Apples have long been hailed as a staple of a nutritious diet, promising an array of health benefits and a refreshing burst of flavor. However, their acidic nature often brings about concerns regarding its impact on our well-being. In this article, you will uncover the true extent of apple’s acidity levels, unraveling the science behind their tangy taste and determining whether it poses any risks to your health. Prepare to discover the truth behind the pH of everyone’s favorite fruit.

The pH Scale and Acidity
Explanation of the pH scale
The pH scale is a scale used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being highly acidic, 14 being highly alkaline, and 7 considered neutral. The pH level is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. A lower pH indicates a higher concentration of hydrogen ions and thus a higher level of acidity. Acidity is an important characteristic to consider when discussing fruits, including apples, as it can impact their taste, texture, and potential health benefits.
The meaning of acidity
Acidity refers to the presence of acid in a substance. In the context of fruits, such as apples, acidity plays a crucial role in their flavor profile. Acidity provides tartness and a distinct tangy taste that can enhance the overall eating experience. The level of acidity in apples can vary depending on factors like the variety, ripeness, and growing conditions. Understanding the acidity of fruits is not only important for culinary purposes but also for potential health benefits that may be associated with consuming acidic foods.
pH levels and acidity in fruits
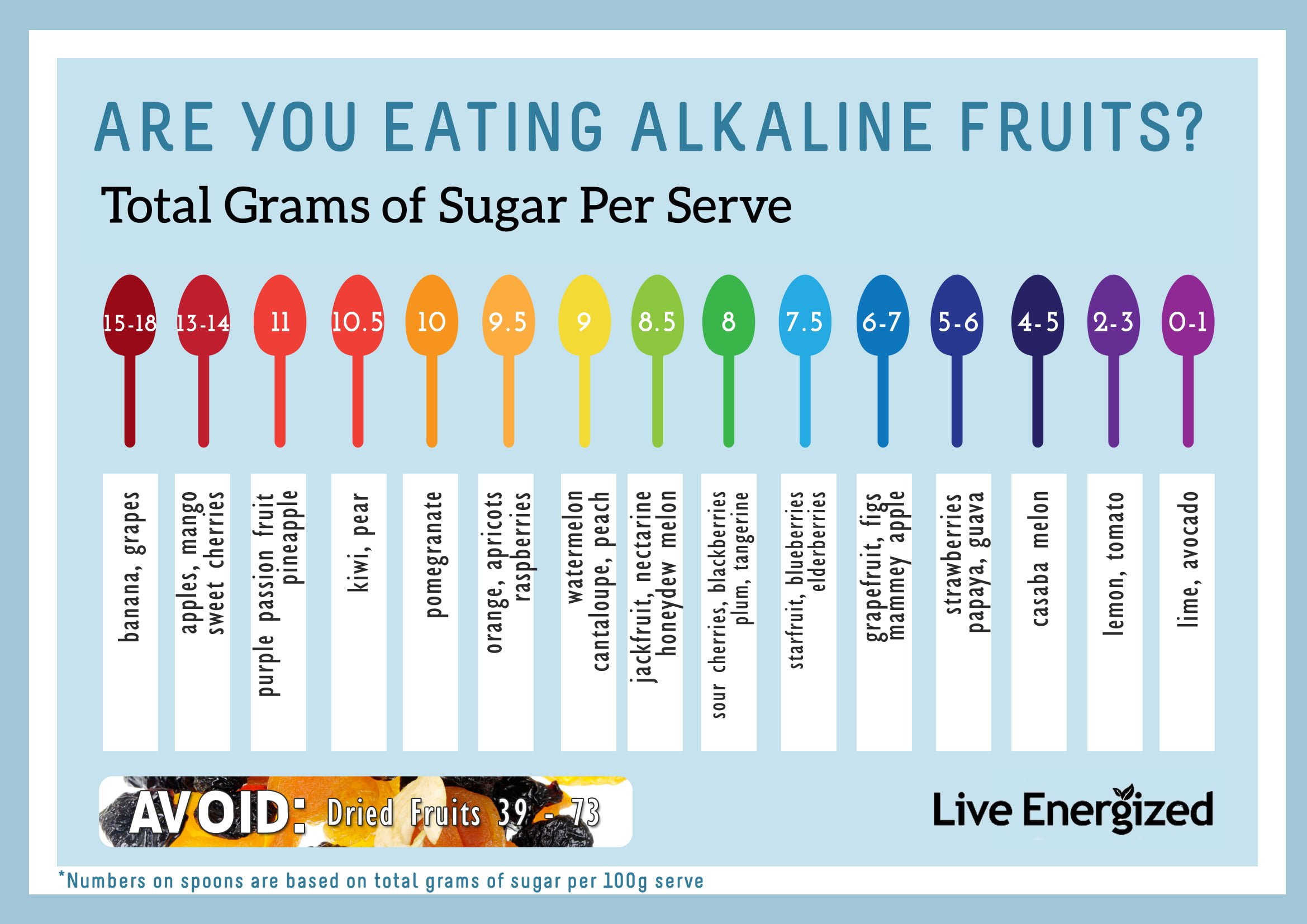
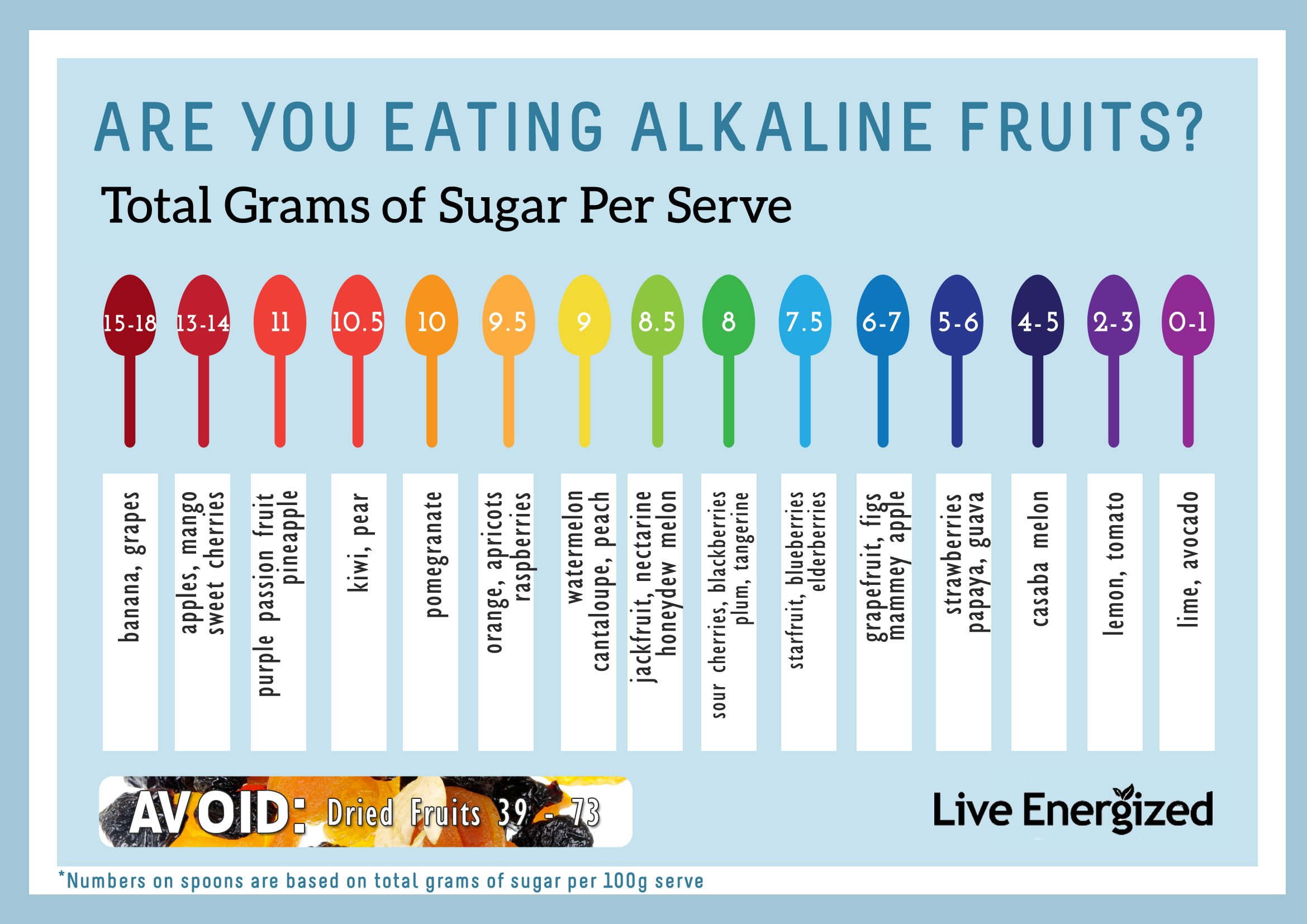
