Concord grapes, known for their vibrant purple hue and uniquely intense flavor, have a rich history that dates back to the mid-1800s. These luscious grapes, with their distinctive sweet-tart taste, trace their origins to the United States. Specifically, they were first discovered and cultivated in the quaint town of Concord, Massachusetts. This article delves into the fascinating journey of Concord grapes, exploring their humble beginnings, their significance in American agriculture, and their enduring popularity in the world of winemaking and beyond. Prepare to embark on a journey through time and discover the captivating origins of the beloved Concord grapes.

The History of Concord Grapes
Origins of Concord Grapes in North America
The story of Concord grapes begins in North America, where these delicious fruits are native to the United States. Their origins can be traced back to the early 19th century when Ephraim Wales Bull, a horticulturist from Massachusetts, embarked on a journey to develop a grape variety that could thrive in the harsh New England climate.
Discovery of the Concord Grape variety
After years of dedicated work and experimentation, Bull successfully cultivated a new grape variety that would later be named after his hometown, Concord, Massachusetts. In 1849, he discovered the first Concord grape vine in his garden, distinguishing it from the other grape varieties with its unique characteristics.
Cultivation and popularity of Concord Grapes
Once Bull introduced his new grape variety to the public, its popularity quickly grew. Concord grapes were found to be hardy and able to withstand the colder climates of the northern United States, making them a desirable choice for grape production. Their rich flavor and versatility in various culinary applications further contributed to their popularity among consumers.
Features of Concord Grapes
Appearance
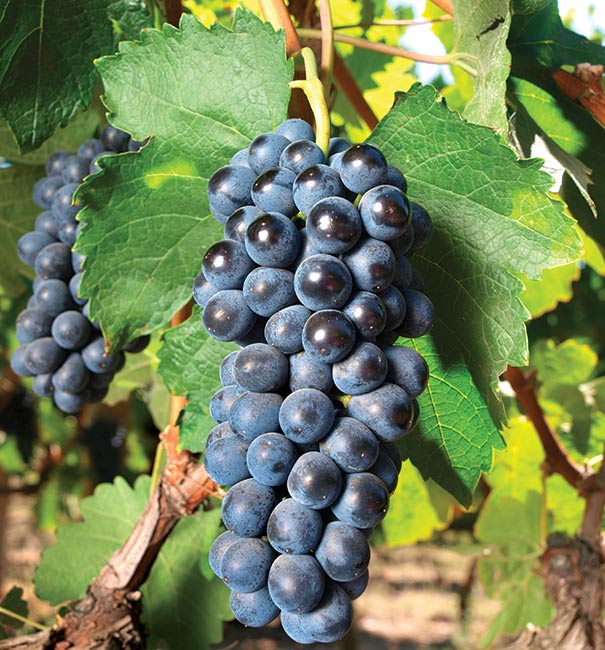
Concord grapes are medium to large in size and famously deep purple in color. They have a thick skin that encases the juicy pulp and seeds. The grapes grow in tight clusters, making them visually appealing and easy to harvest.
Taste
Known for their bold and sweet flavor, Concord grapes have a unique taste profile. They are naturally rich in sugars, providing a delightful burst of sweetness with each bite. The fruit also offers a subtle tartness, adding complexity to its flavor.
Aroma
Concord grapes offer a distinct aroma that is both sweet and musky. The fragrance is reminiscent of ripe berries and can be quite aromatic, making the grapes appealing to the senses.

Growing Regions for Concord Grapes
Native to the United States
As mentioned earlier, Concord grapes are native to the United States due to their discovery and cultivation by Ephraim Wales Bull in Concord, Massachusetts. They grew well in the New England region, surviving the often harsh and unpredictable weather conditions.
Concord Grapes in New York
While native to Massachusetts, Concord grapes found their true home in New York. The unique climate and fertile soil of the Finger Lakes region of New York proved to be ideal for the cultivation of these grapes. Today, New York is the largest producer of Concord grapes in the United States.
Concord Grapes in California
In addition to their success in the Northeast, Concord grapes soon made their way to the fertile lands of California. The temperate climate and longer growing season of California allowed for the cultivation of high-quality Concord grapes. The state’s Central Valley, in particular, became a prominent region for Concord grape production.
Other regions for Concord Grape cultivation
Though New York and California are the main players in Concord grape cultivation, other regions in the United States have also adopted the grape variety. The Great Lakes region, including Michigan and Ohio, has seen success with Concord grapes, thanks to the favorable conditions found near the lakes.
Cultivation of Concord Grapes
Climatic requirements
Concord grapes thrive in temperate climates where summers are warm and winters are cold. They require a frost-free growing season of approximately 150 to 180 days. The ideal temperature range for their cultivation is between 70°F to 90°F (21°C to 32°C) during the growing season.
Soil preferences
Concord grapes prefer well-drained soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. They can tolerate a variety of soil types, including sandy loam, loam, and clay loam. The soil should have good water retention capabilities to ensure adequate hydration for the grapevines.
Planting and propagation
Concord grapes can be propagated through both cuttings and seedlings. However, the most common method is by planting rooted grapevine cuttings. The cuttings are typically planted in early spring, once the soil has thawed and the risk of frost has passed. It is important to provide proper support, such as trellises or wire frameworks, to ensure the growing vines have a structure to climb.
Maintenance and care
Proper pruning is essential to maintain healthy and productive Concord grapevines. Pruning should be done during the dormant season, typically in late winter or early spring. It helps to control the vine’s growth, improve air circulation, and maximize grape production. Regular watering and fertilization are also important to support vigorous growth and fruit development.

