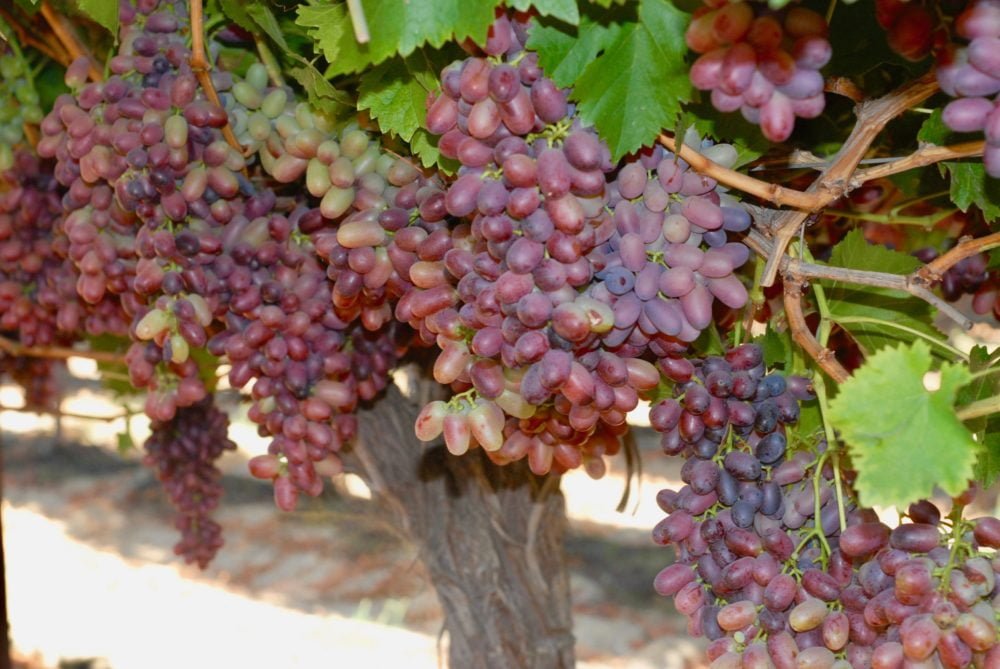
California is renowned for its vast vineyards and high-quality grape production. If you’re curious about when these sweet and juicy fruits are in season in the Golden State, you’ve come to the right place. Understanding the specific timing of grape harvests in California can help both consumers and businesses plan their purchases wisely, ensuring the freshest and most flavorful grapes on their tables. In this article, you will explore the window of grape seasonality in California, discovering the optimal times to enjoy these delectable fruits at their finest. So, let’s delve into the timeline of when grapes are in season in California.
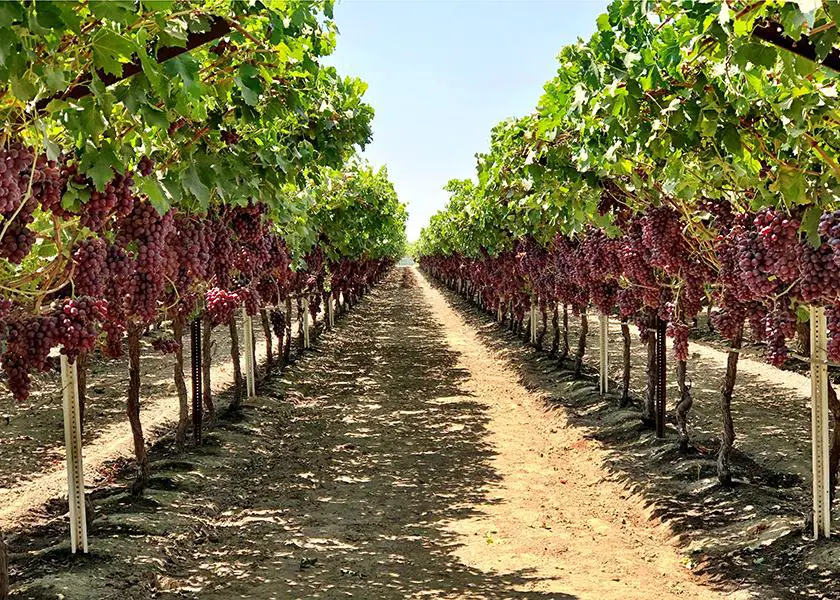

Factors Affecting Grape Season in California
California is renowned for its grape production, supplying a significant portion of the country’s grapes. Several factors influence the grape season in California, ranging from the variety of grapes grown to the timing of harvest. In this article, we will explore the various factors that impact the grape season in California, including the variety of grapes, climate and weather conditions, geographical location, timing of harvest, and the availability of water resources. Understanding these factors is crucial for grape growers and consumers alike.