Fruits exhibit varying levels of acidity, which can be measured using the pH scale. While the pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, most fruits fall within the range of 2 to 4 on the pH scale, indicating moderate to high levels of acidity. The acidity in fruits comes from organic acids, such as citric acid, malic acid, and tartaric acid. These acids contribute to the flavor and preservation of fruits. Apples, with their crisp, refreshing taste, are known to have a slightly acidic pH level, typically ranging from 3 to 4, making them moderately acidic fruits.
pH Level of Apples
Factors affecting the pH level of apples
Several factors influence the pH level of apples. One significant factor is the variety of apple. Different apple varieties have varying levels of natural acidity due to their genetic makeup. Environmental conditions, such as soil pH, climate, and sunlight exposure, can also impact the acidity of apples. The stage of ripeness at which the apple is picked can also affect its pH level. Generally, as apples ripen, they tend to become less acidic. Lastly, post-harvest storage and handling practices can influence the acidity of apples.
Types of apples and their pH levels
There are numerous apple varieties, each with its unique characteristics, including flavor and acidity. For example, Granny Smith apples are known for their higher acidity, typically having a pH level of around 3.0 to 3.3. On the other hand, Golden Delicious apples have a slightly lower acidity, with pH levels ranging from 3.3 to 3.6. Other popular apple varieties, such as Pink Lady, Fuji, and Gala, also have distinct levels of acidity, contributing to their specific flavors and textures.
How acidity varies within apple varieties
Even within a specific apple variety, acidity can vary. This variability is mainly driven by the growing conditions and the stage of ripeness. Apples grown in cooler climates or higher altitudes tend to have a higher acidity level than those grown in warmer regions. The time of harvest also affects apple acidity, with earlier harvested apples often having a higher acidity compared to fully ripe ones. It is worth noting that some apple enthusiasts prefer the crisp tartness of slightly more acidic apples, while others may favor sweeter, less acidic varieties.
