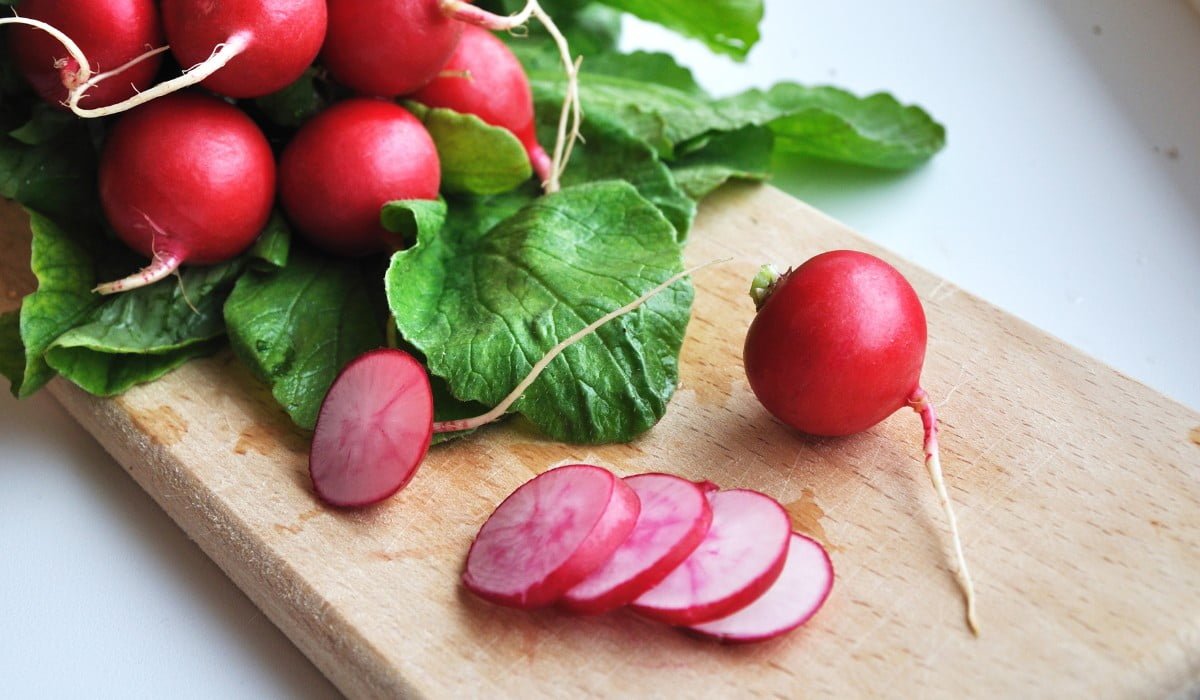
Have you ever taken a bite of a radish and been taken aback by its unexpected spiciness? Well, you’re not alone. Radishes, those vibrant and crisp root vegetables, can pack quite a fiery punch. But have you ever wondered why? In this article, we will delve into the fascinating science behind the heat of radishes, exploring the compounds and biological processes that give them their spicy kick. Get ready to have your taste buds ignited as we uncover the secrets of these fiery little vegetables.
The Spicy Side of Radishes: Exploring the Science Behind Their Heat
Radishes, commonly known for their bright colors and crisp texture, also possess a surprising amount of heat. If you’ve ever taken a bite of a radish expecting a milder taste, only to be hit with a fiery kick, you may have wondered what makes radishes spicy. In this article, we will delve into the science behind the heat of radishes, exploring the chemical compounds responsible for their spiciness, how different varieties differ in spiciness, the factors that affect the spiciness of radishes, and even their culinary and medicinal uses.

What Makes Radishes Spicy?
Radishes owe their spiciness to a group of compounds that are responsible for the heat in many other spicy foods. These compounds cause a burning sensation when they come into contact with the taste receptors in our mouths. So, next time you take a bite of a radish and feel that intense heat, remember that it’s the result of specific chemical components present in these root vegetables.
Chemical Compounds Responsible for the Heat
One of the primary chemical compounds responsible for the spiciness of radishes is capsaicin. Capsaicin is a naturally occurring compound found in many spicy foods, such as chili peppers. It binds to specific receptors in our mouths, triggering a sensation of heat and pain. However, capsaicin is not the only compound found in radishes that contributes to their spiciness.