Variety of Grapes
The variety of grapes grown in California plays a significant role in determining the grape season. Different grape varieties have different maturation periods, resulting in varying seasons. California cultivates a diverse array of grape varieties, including table grapes (Vinifera), raisin grapes (Muscat), and wine grapes (such as Cabernet Sauvignon and Chardonnay). Each variety has its own specific season, ensuring a continuous supply of grapes throughout the year.

Climate and Weather Conditions
The climate and weather conditions in California greatly impact the grape season. California is known for its Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild winters. This climate creates an ideal environment for grape cultivation, allowing the grapes to thrive. However, variations in temperature and precipitation can influence the grape season. Heatwaves during the growing season can accelerate the ripening process, leading to an earlier grape season. Conversely, cool and wet weather conditions can delay the grape season.
Geographical Location
California’s vast geographical area and diverse landscapes contribute to variations in the grape season across different regions. The state can be divided into several distinct wine-growing regions, each with its own microclimates and terroir. The Central Valley, Sierra Foothills, North Coast, and Central Coast are among the prominent grape-growing regions in California. These regions experience variations in temperature, elevation, and soil composition, all of which influence the grape season.

Timing of Harvest
The timing of harvest is a crucial factor in determining the grape season in California. Grape growers carefully monitor the maturation of their grapes to determine the optimal time for harvest. Harvesting too early can result in underripe grapes, while delaying the harvest can lead to overripe grapes. The grape variety, climate conditions, and intended use of the grapes (table grapes, raisins, or winemaking) all impact the timing of harvest. Grape growers strive to achieve the perfect balance of flavors, sugars, and acidity before harvesting their grapes.
Availability of Water Resources
Water availability plays a significant role in the grape season in California. The state faces periodic droughts, and grape growers rely on irrigation systems to provide water to their vineyards. Insufficient water resources can impact the grape season, affecting grape quality and yield. Adequate water resources are crucial for ensuring healthy grapevines throughout the growing season.

Different Grape Varieties and Their Seasons
California cultivates a wide range of grape varieties, each with its distinct season. Here are some of the major grape varieties grown in California and their respective seasons:
Table Grapes (Vinifera)
Table grapes, such as Thompson Seedless and Red Globe, are typically harvested from late July to September. These grapes are primarily enjoyed fresh or used in salads, desserts, and a variety of culinary applications. Table grapes are valued for their sweet, juicy flavor and crisp texture.
Raisin Grapes (Muscat)
Raisin grapes, particularly the Muscat variety, are primarily used for producing raisins. The raisin season typically begins in late July and extends through October. Raisin grapes are allowed to dry on the vine before being harvested and processed into raisins. These grapes offer a unique sweetness and aromatic flavor.
Wine Grapes (Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, etc.)
Wine grapes, which include popular varieties like Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, and Pinot Noir, follow specific maturation timelines based on their intended use. The wine grape season typically spans from August to late October, allowing winemakers to harvest grapes at their optimal ripeness for producing various styles of wine.
Grape Season by Region in California
California’s diverse wine-growing regions contribute to the variations in the grape season. Here are some of the prominent grape-growing regions in California and their typical grape seasons:
Central Valley
The Central Valley, one of California’s largest grape-growing regions, experiences a warm and dry climate. The grape season in the Central Valley usually starts in early June and extends into October. This region is known for producing a wide variety of grapes, including table grapes, raisin grapes, and wine grapes.