Potential Health Benefits of Acidic Foods
Acidic foods and digestion
Acidic foods, including apples, can have various effects on digestion. The natural acids present in apples, such as malic acid and tartaric acid, can stimulate the production of digestive enzymes. These enzymes promote the breakdown of food particles and aid in the absorption of nutrients. The acidity in apples may contribute to improved digestion and alleviate certain digestive issues like bloating and indigestion. However, it is important to note that excessive consumption of acidic foods can have adverse effects on digestion for some individuals, particularly those with underlying digestive conditions.
The body’s response to acidic foods
When acidic foods are consumed, the body aims to maintain a stable pH level in the blood and other bodily fluids. It achieves this by utilizing buffering systems, which involve the release of bicarbonate ions to neutralize excess acidity. This buffering process helps regulate the body’s pH, preventing it from becoming too acidic or too alkaline. However, the body’s ability to maintain this balance can vary among individuals, and consuming highly acidic foods in excess may put additional strain on the buffering systems.
Nutritional composition of apples
Apples are not only a good source of acidity but also provide essential nutrients. They are low in calories and fat, making them a healthy snack option. Apples are rich in dietary fiber, which promotes digestion and keeps you feeling full. They also contain vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function and aids in collagen production. Additionally, apples offer various minerals such as potassium, which plays a role in maintaining heart health, and small amounts of other vitamins like vitamin A, vitamin E, and vitamin K.
