderate to warm climates, where they receive a sufficient amount of sunlight and heat. The availability of these favorable conditions enables the grapes to develop and ripen properly. Regions with Mediterranean-like climates, such as California, Southern Europe, and parts of Australia, are known for their ideal grape-growing conditions, resulting in consistent grape seasonality.
Growing Regions
Different grape-growing regions around the world also contribute to variations in green grape seasonality. As grapes are cultivated in various latitudes and climates, each region has its own unique timing for grape harvest. For example, the Southern Hemisphere experiences opposite seasons compared to the Northern Hemisphere, allowing for a year-round availability of grapes worldwide. Understanding these regional variations is important for both consumers and grape growers, as it allows for better planning and anticipation of grape availability.
Cultivation Techniques
The techniques used in grape cultivation can influence the seasonality of green grapes. Grape growers employ various cultivation methods, including trellising, canopy management, and pest control, to optimize grape production. These techniques can affect the growth, development, and ripening of the grapes, ultimately impacting the timing of harvest. Skillful cultivation practices can help grape growers align their harvests with the appropriate season, ensuring high-quality green grapes for consumers.
Pruning and Training of Grapevines
Pruning and training are crucial aspects of grapevine management that also contribute to grape seasonality. Pruning refers to the removal of excess grapevine shoots and leaves, which helps to control grape production and improve fruit quality. Training involves guiding the growth of the grapevine along a trellis system, allowing for better exposure to sunlight and airflow. Proper pruning and training techniques enable grape growers to manage the timing and yield of green grapes, leading to a more consistent and predictable harvest.
Fruit Set and Ripening Period
The fruit set, which refers to the development of grape clusters, and the subsequent ripening period are vital factors in determining green grape seasonality. Environmental conditions, such as temperature and moisture, during the flowering and fruit set stages can influence the number of grape clusters that successfully develop. Similarly, the ripening period is affected by climate factors, with warmer temperatures accelerating the ripening process. Grape growers carefully monitor these stages to ensure optimal fruit set and ripening, allowing for a well-timed harvest.

Varieties of Green Grapes