Sierra Foothills
The Sierra Foothills region, known for its rugged terrain and higher elevation, offers a unique grape-growing environment. The grape season in the Sierra Foothills typically begins in late July and continues through October. This region specializes in growing wine grapes, including Zinfandel and Syrah, known for their bold flavors and distinctive characteristics.
North Coast
The North Coast region, encompassing renowned wine regions like Napa Valley and Sonoma County, is famous for its premium wine production. The grape season in the North Coast starts in late July or early August and lasts until October. This region’s cooler climate and diverse terroir create ideal conditions for growing high-quality wine grapes like Cabernet Sauvignon and Chardonnay.
Central Coast
The Central Coast region, stretching from Santa Barbara County to Monterey County, boasts a coastal influence that shapes its grape-growing season. The grape season on the Central Coast typically begins in August and continues into November. This region is known for producing a wide range of grape varieties, including Pinot Noir, Syrah, and Chardonnay.

Early Season Grapes in California
Early-season grapes offer the first taste of the grape season in California. These grape varieties are characterized by their ability to ripen earlier than other varieties, providing an early harvest. Some of the early-season grapes in California include:
Early Muscat
The Early Muscat grape variety ripens in late June to early July, marking the beginning of the grape season in California. These grapes are aromatic and have a sweet flavor. They are often enjoyed fresh and used in desserts and fruit salads.
Perlette
Perlette grapes are typically harvested in late July or early August. These white seedless grapes are popular for their juicy texture and mildly sweet flavor. Perlette grapes are frequently used in wine production, as well as eaten fresh or added to salads and other dishes.
Albariño
Albariño is a white wine grape variety that ripens in early to mid-August. While primarily used for winemaking, Albariño grapes can also be enjoyed fresh. They offer a crisp acidity and distinct flavors of stone fruit and citrus.
Mid-Season Grapes in California
Mid-season grapes bridge the gap between early and late-season varieties, providing a continuous supply of grapes during the peak of the grape season. Here are some mid-season grape varieties commonly grown in California:
Ruby Seedless
Ruby Seedless grapes ripen in late August and early September. These red seedless grapes are known for their vibrant color, sweet flavor, and juicy texture. They are enjoyed fresh and often used in jams, jellies, and juices.
Flame Seedless
Flame Seedless grapes are typically harvested from late August to early September. These red seedless grapes are prized for their crisp texture and sweet, slightly tart flavor. Flame Seedless grapes are a popular choice for snacking, as well as making grape juice and raisins.
Sauvignon Blanc
Sauvignon Blanc grapes, a popular white wine grape variety, typically ripen in late August or early September. These grapes produce aromatic wines with herbaceous and citrus flavors. While predominantly used for winemaking, Sauvignon Blanc grapes can also be enjoyed fresh.
Late Season Grapes in California
Late-season grapes bring the grape season in California to a close, providing a last burst of flavor before the onset of winter. Some of the late-season grape varieties grown in California include:
Crimson Seedless
Crimson Seedless grapes are typically harvested in mid-September to mid-October. These red seedless grapes offer a satisfying crunch, with a sweet and mildly tangy flavor. They are often used in fresh fruit platters, desserts, and preserves.
Autumn Royal
Autumn Royal grapes ripen in October, towards the end of the grape season. These black seedless grapes are prized for their deep color, sweet taste, and juicy texture. Autumn Royal grapes are enjoyed fresh and can also be used in making wine, jams, and desserts.
Zinfandel
Zinfandel grapes, primarily used for winemaking, have a late-season harvest that lasts until mid-to-late October. These grapes produce robust red wines with rich flavors of blackberry, spice, and pepper. Zinfandel grapes require a longer growing season to reach their full ripeness, contributing to the late-season grape harvest.