Impact of Acidity on Flavor
Relationship between acidity and flavor
Acidity plays a vital role in shaping the flavor of fruits, including apples. It contributes to the overall taste profile by providing a pleasant tartness and balancing the sweetness. The acidity in apples enhances their natural flavors, making them more vibrant and refreshing. It adds complexity and depth to apple-based dishes, whether in savory recipes or sweet desserts.
Differences in taste based on pH levels
The taste of apples can vary based on their pH levels. Apples with a higher acidity level tend to have a sharper, tangier taste, often described as sour or tart. In contrast, apples with a lower acidity level exhibit a milder, sweeter taste profile. The balance between sweetness and acidity is what gives apples their distinct flavor and makes them enjoyable to eat in various preparations.
The balance between sweet and sour
The balance between sweetness and sourness is a crucial aspect of apple flavor. This balance is determined by the specific variety and the stage of ripeness. Apples with higher acidity are known for their delightful tartness, which can be particularly appealing in baking or pairing with savory ingredients. Conversely, apples with lower acidity levels, such as Red Delicious or Fuji, offer a more pronounced sweetness, making them enjoyable for fresh consumption or in desserts.

Effects of Acidic Foods on Teeth
Acidic foods and tooth enamel
Consuming acidic foods, including apples, can have implications for dental health. The acids present in foods can erode the protective layer of tooth enamel over time. While apples themselves are not highly erosive, their acidity can contribute to enamel wear when consumed in excess or combined with poor oral hygiene practices. Maintaining good dental hygiene, such as regular brushing and flossing, along with moderation in acidic food consumption, can help mitigate potential dental damage.
Enamel erosion and dental health
Enamel erosion refers to the gradual wearing away of tooth enamel, which can lead to tooth sensitivity, discoloration, and an increased risk of tooth decay. Acidic foods, especially when consumed frequently or in large quantities, can contribute to this erosion. It is important to note that the severity of enamel erosion depends on various factors, including the individual’s oral hygiene practices, the overall diet, and the acidity level and duration of exposure to acidic foods.
Tips for minimizing dental damage
To minimize the impact of acidic foods on dental health, it is advisable to practice good oral hygiene habits. Regular brushing with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and rinsing with an alcohol-free mouthwash can help remove acid-containing food particles and maintain overall oral health. Additionally, it is recommended to wait at least 30 minutes after consuming acidic foods before brushing, as immediate brushing can further weaken the enamel. Limiting the frequency and duration of acidic food consumption and using a straw when drinking acidic beverages can also help reduce the contact of acids with tooth surfaces.
Apples as a Source of Vitamin C
The importance of vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a crucial nutrient that the body needs for overall health and proper functioning. It is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage, supports the immune system, aids in collagen production, and assists in iron absorption. Since the human body cannot produce vitamin C on its own, it is essential to obtain an adequate amount through the diet.
Vitamin C content in apples
Apples are a good source of vitamin C, albeit not as high as some other fruits like oranges and strawberries. The vitamin C content in apples varies depending on the variety and ripeness. On average, a medium-sized apple provides about 8-10% of the daily recommended intake of vitamin C for an adult. While the concentration may not be exceptionally high, consuming apples as part of a balanced diet contributes to overall vitamin C intake and its associated health benefits.
Contributing to overall health
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, from maintaining healthy skin and promoting wound healing to supporting the immune system’s defense against infections. As an antioxidant, vitamin C helps combat free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage. Including apples, with their vitamin C content, in your diet can support overall health and contribute to the body’s antioxidant defense system.
Choosing Apples Based on Acidity
Preferences for acidic or less acidic apples
When choosing apples, personal taste preferences play an important role in determining whether to opt for acidic or less acidic varieties. Some individuals enjoy the crisp, tangy flavor of more acidic apples, while others prefer the delicate sweetness of less acidic options. It can be helpful to try different apple varieties and note the specific flavors and textures that appeal to you. Experimenting with both acidic and less acidic apples enables you to discover your preferred choice for different culinary uses or snacking purposes.