Harvesting Concord Grapes
Timing of harvest
Concord grapes are typically harvested in late summer or early fall, depending on the specific region and local climate. The grapes should be fully ripened, with a deep purple color and slightly softened texture. Harvesting too early may result in underripe grapes, while waiting too long can lead to overripe or shriveled fruit.
Methods of harvesting
Concord grapes are harvested by hand, as the clusters grow close together and need delicate handling to avoid damaging the fruit. Skilled workers carefully cut the clusters from the vine using pruning shears or similar tools. The harvested grapes are then carefully transferred to baskets or crates to prevent bruising or crushing.
Post-harvest processing
After the grapes are harvested, they undergo various forms of post-harvest processing depending on their intended use. Some grapes are sold fresh for immediate consumption, while others are processed into juice, jelly, or wine. The processing methods may include crushing, pressing, filtering, and pasteurization to ensure quality and safety.
Uses of Concord Grapes
Fresh Consumption
One of the simplest and most enjoyable ways to enjoy Concord grapes is by eating them fresh. Their deliciously sweet and tart flavors make them a popular snack on their own or added to fruit salads and cheese platters. Some people even freeze them to enjoy as a refreshing treat during the warmer months.
Wine Production
Concord grapes have long been a favorite choice for winemaking, particularly in the United States. Their bold flavor and high sugar content make them suitable for producing rich, full-bodied red wines. Concord wine is often described as having a distinct “foxy” character, which sets it apart from other grape varieties.
Juice and Jelly Production
Concord grapes are also widely used in the production of grape juice and jelly. The grapes are pressed to extract the juice, which can be enjoyed on its own or used as a base for other beverages and culinary creations. Concord grape jelly, with its intense flavor and vibrant color, is a popular spread for toast, pastries, and sandwiches.

Health Benefits of Concord Grapes
Rich in Antioxidants
Concord grapes are packed with antioxidants, including resveratrol and flavonoids. These compounds help protect the body’s cells from oxidative damage caused by harmful free radicals. Regular consumption of Concord grapes may contribute to overall health and well-being.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Studies have suggested that the antioxidants found in Concord grapes may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. They may help reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and improve blood circulation. These benefits could potentially lower the risk of heart disease and improve overall heart health.
Potential Anti-Cancer Properties
Some research has explored the potential anti-cancer properties of Concord grapes. The grape’s high antioxidant content, particularly resveratrol, has shown promise in inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the risk of certain types of cancer. However, further studies are needed to fully understand and confirm these potential benefits.
Concord Grape Products
Concord Grape Juice
Concord grape juice is a popular and widely available product made from the pressing of Concord grapes. It retains the grape’s natural sweetness and flavor, offering a refreshing and nutritious beverage option. The juice can be enjoyed on its own, mixed with other juices, or used as an ingredient in cocktails and smoothies.
Concord Grape Jam
Concord grape jam is a classic spread made from cooked Concord grapes and sweetened with sugar or other natural sweeteners. The jam’s vibrant purple color and intense flavor make it a delightful addition to toast, biscuits, and pastries. The natural pectin present in Concord grapes gives the jam its desired consistency.
Concord Grape Concentrate
Concord grape concentrate is a concentrated form of the grape’s juice, obtained by removing water through evaporation. It is often used as a flavoring or sweetener in various food and beverage products, such as candies, ice creams, and sauces. The concentrate provides a concentrated burst of the grape’s distinctive flavor.

Celebrating Concord Grapes
Concord Grape Festival
To celebrate the rich history and importance of Concord grapes, many communities hold annual Concord Grape festivals. These festivals offer a variety of activities, including grape-picking contests, grape stomping, live music, food stalls, and wine tastings. They are a great way for both locals and visitors to come together and appreciate the beauty and flavor of Concord grapes.
Concord Grape Recipes
Concord grapes are a versatile ingredient that can be used in a wide range of culinary creations. From pies and tarts to salads and sauces, there are endless possibilities for incorporating these grapes into delicious recipes. Some popular Concord grape recipes include grape pie, grape salsa, and roasted grape and goat cheese crostini.
Challenges in Concord Grape Cultivation
Disease susceptibility
Concord grapes, like many other grape varieties, are susceptible to various diseases, including fungal infections and grapevine viruses. The most common diseases affecting Concord grapes include powdery mildew, downy mildew, and black rot. Proper pest management, regular pruning, and the use of disease-resistant varieties are important for preventing and controlling these diseases.
Bird and pest control
Birds and other pests are also a challenge in Concord grape cultivation. Birds, in particular, can cause significant damage to grape clusters by feeding on the ripe fruit. To prevent bird damage, growers often use netting or scare devices to deter birds from accessing the grapevines. Additionally, pest control measures may be necessary to address potential insect infestations.
Weather-related challenges
Concord grapes are vulnerable to extreme weather conditions, including frost, hailstorms, and excessive rains. Late spring frost can destroy new buds and delay the grapevine’s growth, affecting the overall productivity. Hailstorms can cause physical damage to the grapes, leading to reduced quality and yield. Growers must take precautions and implement protective measures, such as using covers or sprinkler systems, to mitigate these weather-related risks.
In conclusion, the Concord grape has a rich and fascinating history in North America. From its humble beginnings as a horticulturist’s experiment to its prominence in the grape industry, Concord grapes have become a beloved part of American agriculture and culinary traditions. With their attractive appearance, delicious taste, and numerous health benefits, Concord grapes continue to captivate both growers and consumers alike. Whether enjoyed fresh, transformed into wines, juices, or jams, or celebrated at grape festivals, the Concord grape remains a true treasure of the American agricultural landscape.