The Impact of Climate Change on Grape Season in California
Climate change has started affecting the grape season in California, leading to shifts in harvest times, changes in quality and flavor, and effects on vineyard management. These impacts have prompted grape growers to adapt their practices to maintain the integrity of their grapes and wines.
Shifting Harvest Times
Climate change has caused shifts in the timing of harvest for grape growers in California. Rising temperatures during the growing season have resulted in earlier harvest dates for many grape varieties. This shift can impact the overall grape season, as well as the availability of specific grape varieties at particular times.
Changes in Quality and Flavor
The changing climate can also impact the quality and flavor of grapes and wines. Higher temperatures can cause grapes to ripen too quickly, leading to imbalanced sugar and acidity levels. This can result in wines with lower acidity and higher alcohol content. Changes in temperature and weather patterns may also affect the development of desirable flavor compounds in grapes, altering the character of the resulting wines.
Effects on Vineyard Management
Grape growers have had to adapt their vineyard management practices to mitigate the effects of climate change. Strategies such as adjusting irrigation techniques, implementing shade structures, and modifying canopy management have become increasingly important for maintaining grape quality and managing water resources effectively. Vineyard management practices that promote vine health and resilience have become crucial in the face of changing climatic conditions.
The Importance of Timing in Grape Harvesting
Timing is of utmost importance in grape harvesting, as it directly impacts the quality and characteristics of the grapes and the resulting wines. Grape growers meticulously monitor the ripeness of the grapes to determine the optimal time for harvesting. Several factors need to be considered:
Ripeness and Sugars
The ripeness of grapes is often measured by their sugar content, which is measured in Brix. The ideal ripeness varies depending on the grape variety and its intended use (e.g., table grapes, raisins, or winemaking). For table grapes and raisins, a higher sugar content and greater sweetness are desired, while wine grapes require a balance between sugar and acidity for optimal winemaking.
Tannin Development
In the case of red wine grapes, the ripeness of tannins also plays a crucial role. Tannins are a group of compounds present in grape skins and seeds that contribute to the structure and aging potential of red wines. Harvesting grapes at the appropriate time ensures optimal tannin development, resulting in well-structured and balanced wines.
Acidity Levels
Acidity is another important factor to consider when determining the timing of grape harvesting. Acidity provides freshness and balance to wines, particularly white wines. Grape growers aim to harvest grapes when acidity levels are at their optimal range, ensuring bright and vibrant flavors in the resulting wines.
Methods for Extending the Grape Season in California
Grape growers in California employ various techniques to extend the grape season, ensuring a continuous supply of grapes for consumers and maintaining a stable market. Here are some methods commonly used to prolong the grape season:
Crop Thinning
Crop thinning involves selectively removing excess grape clusters from the vine to concentrate the vine’s energy on fewer grapes. This technique helps ensure that the remaining grapes receive ample nutrients and reach optimal ripeness. Crop thinning can be particularly beneficial in cases where a specific grape variety’s growing season needs to be extended.
Canopy Management
Canopy management refers to the manipulation of the vine’s foliage to optimize light exposure and airflow around the grape clusters. By strategically trimming and positioning the vine’s canopy, grape growers can control the grape’s sun exposure and ripening process. This technique can help extend the grape season by slowing down or accelerating ripening, depending on the desired outcome.
Use of Protective Covers
Protective covers, such as shade cloth or netting, can be used to shield grapevines from extreme weather conditions, including excess heat or rain. These covers provide a buffer between the vine and the surrounding environment, helping maintain more stable growing conditions. By mitigating the impact of unfavorable weather, protective covers can contribute to a more extended grape season.
Conclusion
The grape season in California is influenced by several key factors, including grape variety, climate and weather conditions, geographical location, timing of harvest, and water availability. Understanding these factors is crucial for grape growers and consumers alike, as it allows for a better appreciation of the diverse grape industry in California. Climate change poses both challenges and opportunities for grape growers, necessitating adaptations in vineyard management to maintain grape quality and sustainability. Ultimately, the careful timing of grape harvesting ensures the production of high-quality grapes and wines, ensuring the enjoyment of California’s bounty throughout the grape season.