Taste profiles and culinary uses
The acidity level of apples affects their taste profiles and culinary applications. More acidic apples, such as Granny Smith, are commonly used in baking and cooking due to their tartness and ability to hold their shape when cooked. Their acidity provides a balance and contrast when combined with other ingredients. Less acidic varieties, like Golden Delicious or Red Delicious, are often favored for fresh consumption or as ingredients in salads and desserts where a milder, sweeter flavor is desired.
Considerations for specific recipes
Different recipes may call for apples with specific acidity levels to achieve the desired flavor and texture. For instance, a recipe for apple pie may suggest using a mix of tart and sweet apples to create a well-balanced filling. On the other hand, a recipe for a delicate apple tart might require a less acidic apple variety to complement the other flavors. Understanding the acidity levels of different apple varieties can help you make informed choices while preparing specific recipes.
Balancing Acidic Foods in the Diet
Establishing a healthy dietary balance
Maintaining a healthy dietary balance involves considering the overall composition of one’s diet, including the intake of both acidic and alkaline foods. While acidic foods, including fruits like apples, can be part of a nutritious diet, it is essential to balance them with alkaline foods to promote overall well-being. A diet rich in a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps ensure a diverse nutrient intake and supports overall health.
Effects of excessive acidity
Consuming an excessive amount of acidic foods can have potential health implications. In some cases, it may lead to digestive discomfort, heartburn, or acid reflux symptoms. Highly acidic diets, coupled with other lifestyle factors, may also contribute to long-term conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or certain types of kidney stones. It is crucial to strike a balance and consume acidic foods in moderation as part of a well-rounded diet.
Pairing apples with alkaline ingredients
To create a balanced and enjoyable meal, consider pairing apples, with their natural acidity, with alkaline ingredients. Alkaline foods, such as leafy greens, root vegetables, nuts, and legumes, can help neutralize the acids present in more acidic foods. For example, enjoying a salad with fresh apple slices alongside alkaline-rich greens like spinach, kale, or arugula can create a harmonious combination of flavors and nutrients.

Acidity and Apple Storage
Acidity and shelf life of apples
The acidity of apples can impact their shelf life and overall storage quality. Apples with higher levels of acidity tend to have a longer shelf life compared to less acidic varieties. The organic acids naturally present in apples act as preservatives, inhibiting the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms. The higher acidity helps maintain the freshness and crispness of apples for an extended period, making them a favorable choice for long-term storage.
Storage conditions that preserve acidity
Proper storage conditions are crucial for preserving the acidity of apples. Apples should be stored in a cool environment with controlled humidity to prevent them from becoming soft or mealy. Ideally, a temperature range of 32 to 40 degrees Fahrenheit (0 to 4 degrees Celsius) and humidity levels around 90% are suitable for apple storage. Additionally, it is important to store apples separately from other fruits, as they release ethylene gas, which can accelerate the ripening and degradation of other produce.
Changes in pH during ripening
As apples ripen, their pH levels may change due to metabolic processes occurring within the fruit. The breakdown of organic acids during the ripening process can lead to a decrease in acidity. Consequently, fully ripe apples may have a slightly lower pH compared to their less ripe counterparts. It is essential to consider the stage of ripeness when selecting apples for different purposes, as the changes in acidity can affect their taste, texture, and culinary applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the acidity of apples plays a significant role in their taste, nutritional composition, and potential health benefits. The pH scale serves as a useful tool for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of substances, including fruits like apples. Understanding the factors that influence apple acidity, such as variety, growing conditions, and ripeness, can help in selecting apples that align with personal taste preferences and specific culinary needs. While acidic foods, including apples, offer potential health benefits and contribute to a balanced diet, it is important to maintain moderation and consider factors like dental health and overall dietary balance. By striking a balance and appreciating the diversity of flavors and textures in apples, individuals can enjoy the unique characteristics and potential health advantages of this popular fruit.