The Role of Allyl Isothiocyanate
Allyl isothiocyanate is another important compound found in radishes, particularly in the spicy varieties. This compound is responsible for the distinct pungent flavor and heat that radishes possess. When you bite into a radish, the allyl isothiocyanate releases its potent aroma, which can be both invigorating and slightly overwhelming. But why do some radishes have higher concentrations of allyl isothiocyanate than others?
The Effect of Glucosinolates
The spiciness of different radish varieties is determined by the concentrations of specific compounds called glucosinolates. Glucosinolates are a group of sulfur-containing compounds found in cruciferous vegetables, such as radishes. When radishes are crushed or chewed, glucosinolates are broken down into various byproducts, including allyl isothiocyanate. The higher the concentration of glucosinolates, the spicier the radish will be.

How Different Varieties Differ in Spiciness
Radishes come in various shapes, sizes, and colors, and each variety can differ in terms of spiciness. The red radishes, commonly found in grocery stores, tend to have a moderate level of spiciness. On the other hand, the black radishes, often considered the spiciest, pack a real punch with their intense heat. White radishes or daikon radishes, with their milder flavor, offer a refreshing contrast to the spiciness of their colorful counterparts. It’s worth trying different varieties to explore the range of spiciness in radishes.
Factors Affecting the Spiciness of Radishes
While the concentration of glucosinolates plays a crucial role in determining the spiciness of radishes, there are other factors that can also influence their heat levels. Environmental factors, harvesting and storage methods, and even cooking techniques can affect the spiciness of radishes.

Impact of Environmental Factors on Spiciness
The environment in which radishes grow can influence their spiciness. Radishes that are exposed to higher temperatures and dry conditions tend to have more intense flavors. The stress caused by these environmental factors can increase the production of glucosinolates, leading to spicier radishes. So, if you’re looking to add some extra kick to your dishes, opting for radishes grown under stress-inducing conditions might be the way to go.
The Influence of Harvesting and Storage
The timing of harvesting and the storage conditions can also impact the spiciness of radishes. When radishes are harvested too early or stored for an extended period, their glucosinolate levels may not reach their peak, resulting in a milder flavor. Conversely, allowing the radishes to mature fully before harvesting and storing them properly can enhance their spiciness. So, if you prefer your radishes on the spicier side, make sure to pick them at the right time and store them appropriately.

The Effect of Cooking Methods on Spiciness
Cooking radishes can alter their spiciness. When radishes are exposed to heat, the volatile compounds responsible for their pungent flavor and spiciness may dissipate. Therefore, cooking radishes, whether by boiling, roasting, or sautéing, can reduce their heat levels. If you want to retain the spiciness of radishes in your dishes, it’s best to consume them raw or lightly cooked.
Culinary and Medicinal Uses of Spicy Radishes
Despite their intense spiciness, radishes have found a place in various culinary traditions worldwide. They are often used fresh in salads, pickled for added tanginess, or incorporated into stir-fries and curries for a kick of heat. The spicy flavor of radishes can provide a bright and vibrant contrast to milder ingredients in many dishes. Additionally, the heat-inducing compounds in radishes, such as capsaicin and allyl isothiocyanate, have been studied for their potential medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects.
In conclusion, when you bite into a radish and experience that unexpected burst of spiciness, it’s due to the presence of chemical compounds like capsaicin and allyl isothiocyanate. The concentration of these compounds, which is influenced by factors like glucosinolate levels, environmental conditions, harvesting and storage practices, and cooking methods, determines the heat intensity of radishes. So, whether you enjoy radishes for their fiery kick or prefer milder varieties, understanding the science behind their spiciness adds a new layer of appreciation for these versatile root vegetables.